📌 相关文章
- 数据结构示例-双向链表的末尾删除节点(1)
- 数据结构示例-双向链表的末尾删除节点
- 数据结构示例-双向链表的开头插入新节点
- 数据结构示例-双向链表的开头插入新节点(1)
- 数据结构示例-双向链表的中间插入新节点
- 数据结构示例-双向链表的中间插入新节点(1)
- 数据结构示例-旋转n个节点的双向链表(1)
- 数据结构示例-旋转n个节点的双向链表
- 数据结构示例-创建n个节点的双向链表并计算节点数
- 数据结构示例-创建n个节点的双向链表并计算节点数(1)
- 数据结构示例-删除循环链表的末尾节点(1)
- 数据结构示例-删除循环链表的末尾节点
- 数据结构示例-双向链表删除中间一个节点
- 数据结构示例-双向链表删除中间一个节点(1)
- 数据结构示例-双向链表中查找最大和最小值节点(1)
- 数据结构示例-双向链表中查找最大和最小值节点
- 数据结构示例-双向链表中的元素排序(1)
- 数据结构示例-双向链表中的元素排序
- 删除双向链表中的节点(1)
- 删除双向链表中的节点
- 数据结构示例-单向链表删除末尾节点
- 数据结构示例-单向链表删除末尾节点(1)
- 数据结构示例-二叉树转换为双向链表(1)
- 数据结构示例-二叉树转换为双向链表
- 数据结构示例-循环链表的开头插入新节点
- 删除双向链表中节点的 C 程序(1)
- 删除双向链表中节点的 C 程序
- 从双向链表中删除所有质节点(1)
- 从双向链表中删除所有质节点
📜 数据结构示例-双向链表的末尾插入新节点
📅 最后修改于: 2020-10-15 05:31:09 🧑 作者: Mango
问:程序在双链表的末尾插入一个新节点。
说明
在此程序中,我们将创建一个双向链接列表,并将每个新节点插入列表的末尾。如果列表为空,则头和尾将指向新添加的节点。如果list不为空,则在列表末尾插入新节点,以使尾部的下一个指向新节点。将新节点设置为列表的新尾部,其下一个将指向null。
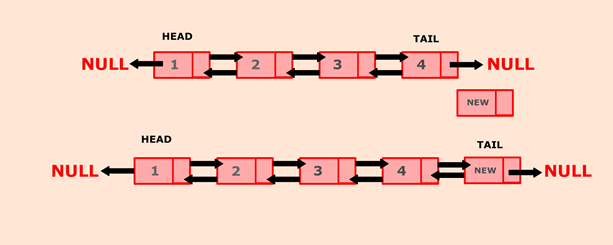
在上面的示例中,节点4是列表的尾部。现在,新节点将插入到列表的末尾,以便节点4的下一个将指向新节点。将新节点作为列表的尾部,其下一个将指向null。
算法
- 定义一个Node类,该类代表列表中的一个节点。它具有三个属性:数据,前一个将指向上一个节点,下一个将指向下一个节点。
- 定义另一个用于创建双向链接列表的类,它具有两个节点:head和tail。最初,头和尾将指向null。
- addAtEnd()将节点添加到列表中:
- 它首先检查head是否为空,然后将节点插入为head。
- 头部和尾部都将指向新添加的节点。
- 头的前一个指针将指向空,而头的下一个指针将指向空。
- 如果head不为null,则新节点将插入列表的末尾,以使新节点的前一个指针指向尾。
- 新的节点将成为新的尾巴。尾巴的下一个指针将指向null。
- display()将显示列表中存在的所有节点。
- 定义一个新节点“当前”,该节点将指向头部。
- 打印current.data直到current指向null。
- 当前将在每次迭代中指向列表中的下一个节点。
示例:
Python
#Represent a node of doubly linked list
class Node:
def __init__(self,data):
self.data = data;
self.previous = None;
self.next = None;
class InsertEnd:
#Represent the head and tail of the doubly linked list
def __init__(self):
self.head = None;
self.tail = None;
#addAtEnd() will add a node to the end of the list
def addAtEnd(self, data):
#Create a new node
newNode = Node(data);
#If list is empty
if(self.head == None):
#Both head and tail will point to newNode
self.head = self.tail = newNode;
#head's previous will point to None
self.head.previous = None;
#tail's next will point to None, as it is the last node of the list
self.tail.next = None;
#Add newNode as new tail of the list
else:
#newNode will be added after tail such that tail's next will point to newNode
self.tail.next = newNode;
#newNode's previous will point to tail
newNode.previous = self.tail;
#newNode will become new tail
self.tail = newNode;
#As it is last node, tail's next will point to None
self.tail.next = None;
#display() will print out the nodes of the list
def display(self):
#Node current will point to head
current = self.head;
if(self.head == None):
print("List is empty");
return;
print("Adding a node to the end of the list: ");
while(current != None):
#Prints each node by incrementing pointer.
