先决条件–简化的数据加密标准|套装1
简化数据加密标准是具有10位密钥和8位纯文本的数据加密标准的简单版本。它比DES算法小得多,因为它仅占用8位纯文本,而DES却占用64位纯文本。它是为教育目的而开发的,因此了解DES变得容易。它是一种分组密码算法,并使用对称密钥作为其算法,即它们使用相同的密钥进行加密和解密。它有2个加密轮,使用两个不同的密钥。
首先,我们需要在加密之前生成2个密钥。生成密钥后,我们将其传递给每个单独的回合以进行s-des加密。下图显示了s-des算法中涉及的步骤。
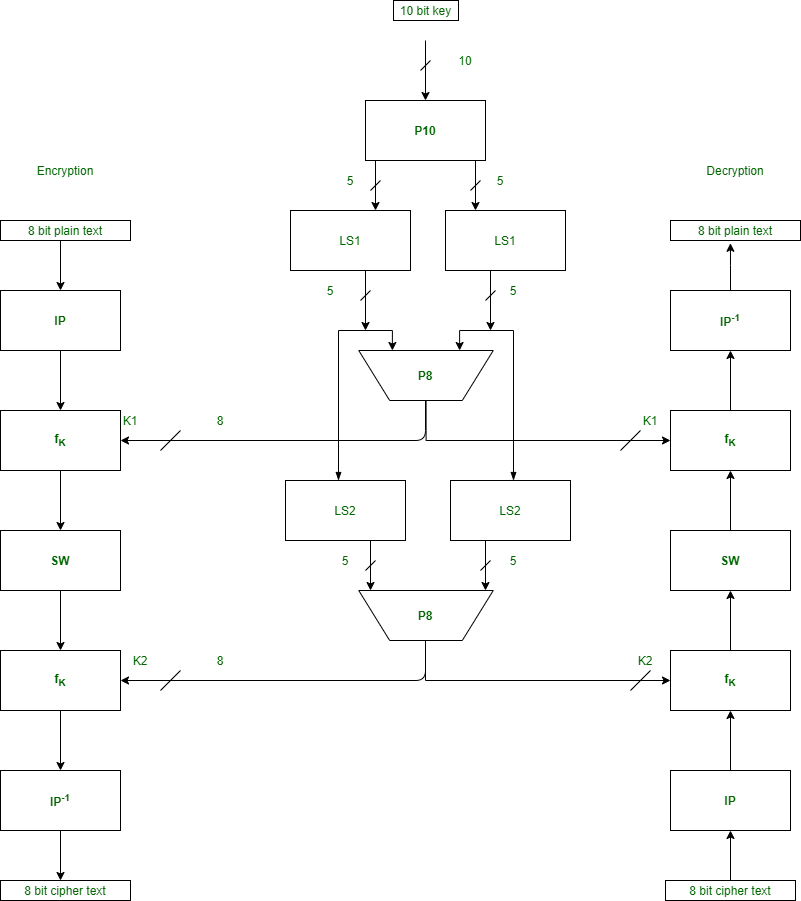
组件 :
S-DES加密涉及四个功能–
1.初始置换(IP)–
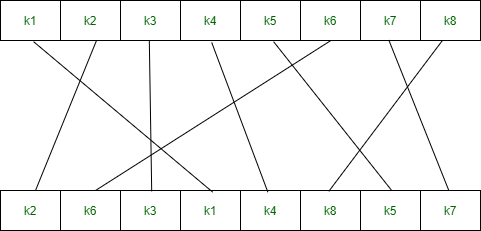
2.复数函数(f k )–
它是置换和置换函数的组合。下图表示一轮加密和解密。在每个加密和解密过程中,此回合重复两次。
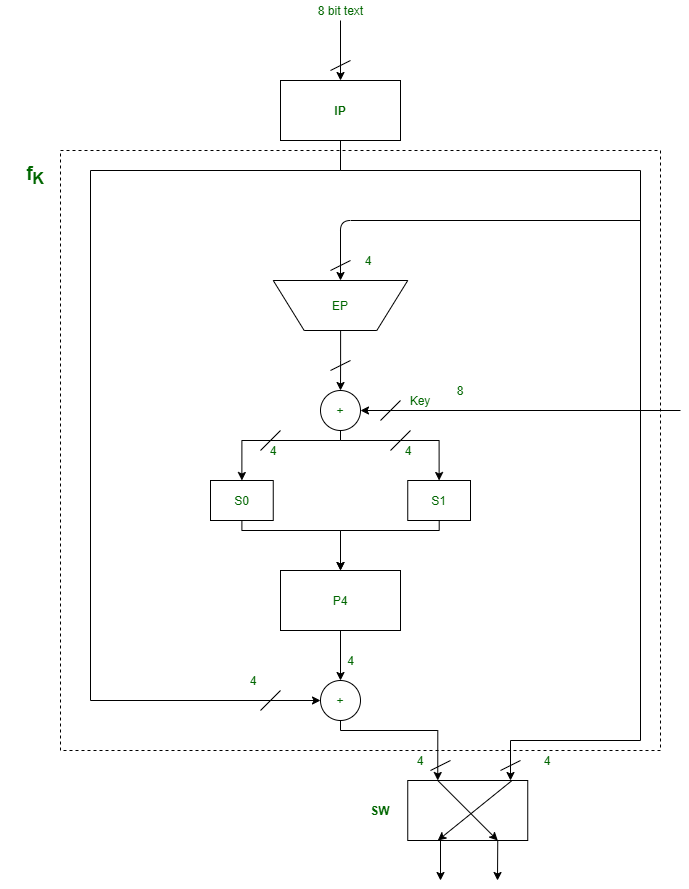
f k中的成分是–
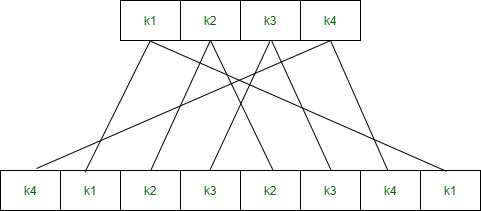
一种。扩展排列(EP)–
它采用4位输入并将其转换为8位输出。
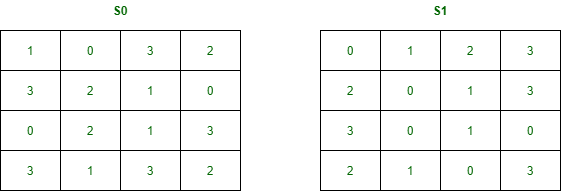
b。 S盒(S0和S1)–
它是执行替换的对称密钥算法的基本组成部分。
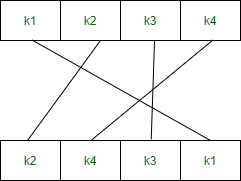
C。排列P4 –
3.开关(SW)–

4.初始置换的倒数(IP -1 )–
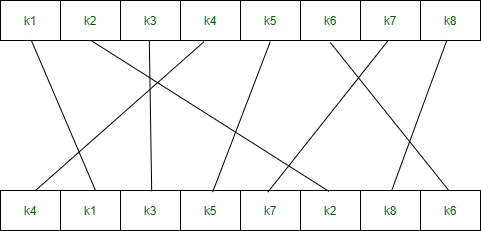
首先,我们需要在加密之前生成2个密钥。
Consider, the entered 10-bit key is - 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0所以,
Key-1 is - 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 0
Key-2 is - 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 1加密–
Entered 8-bit plaintext is - 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 1步骤1:
我们使用IP表对8位纯文本执行初始置换。初始排列定义为–
IP(k1, k2, k3, k4, k5, k6, k7, k8) = (k2, k6, k3, k1, k4, k8, k5, k7)
After ip = 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 1第2步:
初始置换后,我们得到一个8位的文本块,我们将其分成2个半部分,每个部分4位。
l = 0 1 0 1 and r = 1 1 0 1在右半部分,我们使用EP表执行扩展排列,该表将4位转换为8位。扩展排列定义为–
EP(k1, k2, k3, k4) = (k4, k1, k2, k3, k2, k3, k4, k1)After ep = 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 1我们使用第一个键K1与扩展排列的输出执行XOR操作。
Key-1 is - 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 0
(1 0 1 0 0 1 0 0) XOR (1 1 1 0 1 0 1 1) = 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 1
After XOR operation with 1st Key = 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 1同样,我们将XOR的输出分成两个半部分,每个半部分为4位。
