推力或拉力是由于对象或身体与另一个对象的交互作用而在对象上产生的力。推或拉仅作为交互作用的结果而存在,例如将物体或物体或材料被推或拉时称为力。由于动作而产生的力会在物体中产生运动。
推力或拉力也有方向。这意味着如果大小或方向发生变化,它就是一个向量,它会直接影响两种力的类型。如果力的方向与移动的物体相反,则它将减小力。如果物体在运动,则外部推拉可能会改变该物体的状态或运动方向。物体或身体中运动状态的变化通常由其速度和运动方向来解释。
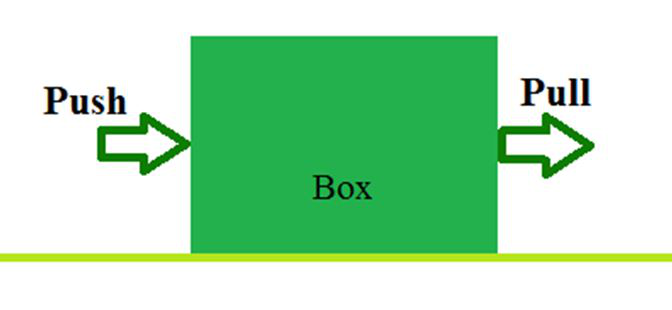
推拉箱子。
对从箱而这是在相同的方向上作用的拉力的左侧施加但施加在右推力:现在,可以在以上所述框趋于由于移动到两个力中所示的图像中可以看出盒子的侧面。即使在性质上有所不同之后,这两种力量也会使盒子在右侧移动。在“推力”中,对象从力源移开,但场景的拉力不同。在拉力作用下,物体向力源移动。
什么是推?
推力可以定义为导致物体从静止状态移动的力。在“推力”中,对象从力源移开。
简而言之,可以说物体从施加力的表面移开了。移动物体所需的时间取决于物体或身体施加的反作用力。推力不仅由我们施加,而且许多机器都使用推力将材料的形状修补为所需的形状。
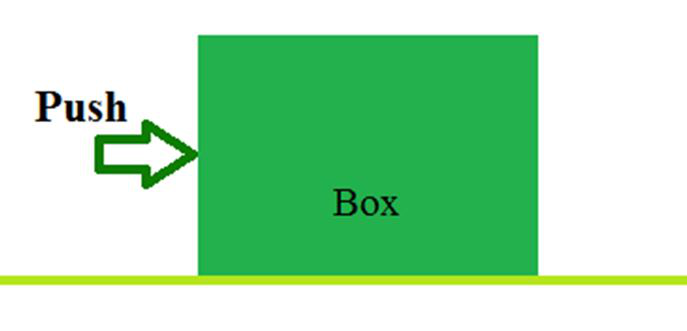
推箱子上的力。
Examples of Push
- Pushing the trolley when we go to shopping malls or markets.
- Pushing of the cart to move it from one place to another one.
- Pushing the Bed from one place to another in a room
- Pushing the door to open it.
- Pushing the switch to make it on.
- Pushing the dough to make small rolls for making tortillas.
什么是拉力?
拉力可以描述为或表示为一个力,该力导致物体从静止状态移动,但与推力相比方向相反。在拉力作用下,物体向力源移动。
简而言之,可以说物体从施加力的表面移开了。移动物体所需的时间取决于物体或身体施加的反作用力。
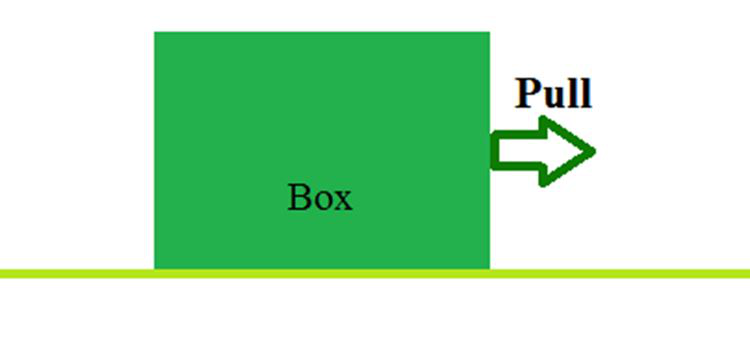
拉力作用在盒子上。
Examples of Pull
- Pulling the curtains to let us open the window panes.
