给定具有V个顶点和E个边缘的二进制值无向图,任务是找到图的所有连接组件的八进制等效项。可以将二进制值图视为仅具有二进制数(0或1)作为顶点值。
例子:
Input: E = 4, V = 7
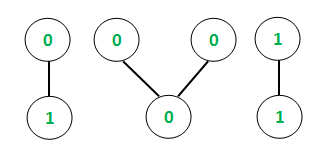
Output:
Chain = 0 1 Octal equivalent = 1
Chain = 0 0 0 Octal equivalent = 0
Chain = 1 1 Octal equivalent = 3
Explanation:
In case of the first connected component, the binary chain is [0, 1]
Hence, the binary string = “01” and binary number = 01
Therefore, the octal equivalent is 1
Input: E = 6, V = 10
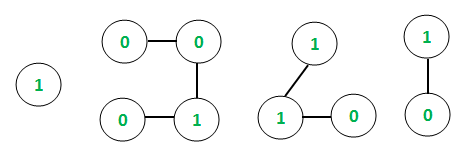
Output:
Chain = 1 Octal equivalent = 1
Chain = 0 0 1 0 Octal equivalent = 2
Chain = 1 1 0 Octal equivalent = 6
Chain = 1 0 Octal equivalent = 2
方法:想法是使用深度优先搜索遍历来跟踪无向图中的连接组件,如本文所述。对于每个连接的组件,将显示二进制字符串,并根据二进制值计算出等效的八进制值(如本文中所述)并进行打印。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ implementation to find
// octal equivalents of
// all connected components
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to traverse the undirected
// graph using the Depth first traversal
void depthFirst(int v, vector graph[],
vector& visited,
vector& storeChain)
{
// Marking the visited
// vertex as true
visited[v] = true;
// Store the connected chain
storeChain.push_back(v);
for (auto i : graph[v]) {
if (visited[i] == false) {
// Recursive call to
// the DFS algorithm
depthFirst(i, graph,
visited, storeChain);
}
}
}
// Function to create map between binary
// number and its equivalent octal value
void createMap(unordered_map* um)
{
(*um)["000"] = '0';
(*um)["001"] = '1';
(*um)["010"] = '2';
(*um)["011"] = '3';
(*um)["100"] = '4';
(*um)["101"] = '5';
(*um)["110"] = '6';
(*um)["111"] = '7';
}
// Function to return octal
// equivalent of each connected
// component
string Octal(string bin)
{
int l = bin.size();
int t = bin.find_first_of('.');
// length of string before '.'
int len_left = t != -1 ? t : l;
// add min 0's in the beginning to make
// left substring length divisible by 3
for (int i = 1;
i <= (3 - len_left % 3) % 3;
i++)
bin = '0' + bin;
// if decimal point exists
if (t != -1) {
// length of string after '.'
int len_right = l - len_left - 1;
// add min 0's in the end to make right
// substring length divisible by 3
for (int i = 1;
i <= (3 - len_right % 3) % 3;
i++)
bin = bin + '0';
}
// create map between binary and its
// equivalent octal code
unordered_map bin_oct_map;
createMap(&bin_oct_map);
int i = 0;
string octal = "";
while (1) {
// one by one extract from left,
// substring of size 3 and
// add its octal code
octal += bin_oct_map[bin.substr(i, 3)];
i += 3;
if (i == bin.size())
break;
// if '.' is encountered
// add it to result
if (bin.at(i) == '.') {
octal += '.';
i++;
}
}
// required octal number
return octal;
}
// Function to find the octal equivalents
// of all connected components
void octalValue(
vector graph[], int vertices,
vector values)
{
// Initializing boolean array
// to mark visited vertices
vector visited(1001, false);
// Following loop invokes DFS algorithm
for (int i = 1; i <= vertices; i++) {
if (visited[i] == false) {
// Variable to hold
// temporary length
int sizeChain;
// Container to store each chain
vector storeChain;
// DFS algorithm
depthFirst(i, graph,
visited, storeChain);
// Variable to hold each chain size
sizeChain = storeChain.size();
// Container to store values
// of vertices of individual chains
int chainValues[sizeChain + 1];
// Storing the values of each chain
for (int i = 0; i < sizeChain; i++) {
int temp
= values[storeChain[i] - 1];
chainValues[i] = temp;
}
// Printing binary chain
cout << "Chain = ";
for (int i = 0; i < sizeChain; i++) {
cout << chainValues[i] << " ";
}
cout << "\t";
// Converting the array with vertex
// values to a binary string
// using string stream
stringstream ss;
ss << chainValues[0];
string s = ss.str();
for (int i = 1; i < sizeChain; i++) {
stringstream ss1;
ss1 << chainValues[i];
string s1 = ss1.str();
s.append(s1);
}
// Printing the octal values
cout << "Octal equivalent = ";
cout << Octal(s) << endl;
}
}
}
// Driver code to test above function
int main()
{
// Initializing graph in the
// form of adjacency list
vector graph[1001];
// Defining the number
// of edges and vertices
int E, V;
E = 4;
V = 7;
// Assigning the values for each
// vertex of the undirected graph
vector values;
values.push_back(0);
values.push_back(1);
values.push_back(0);
values.push_back(0);
values.push_back(0);
values.push_back(1);
values.push_back(1);
// Constructing the undirected graph
