在研究球面镜对光的反射以及球面镜对图像的形成时,需要学习一组符号约定,以了解测量焦距,物体或图像与反射镜的距离以及放大率。镜子。
之前,了解球面镜符号约定的概念首先讨论了球面镜中的一些常用术语。
球面镜中的常用术语
1.孔径–球面镜的一部分,暴露于入射在其上的所有光线,被称为球面镜的孔径。换句话说,凹面镜和凸面镜的孔径的直径(XY)在图1中显示,称为孔径。
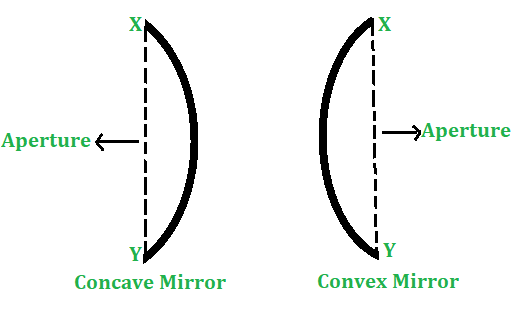
图1
2.曲率中心–弯曲或球面镜构成其一部分的空心球的中心称为曲率中心。它用C表示(如图2和3所示)。
3.曲率半径–球面镜所组成的空心球的半径称为曲率半径。用R表示。
4.极点–球面的中心称为极点。用P表示。
5.主轴线–连接球面镜的曲率中心(C)和极点(P)并在任一侧延伸的线称为主轴线。
6.主焦点–球面镜主轴上平行于主轴的光线在从球面镜反射后会合或看起来会合的点称为主焦点。用F表示。
- 对于凹面镜,反射后平行于主轴的光线实际上会在F处遇到主轴,如图2所示。因此,凹面镜的主焦点是真实的。
- 对于凸镜,反射后与主轴平行的光线似乎在F处会合或偏离主轴,如图3所示。因此,凸镜的主焦点是虚拟的。
7.焦平面–垂直于或垂直于主轴并通过球面镜的主焦点(F)的平面称为球面镜的焦平面。
8.焦距–球面反射镜的极点(P)与主焦点(F)之间的距离称为反射镜的焦距。用f表示。在图2和3中,反射镜的焦距用PF表示。
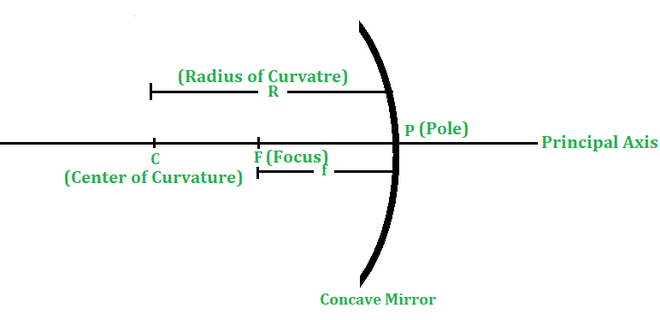
图2
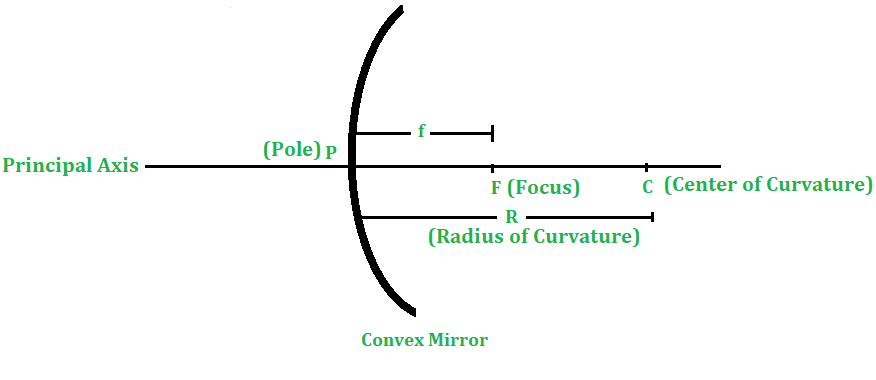
图3
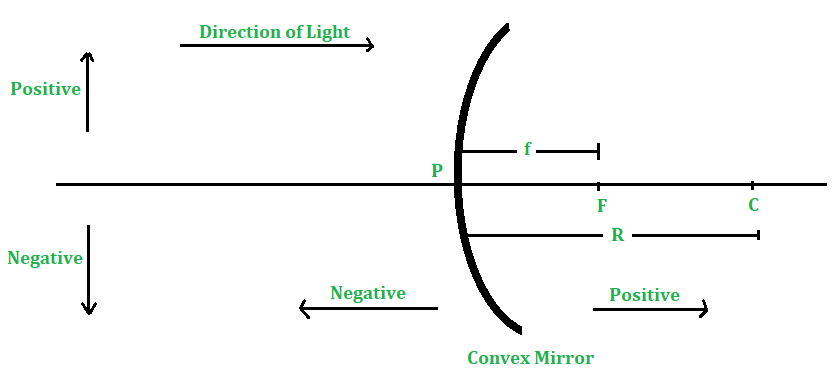
球面镜的标志惯例
为图像距离,物距,焦距等设置符号以在图像形成期间进行数学计算的一组准则称为符号约定。考虑到球面镜始终放置在镜的左侧,使得入射光的方向是从左到右,因此制定球面镜的符号约定。任何球面镜遵循的符号约定为:
1)所有距离均从球面误差的极点开始测量。
2)以在入射光方向上测得的距离为正,而在与入射光方向相反的方向上测得的距离为负。
3)垂直于主轴的向上距离为正,而垂直于主轴的向下距离为负。
- 为了方便起见,假定将对象放置在镜子的左侧。因此,物体与球面镜的极点之间的距离为负。
