使用STL中的队列和向量的BFS的基于STL的简单实现。邻接表是使用vector的向量表示的。
In BFS, we start with a node.
1) Create a queue and enqueue source into it.
Mark source as visited.
2) While queue is not empty, do following
a) Dequeue a vertex from queue. Let this
be f.
b) Print f
c) Enqueue all not yet visited adjacent
of f and mark them visited.
下面是一个从源顶点1开始的BFS示例。请注意,图形可能存在多个BFS(甚至来自特定顶点)。 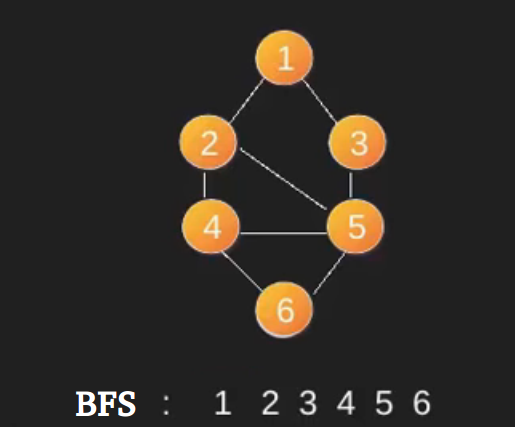
有关BFS的更多详细信息,请参阅此文章。
此处的代码经过简化,可用于竞争性编码。
// A Quick implementation of BFS using
// vectors and queue
#include
#define pb push_back
using namespace std;
vector v;
vector > g;
void edge(int a, int b)
{
g[a].pb(b);
// for undirected graph add this line
// g[b].pb(a);
}
void bfs(int u)
{
queue q;
q.push(u);
v[u] = true;
while (!q.empty()) {
int f = q.front();
q.pop();
cout << f << " ";
// Enqueue all adjacent of f and mark them visited
for (auto i = g[f].begin(); i != g[f].end(); i++) {
if (!v[*i]) {
q.push(*i);
v[*i] = true;
}
}
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int n, e;
cin >> n >> e;
v.assign(n, false);
g.assign(n, vector());
int a, b;
for (int i = 0; i < e; i++) {
cin >> a >> b;
edge(a, b);
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (!v[i])
bfs(i);
}
return 0;
}
Input:
8 10
0 1
0 2
0 3
0 4
1 5
2 5
3 6
4 6
5 7
6 7
Output:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
如果您希望与行业专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅《 Geeks现场课程》和《 Geeks现场课程美国》。