- Dragging the box to our desired position.
- Opening of the door to get in.
- Pulling the kite yarn to make it fly higher.
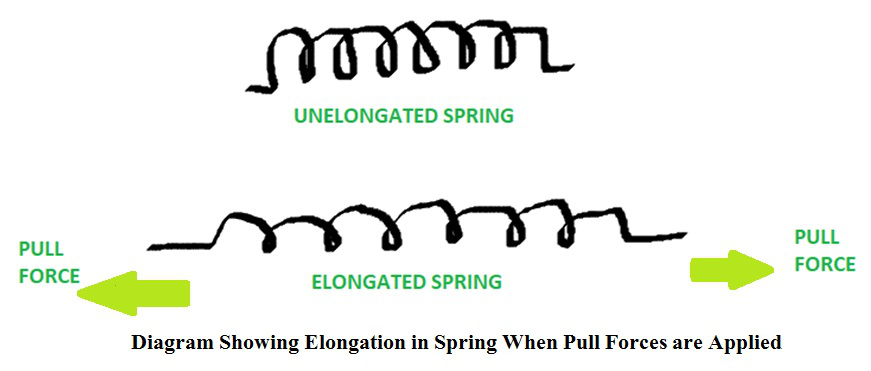
- Pulling a string to make it elongated.
- A spring balance measures the weight of an object by judging the pulling force by it.
- The game of tug war has two teams that apply pulling forces on each other. Either team which will exert a greater pull force to the rope with a greater force wins.
力量
力可以定义为对物体或身体的推动或拉动。对于施加的任何力,物体的运动,物体的状态,其形状,大小等都会发生变化。力既有大小又有方向,因为它是既有矢量又有矢量的向量。通过使用弹簧秤将物体或材料放在挂钩末端,可以非常轻松地进行测量。
The state of “stationary position” or “rest” of an object is considered to be the zero speed, as:
- An object or a stationary body cannot move by itself.
- An object or a stationary block cannot change its speed by itself.
- An object or a stationary body cannot change its direction by itself.
- An object or a body at rest cannot change by itself.
Therefore, it can be interpreted that a push or pull force can do the following actions itself:
- A push or pull force may make an object move from rest.
- A push or pull force may change the speed of a moving object.
- A push or pull force may change the direction of a moving object.
- A push or pull force on an object or body may change the shape of an object.
基本上,力有两种类型:
- 接触力
- 非接触力
接触力
接触力是需要与表面接触的任何力。接触力无处不在,并负责宏观物质之间几乎所有可见的相互作用。接触力起作用的一些日常示例是将汽车推上山坡或将球踢过房间。
接触力通常分为两种:摩擦力和肌肉力:
1.摩擦力:
它是相反的或向后的拉力,与一个物体在另一个物体的表面上的运动相反。任何物体在另一个物体或身体上的运动都是非常必要的。摩擦力是指两个彼此滑动,相互接触或非常试图滑动的表面之间的力。摩擦总是会降低运动物体的速度。
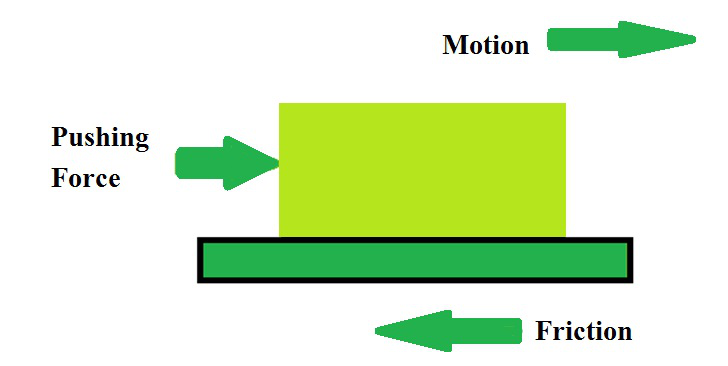
摩擦力
e.g.:
- Walking, we are able to walk because there is friction, and we are walking at a certain low speed because of the opposing force provided by friction.