l = 0 1 0 0 and r = 1 1 1 1我们将S盒的第一和第四位作为行,将第二和第三位作为列。
S0 = [1,0,3,2
3,2,1,0
0,2,1,3
3,1,3,2]
S1= [0,1,2,3
2,0,1,3
3,0,1,0
2,1,0,3]
For l = 0 1 0 0
row = 00 = 0, column = 10 = 2
S0 = 3 = 11
For r = 1 1 1 1
row = 11 = 3, column = 11 = 3
S1 = 3 = 11
After first S-Boxes combining S0 and S1 = 1 1 1 1S框提供2位输出,我们将其组合得到4位,然后使用P4表执行置换。 P4被定义为–
P4(k1, k2, k3, k4) = (k2, k4, k3, k1)
After P4 = 1 1 1 1我们将P4表的输出与初始排列表(即IP表)的左半部分进行XOR运算。
(0 1 0 1) XOR (1 1 1 1) = 1 0 1 0
After XOR operation with left nibble of after ip = 1 0 1 0我们将两个部分组合在一起,即初始排列的右半部分和ip的输出。
Combine 1 1 0 1 and 1 0 1 0
After combine = 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 1步骤3:
现在,将输出分成两半,每个半为4位。再次合并它们,但是现在左侧部分应该变为右侧,而右侧部分应该变为左侧。
After step 3 = 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 0第四步:
再次执行步骤2,但这一次在扩展排列后执行XOR操作时,使用键2而不是键1。
Expand permutation is defined as - 4 1 2 3 2 3 4 1
After second ep = 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1
After XOR operation with 2nd Key = 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 0
After second S-Boxes = 1 1 1 1
P4 is defined as - 2 4 3 1
After P4 = 1 1 1 1
After XOR operation with left nibble of after first part = 0 0 1 0
After second part = 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0
l = 1 1 0 1 and r = 1 0 1 0在右半部分,我们使用EP表执行扩展排列,该表将4位转换为8位。扩展排列定义为–
EP(k1, k2, k3, k4) = (k4, k1, k2, k3, k2, k3, k4, k1)
After second ep = 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1我们使用第二个键K2与扩展排列的输出执行XOR操作。
Key-2 is - 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 1
(0 1 0 0 0 0 1 1) XOR (0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1) = 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 0