- 由于入射光始终从左向右传播,因此从反射镜的极点(P)到右侧的所有距离都将被视为正值(因为它们在与入射光相同的方向上)。另一方面,从反射镜的极点(P)到左侧的所有距离均为负值(因为它们是相对于入射光的方向测量的)
要记住的要点:
- 根据符号约定,朝向镜子左侧的距离为负。由于物体总是放置在镜子的左侧,因此,物体距离(u)始终为负。
- 由凹面镜形成的图像可以在镜子后面(虚拟),也可以在镜子前面(真实)。因此,根据图像的位置,凹面镜的像距()可以为正也可以为负。
- 如果图像形成在凹面镜后面,则图像距离(v)为正,但是如果图像形成在凹镜之前,则图像距离将为负。
- 在凸面镜中,图像始终形成在右侧(在反射镜后面),因此凸面镜的像距(o)将始终为正。
- 凹面镜的焦点在左侧镜的前面,因此凹面镜的焦距为负(并带有减号,例如-10 cm)。
- 另一方面,凸镜的焦点在右侧镜的后面,因此凸镜的焦距(并加上加号,例如+20 cm或仅20 cm)是正的。
- 凹面镜的焦距和曲率半径为负。
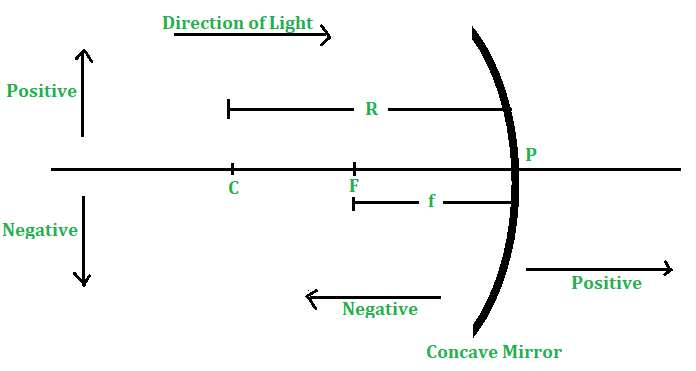
图4-凹面镜
- 凸镜的焦距和曲率半径为正。
凹凸镜
镜面配方
物体在主轴上的位置与球面镜的极点之间的距离称为物体距离。用u表示。
物体的图像在主轴上的位置与球面镜的极点之间的距离称为图像距离。用v表示。
球面反射镜的v和f之间的关系称为反射镜公式。
它是由
1/u + 1/v =1/f
or 1/object distance + 1/image distance = 1/ focal length
放大倍率(或线性放大倍率)
镜面产生的线性放大倍数定义为图像尺寸(或高度)与物体尺寸(或高度)之比。用m表示。
如果h’=镜子产生的图像的大小(或高度),并且h =对象的大小(或高度)。
然后,线性放大,
m = h‘ / h
or m= height of image/ height of object
线性放大倍数没有单位。
样本问题
示例1:凹面镜会产生一个两倍的实物图像,该图像位于物体前方10厘米处。查找图像的位置。
解决方案:
Here, -10 cm (Sign convention)
m=- 2 ( Image is real).