- When we move a heavy almirah from one room to another it is very difficult to move it because of the opposing frictional force that gets generated during motion.
- When we rub our hands we can feel the heat due to friction between the rough surfaces.
2.肌肉力量:
我们身体的肌肉所施加的力量被称为肌肉力量。我们所有的日常身体活动,例如举起物体,在地面上行走,在地面上奔跑,弯腰拿东西等,都是由于肌肉力量。之所以称其为接触力,是因为肌肉力只能或可以施加在步行,奔跑,跳跃等身体接触上。
e.g.:
- Strolling something from one place to another.
- Lifting anything up or keeping it down.
- Getting up from a seat or a chair
- Crossing a leg, moving from one position to another, etc.
非接触力
非接触力被描述为一种作用在物体或身体上而没有物理接触的力。我们观察到的最熟悉的非接触力是重力,它赋予了重量。在没有两个或多个物体接触的情况下产生或产生的力称为非接触力。
非接触力主要有三种类型,即:磁力,静电力和重力。
1.磁力:
磁力描述了由于带电粒子的运动而在带电粒子之间产生或产生的吸引力或排斥力。它告诉我们有关电动马达的作用力以及磁铁对铁片的吸引力的信息。用非常简单的话说,两个具有相同运动方向的电荷的物体或材料在它们之间具有磁引力,同时存在某种相反的电荷,然后它们彼此排斥。
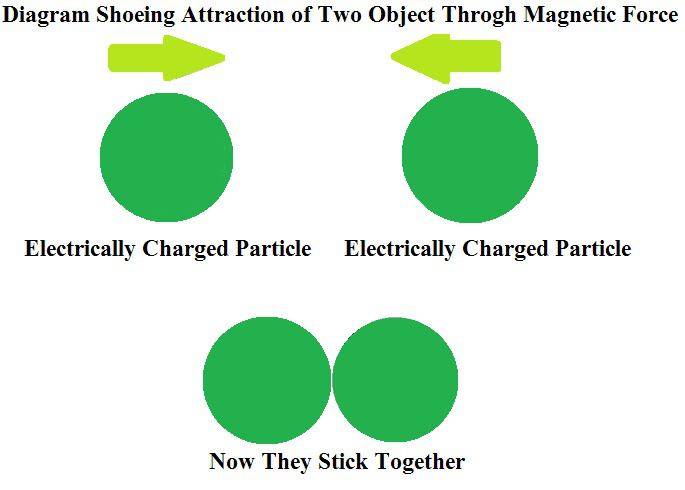
磁力
e.g.:
- The attraction between the magnetic pieces when brought near each other.
- The electromagnets used in machines.
- Working magnets in some machines operate only based upon magnetic forces by a single switch.
2.静电力:
静电力是指两个带电微小颗粒之间的吸引力或排斥力。它存在于静止的粒子或带电的固定粒子中。它通常被称为库仑力。简单来说,就是带电粒子或静止物体之间存在的力。
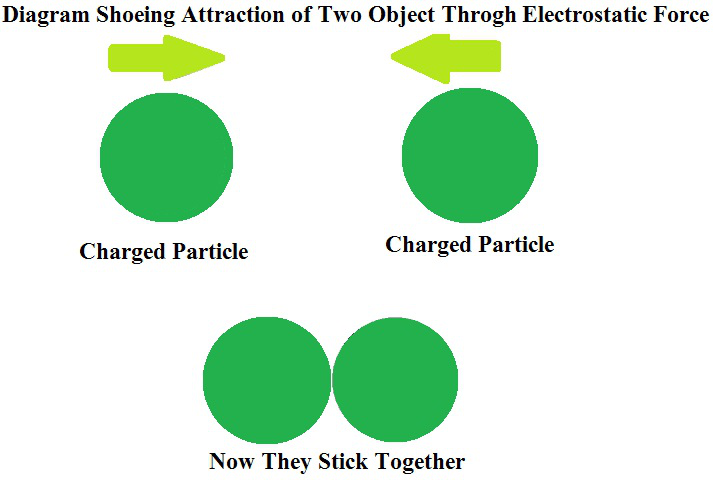
静电力
e.g.:
- Balloons get attracted to each other, whenever one of them is rubbed through our hairs.
