1.交叉汇编器:
交叉汇编程序是在具有一种类型的处理器的计算机上运行但为另一种类型的处理器生成机器代码的汇编程序。例如,如果我们使用具有8086兼容机器语言的PC来生成8085处理器的机器代码,则需要在PC兼容机器上运行但生成8085助记符的机器代码的交叉汇编程序。它以汇编语言为输入,并以机器语言为输出。
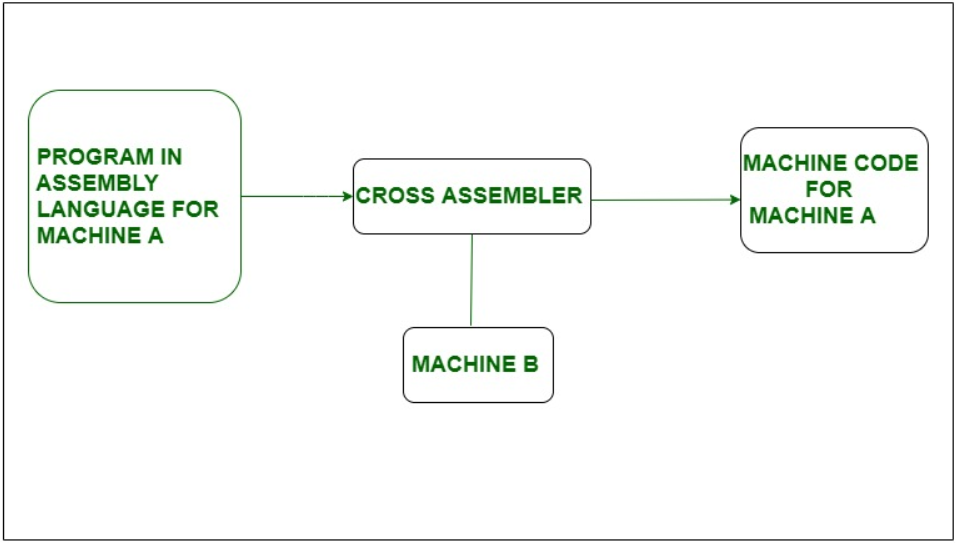
在上面的框图中,我们可以看到在机器B上运行了一个汇编程序,但是将机器A的汇编代码转换为机器代码,该汇编程序是交叉汇编程序。
交叉汇编程序的特点:
- 交叉汇编器用于将汇编语言转换为二进制机器代码。
- 交叉汇编器还用于开发程序,这些程序将在不能独立运行开发环境的游戏机和其他小型电子系统上运行。
- 交叉汇编器可用于在低功耗系统上加快开发速度。
- C 64是交叉汇编程序的最佳示例。
2.编译器:
编译器是将源代码从高级编程语言转换为机器级语言的软件(程序)。它不像汇编程序的翻译那么简单。它必须执行几个步骤以产生机器代码形式的目标文件。编译器的主要工作是检查各种限制,范围,错误等。将高级语言转换为机器语言的过程称为编译。如果代码中有什么错误,那么它将给出错误。
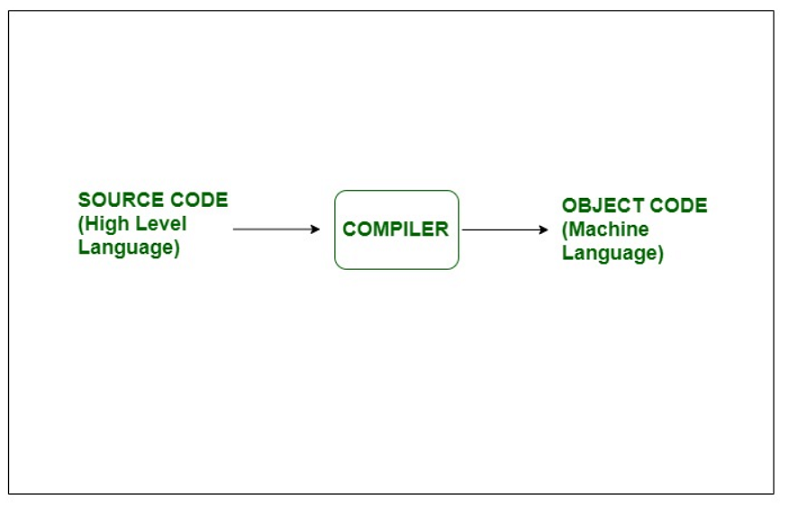
编译器功能:
- 执行程序后,编译器的首要任务是创建.obj文件,然后创建.exe文件。
- 编译器管理代码和变量的存储。
- 编译器负责代码的正确性并突出显示错误。
- 编译器比交叉汇编器更智能。
- MinGW,javac是编译器的示例。
交叉汇编器和编译器之间的区别:
| S.No. | CROSS-ASSEMBLER | COMPILER |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | A cross-assembler is an assembler that runs on a computer with one type of processor but generates machine for different type of processor. | Compiler is used to convert source code from High level language to machine level language. |
| 2 | Cross-assembler inputs assembly language code. | Compiler input source code. |
| 3 | Cross-assembler can’t do this at once. | Compiler can converts the whole code into machine language at a time. |
| 4 | Cross-assembler is less intelligent. | It is more intelligent than cross-assemblers. |
| 5 | The output of cross-assembler is in binary code. | The output of compiler is in machine code. |
| 6 | Cross-assembler can cooperate with two processor at a time. | Whereas compiler works on one processor at a time. |
| 7 | The example of Cross-assembler is C 64. | compiler examples are GCC, javac, MinGW etc. |