print(current.data),
current = current.next;
print();
dList = InsertEnd();
#Adding 1 to the list
dList.addAtEnd(1);
dList.display();
#Adding 2 to the list
dList.addAtEnd(2);
dList.display();
#Adding 3 to the list
dList.addAtEnd(3);
dList.display();
#Adding 4 to the list
dList.addAtEnd(4);
dList.display();
#Adding 5 to the list
dList.addAtEnd(5);
dList.display();
输出:
Adding a node to the end of the list:
1
Adding a node to the end of the list:
1 2
Adding a node to the end of the list:
1 2 3
Adding a node to the end of the list:
1 2 3 4
Adding a node to the end of the list:
1 2 3 4 5
C
#include
//Represent a node of the doubly linked list
struct node{
int data;
struct node *previous;
struct node *next;
};
//Represent the head and tail of the doubly linked list
struct node *head, *tail = NULL;
//addAtEnd() will add a node to the end of the list
void addAtEnd(int data) {
//Create a new node
struct node *newNode = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
newNode->data = data;
//If list is empty
if(head == NULL) {
//Both head and tail will point to newNode
head = tail = newNode;
//head's previous will point to NULL
head->previous = NULL;
//tail's next will point to NULL, as it is the last node of the list
tail->next = NULL;
}
//Add newNode as new tail of the list
else {
//newNode will be added after tail such that tail's next will point to newNode
tail->next = newNode;
//newNode's previous will point to tail
newNode->previous = tail;
//newNode will become new tail
tail = newNode;
//As it is last node, tail's next will point to NULL
tail->next = NULL;
}
}
//display() will print out the nodes of the list
void display() {
//Node current will point to head
struct node *current = head;
if(head == NULL) {
printf("List is empty\n");
return;
}
printf("Adding a node to the end of the list: \n");
while(current != NULL) {
//Prints each node by incrementing pointer.
printf("%d ", current->data);
current = current->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
int main()
{
//Adding 1 to the list
addAtEnd(1);
display();
//Adding 2 to the list
addAtEnd(2);
display();
//Adding 3 to the list
addAtEnd(3);
display();
//Adding 4 to the list
addAtEnd(4);
display();
//Adding 5 to the list
addAtEnd(5);
display();
return 0;
}
输出:
Adding a node to the end of the list:
1
Adding a node to the end of the list:
1 2
Adding a node to the end of the list:
1 2 3
Adding a node to the end of the list:
1 2 3 4
Adding a node to the end of the list:
1 2 3 4 5
JAVA
public class InsertEnd {
//Represent a node of the doubly linked list
class Node{
int data;
Node previous;
Node next;
public Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
//Represent the head and tail of the doubly linked list
Node head, tail = null;
//addAtEnd() will add a node to the end of the list
public void addAtEnd(int data) {
//Create a new node
Node newNode = new Node(data);
//If list is empty
if(head == null) {
//Both head and tail will point to newNode
head = tail = newNode;
//head's previous will point to null
head.previous = null;
//tail's next will point to null, as it is the last node of the list
tail.next = null;
}
//Add newNode as new tail of the list
else {
//newNode will be added after tail such that tail's next will point to newNode
tail.next = newNode;
//newNode's previous will point to tail
newNode.previous = tail;
//newNode will become new tail
tail = newNode;
//As it is last node, tail's next will point to null
tail.next = null;
}
}
//display() will print out the nodes of the list
public void display() {
//Node current will point to head
Node current = head;
if(head == null) {
System.out.println("List is empty");
return;
}
System.out.println("Adding a node to the end of the list: ");
while(current != null) {
//Prints each node by incrementing the pointer.