- When we run a small or tiny piece of paper with the oil in our head with the help of a comb produces electrostatic force.
- When you do ironing on your silk-made cloth or cotton made cloth and keep it right in front of you, they just cling to your body.
- Lightning phenomenon is also a common example of electrostatic force.
2.引力:
所有物体都有一定的重量,或者说是向下的重力,该重力与它们的质量成正比,这是由于地球的质量而产生的。重力是地球在自由落体上的加速度。无论它是什么,它都会作用在每个坠落的物体上,无论大小,大小或粗细。这种普遍的力量作用在地球上的每一件事上。
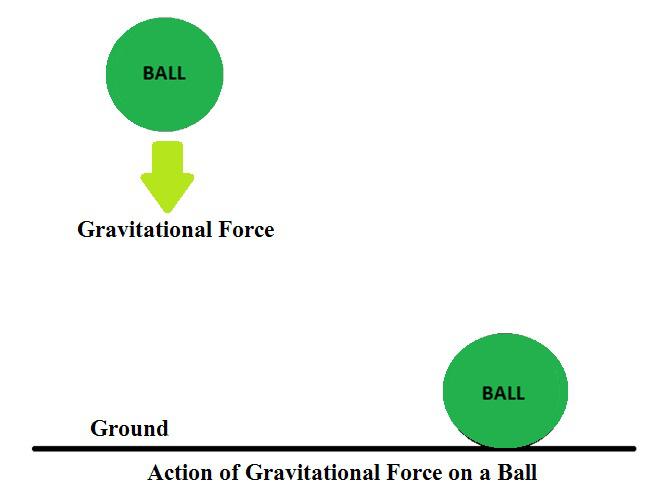
地心引力:
e.g.:
- Whenever we throw a rubber ball up, it falls to the ground due to gravitational force.
- Water from the tap always flows in a downward direction due to this force.
- When we throw a shuttlecock it comes down due to gravity.
样本问题
问题1:什么是以下动作产生的拉力和推力:
将书搬离您较远,向自己打开一扇门,从井中抽水桶,一名足球运动员罚点球,一名板球手打板球,打开一个抽屉。
解决方案:
Pulling forces are:
- Opening a door toward yourself,
- Opening a drawer
- Drawing a bucket of water from a well
Pushing forces are:
- Moving a book far from you
- A football player taking a penalty kick
- A cricket ball hit by a batsman
问题2:磁力是非接触力吗?
解决方案:
Force caused due to magnets are called the magnetic or non-contact magnetic force. This force applies even when magnets and metals are not in contact, so it can be stated as a non-contact force.
问题3:为什么我们的鞋子在一段时间后会磨损?
解决方案:
Our shoes when we walk face frictional force which is a backward pulling force that leads to the wear and tear of our shoes.
问题4:两个女孩试图推开一个靠近他们的障碍物。第一个女孩施加推力时的挡块不会移动,但另一个女孩施加推力时,挡块会从其位置移开。为什么在第一种情况下施加相似的推力倾向于使物体或块移动,而在第二种情况下却不移动?
解决方案:
The movement of a body at rest depends upon the extent of external force applied. If it overcomes the reaction force exerted by the block or object they tend to move it. The push force applied by the girl in the first case cannot overcome the reaction force exerted by the block and so the block doesn’t move whereas in the second case the push force applied by the second girl would have overcome the reaction forces by the block and so it moved.
问题5:一个购物中心里的男孩对应该拉推车还是推推车将其移动到收银台感到非常困惑。建议男孩在工作中应该使用哪种力量?
解决方案:
As since it found easier to pull a cart than pushing. So he must pull the cart to the cash counter. The reason behind this is the pulling forces can overcome the reaction force exerted by the cart somewhat easily than push force.