graph[1].push_back(2);
graph[2].push_back(1);
graph[3].push_back(4);
graph[4].push_back(3);
graph[4].push_back(5);
graph[5].push_back(4);
graph[6].push_back(7);
graph[7].push_back(6);
octalValue(graph, V, values);
return 0;
} Java
// Java implementation to find
// octal equivalents of all
// connected components
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Function to traverse the undirected
// graph using the Depth first traversal
static void depthFirst(int v,
List> graph,
boolean[] visited,
List storeChain)
{
// Marking the visited
// vertex as true
visited[v] = true;
// Store the connected chain
storeChain.add(v);
for(int i : graph.get(v))
{
if (visited[i] == false)
{
// Recursive call to
// the DFS algorithm
depthFirst(i, graph, visited,
storeChain);
}
}
}
// Function to create map between binary
// number and its equivalent hexadecimal
static void createMap(Map um)
{
um.put("000", '0');
um.put("001", '1');
um.put("010", '2');
um.put("011", '3');
um.put("100", '4');
um.put("101", '5');
um.put("110", '6');
um.put("111", '7');
}
// Function to return octal
// equivalent of each connected
// component
static String octal(String bin)
{
int l = bin.length();
int t = bin.indexOf('.');
// Length of string before '.'
int len_left = t != -1 ? t : l;
// Add min 0's in the beginning to make
// left substring length divisible by 3
for(int i = 1;
i <= (3 - len_left % 3) % 3;
i++)
bin = '0' + bin;
// If decimal point exists
if (t != -1)
{
// Length of string after '.'
int len_right = l - len_left - 1;
// Add min 0's in the end to make right
// substring length divisible by 3
for(int i = 1;
i <= (3 - len_right % 3) % 3;
i++)
bin = bin + '0';
}
// Create map between binary and its
// equivalent octal code
Map bin_oct_map = new HashMap();
createMap(bin_oct_map);
int i = 0;
String octal = "";
while (true)
{
// One by one extract from left,
// substring of size 3 and
// add its octal code
octal += bin_oct_map.get(
bin.substring(i, i + 3));
i += 3;
if (i == bin.length())
break;
// If '.' is encountered
// add it to result
if (bin.charAt(i) == '.')
{
octal += '.';
i++;
}
}
// Required octal number
return octal;
}
// Function to find the octal equivalents
// of all connected components
static void octalValue(List> graph,
int vertices,
List values)
{
// Initializing boolean array
// to mark visited vertices
boolean[] visited = new boolean[1001];
// Following loop invokes DFS algorithm
for(int i = 1; i <= vertices; i++)
{
if (visited[i] == false)
{
// Variable to hold
// temporary length
int sizeChain;
// Container to store each chain
List storeChain = new ArrayList();
// DFS algorithm
depthFirst(i, graph, visited, storeChain);
// Variable to hold each chain size
sizeChain = storeChain.size();
// Container to store values
// of vertices of individual chains
int[] chainValues = new int[sizeChain + 1];
// Storing the values of each chain
for(int j = 0; j < sizeChain; j++)
{
int temp = values.get(
storeChain.get(j) - 1);
chainValues[j] = temp;
}
// Printing binary chain
System.out.print("Chain = ");
for(int j = 0; j < sizeChain; j++)
{
System.out.print(chainValues[j] + " ");
}
System.out.print("\t");
// Converting the array with vertex
// values to a binary string
String s = "";
for(int j = 0; j < sizeChain; j++)
{
String s1 = String.valueOf(
chainValues[j]);
s += s1;
}
// Printing the octal values
System.out.println("Octal equivalent = " +
octal(s));
}
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Initializing graph in the
// form of adjacency list
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
List> graph = new ArrayList();
for(int i = 0; i < 1001; i++)
graph.add(new ArrayList());
// Defining the number
// of edges and vertices
int E = 4, V = 7;
// Assigning the values for each
// vertex of the undirected graph
List values = new ArrayList();
values.add(0);
values.add(1);
values.add(0);
values.add(0);
values.add(0);
values.add(1);
values.add(1);
// Constructing the undirected graph
graph.get(1).add(2);
graph.get(2).add(1);
graph.get(3).add(4);
graph.get(4).add(3);
graph.get(4).add(5);
graph.get(5).add(4);
graph.get(6).add(7);
graph.get(7).add(6);
octalValue(graph, V, values);
}
}
// This code is contributed by jithin Chain = 0 1 Octal equivalent = 1
Chain = 0 0 0 Octal equivalent = 0
Chain = 1 1 Octal equivalent = 3
如果您希望与行业专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅《 Geeks现场课程》和《 Geeks现场课程美国》。