System.out.print(current.data + " ");
current = current.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
InsertEnd dList = new InsertEnd();
//Adding 1 to the list
dList.addAtEnd(1);
dList.display();
//Adding 2 to the list
dList.addAtEnd(2);
dList.display();
//Adding 3 to the list
dList.addAtEnd(3);
dList.display();
//Adding 4 to the list
dList.addAtEnd(4);
dList.display();
//Adding 5 to the list
dList.addAtEnd(5);
dList.display();
}
}
输出:
Adding a node to the end of the list:
1
Adding a node to the end of the list:
1 2
Adding a node to the end of the list:
1 2 3
Adding a node to the end of the list:
1 2 3 4
Adding a node to the end of the list:
1 2 3 4 5
C#
using System;
namespace DoublyLinkedList
{
public class Program
{
//Represent a node of the doubly linked list
public class Node{
public T data;
public Node previous;
public Node next;
public Node(T value) {
data = value;
}
}
public class InsertEnd{
//Represent the head and tail of the doubly linked list
protected Node head = null;
protected Node tail = null;
//addAtEnd() will add a node to the end of the list
public void addAtEnd(T data) {
//Create a new node
Node newNode = new Node(data);
//If list is empty
if(head == null) {
//Both head and tail will point to newNode
head = tail = newNode;
//head's previous will point to null
head.previous = null;
//tail's next will point to null, as it is the last node of the list
tail.next = null;
}
//Add newNode as new tail of the list
else {
//newNode will be added after tail such that tail's next will point to newNode
tail.next = newNode;
//newNode's previous will point to tail
newNode.previous = tail;
//newNode will become new tail
tail = newNode;
//As it is last node, tail's next will point to null
tail.next = null;
}
}
//display() will print out the nodes of the list
public void display() {
//Node current will point to head
Node current = head;
if(head == null) {
Console.WriteLine("List is empty");
return;
}
Console.WriteLine("Adding a node to the end of the list: ");
while(current != null) {
//Prints each node by incrementing the pointer.
Console.Write(current.data + " ");
current = current.next;
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
public static void Main()
{
InsertEnd dList = new InsertEnd();
//Adding 1 to the list
dList.addAtEnd(1);
dList.display();
//Adding 2 to the list
dList.addAtEnd(2);
dList.display();
//Adding 3 to the list
dList.addAtEnd(3);
dList.display();
//Adding 4 to the list
dList.addAtEnd(4);
dList.display();
//Adding 5 to the list
dList.addAtEnd(5);
dList.display();
}
}
}
输出:
Adding a node to the end of the list:
1
Adding a node to the end of the list:
1 2
Adding a node to the end of the list:
1 2 3
Adding a node to the end of the list:
1 2 3 4
Adding a node to the end of the list:
1 2 3 4 5
PHP:
data = $data;
}
}
class InsertEnd{
//Represent the head and tail of the doubly linked list
public $head;
public $tail;
function __construct(){
$this->head = NULL;
$this->tail = NULL;
}
//addAtEnd() will add a node to the end of the list
function addAtEnd($data) {
//Create a new node
$newNode = new Node($data);
//If list is empty
if($this->head == NULL) {
//Both head and tail will point to newNode
$this->head = $this->tail = $newNode;
//head's previous will point to NULL
$this->head->previous = NULL;
//tail's next will point to NULL, as it is the last node of the list
$this->tail->next = NULL;
}
//Add newNode as new tail of the list
else {
//newNode will be added after tail such that tail's next will point to newNode
$this->tail->next = $newNode;
//newNode's previous will point to tail
$newNode->previous = $this->tail;
//newNode will become new tail
$this->tail = $newNode;
//As it is last node, tail's next will point to NULL
$this->tail->next = NULL;
}
}
//display() will print out the nodes of the list
function display() {
//Node current will point to head
$current = $this->head;
if($this->head == NULL) {
print("List is empty
");
return;
}
print("Adding a node to the end of the list:
");
while($current != NULL) {
//Prints each node by incrementing pointer.
print($current->data . " ");
$current = $current->next;
}
print("
");
}
}
$dList = new InsertEnd();
//Adding 1 to the list
$dList->addAtEnd(1);
$dList->display();
//Adding 2 to the list
$dList->addAtEnd(2);
$dList->display();
//Adding 3 to the list
$dList->addAtEnd(3);
$dList->display();
//Adding 4 to the list
$dList->addAtEnd(4);
$dList->display();
//Adding 5 to the list
$dList->addAtEnd(5);
$dList->display();
?>
输出:
Adding a node to the end of the list:
1
Adding a node to the end of the list:
1 2
Adding a node to the end of the list:
1 2 3
Adding a node to the end of the list:
1 2 3 4
Adding a node to the end of the list:
1 2 3 4 5