But m =-v/u
-2=-v/u
v=-20 cm
Thus, image of the object is at 20 cm from the pole of the mirror and in front of the mirror.
示例2:将一个尺寸为5厘米的对象放置在距其20厘米的距离处,凹形焦距为15厘米。在距反光镜多少距离的地方,应该放置一个屏幕以获得清晰的图像吗?还要计算图像的尺寸。
解决方案:
Given that,
h=+5 cm
f=- 15.0 cm (Sign convention)
u=- 20 cm (Sign convention)
Determination of the position of image.
Using,
1/u + 1/v =1/f
We get ,
1/v = 1/f-1/u
v=-60cm
So the screen must be placed at a distance of 60 cm in front of the concave mirror.
Determination of size of the image and its nature.
Using,
m= h’/h =-v/u
h‘=-(v/u)h
hi=-15cm
Thus, the size of image -15cm, negative sign with h’ shows that the image is real and inverted.
示例3:将一个4厘米高的物体放置在焦距12厘米的凹面镜前面6厘米的距离处。确定所形成图像的位置,性质和大小。
解决方案:
Sound: It is produced in a material medium by a vibrating source when a material median vibrates it pushes air near it this is called compression (region of high pressure) and when the particle moves backwards it creates a region of low pressure known as rarefaction. due to this compression and rarefaction, sound waves travel. Sound waves required a median to travel material that can be the solid-liquid or the sound speed of sound is highest in solid.
Sound waves are longitudinal mechanical waves.
Sound waves can be divided into 3 categories:
1) Audible sounds:
The frequency of audible sound is between 20hz-20khz the human ear can hear this sound.
2.INFRASONIC SOUNDS:
these sound have a frequency of less than 20kz. Elephants and whales can hear this sound
3. Ultrasonic waves
these have a frequency greater than 20khz we cannot detect these sounds built the creatures like dogs, cats bats and mosquitos can hear it.
When a sound wave reaches our ear it is characterised by 3 factors:
1 pitch and frequency
2 loudness and intensity
3 quality
- Pitch :
- It is thee characteristic of sound which distinguishes a shrilled soundwave from a dull or flat sound.
- The higher the frequency the higher is the pitch and the lower the frequency lower is their pitch.
- Frequency is defined as the number of cycles per unit of time.
2.Loudness:
It relates with the amplitude of the sound higher the amplitude higher is the loudness and lower the amplitude lower is the loudness.]
The intensity of sound at any point is defined as the amount of energy passing normally per unit area helped around that point per unit time si unit of intensity are watt/m2.
The intensity of sound at any point:
a ) Inversely proportional to the square of the distance of a point from the source.]
b) directly proportional to the square of the amplitude, sq of frequency and density of the medium.
I1/I2 = A21/A2 2Unit of loudness is bel
the practical unit of loudness is decibel.
1db = 1/10 bel3. Quality: Quality in that characteristic of sound distinguishes between sound produced by two sources having the same intensity and pitch.
the quality of sound wave depends on factors like frequency and relative intensity of over tunes.zStep 1.
Here size of object, 4 cm
u=-6 cm (sign convention)
f=-12cm (sign convention)
Using, 1/u + 1/v =1/f
We get, Using,
-1/6 + 1/v =-1/12 ]
v=12cm
Image is formed at a distance of 12 cm behind the concave mirror as v is positive. Therefore , image is virtual.
Using, m= h’/h =-v/u
h’=(-12/-6)4
hi=8 cm
示例4:公交车中使用的凸面镜的曲率半径为3.5 m。如果公交车司机将汽车停放在距公交车后10 m的位置,请查找汽车图像的位置,性质和大小。
解决方案:
Here, R = 3-5 m f = R 2 3-5 2 = 1.75m, u = – 100 m.
Determination of the position of the car.
Using, Using, 1/u + 1/v =1/f
1/v =1/f -1/u
1/v= 1/1.75 -1/(-10)
v=1.5m
Thus, the car appears to be at 1.5 m from the convex mirror and behind the mirror.
Determination of the size and nature of the image
Using, m= h’/h =-v/u
m=-1.5/-10
m=0.15
Thus, the size of the image of the car is 0.15 times the actual size of the car.
Since m is positive, so image of the car is virtual and erect (i.e., upright).