After XOR operation with 2nd Key = 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 0同样,我们将XOR的输出分成两个半部分,每个半部分为4位。
l = 0 0 0 1 and r = 0 1 1 0我们将S盒的第一和第四位作为行,将第二和第三位作为列。
S0 = [1,0,3,2
3,2,1,0
0,2,1,3
3,1,3,2]
S1 = [0,1,2,3
2,0,1,3
3,0,1,0
2,1,0,3]
For l = 0 0 0 1
row = 01 = 1 , column = 00 = 0
S0 = 3 = 11
For r = 0 1 1 0
row = 00 = 0 , column = 11 = 3
S1 = 3 = 11
After first S-Boxes combining S0 and S1 = 1 1 1 1S框提供2位输出,我们将其组合得到4位,然后使用P4表执行置换。 P4被定义为–
P4(k1, k2, k3, k4) = (k2, k4, k3, k1)
After P4 = 1 1 1 1我们将P4表的输出与初始排列表(即IP表)的左半部分进行XOR运算。
(1 1 0 1) XOR (1 1 1 1) = 0 0 1 0
After XOR operation with left nibble of after first part = 0 0 1 0我们将两个部分组合在一起,即初始排列的右半部分和ip的输出。
Combine 1 0 1 0 and 0 0 1 0
After combine = 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0
After second part = 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0步骤5:
执行逆初始排列。该表的输出是8位密文。
Output of step 4 : 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0逆初始排列定义为–
IP-1(k1, k2, k3, k4, k5, k6, k7, k8) = (k4, k1, k3, k5, k7, k2, k8, k6)8位密文将为= 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0
Java
/*package whatever //do not write package name here */
import java.io.*;
public class GFG {
// int key[]= {0,0,1,0,0,1,0,1,1,1};
int key[] = {
1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0
}; // extra example for checking perpose
int P10[] = { 3, 5, 2, 7, 4, 10, 1, 9, 8, 6 };
int P8[] = { 6, 3, 7, 4, 8, 5, 10, 9 };
int key1[] = new int[8];
int key2[] = new int[8];
int[] IP = { 2, 6, 3, 1, 4, 8, 5, 7 };
int[] EP = { 4, 1, 2, 3, 2, 3, 4, 1 };
int[] P4 = { 2, 4, 3, 1 };
int[] IP_inv = { 4, 1, 3, 5, 7, 2, 8, 6 };
int[][] S0 = { { 1, 0, 3, 2 },
{ 3, 2, 1, 0 },
{ 0, 2, 1, 3 },
{ 3, 1, 3, 2 } };
int[][] S1 = { { 0, 1, 2, 3 },
{ 2, 0, 1, 3 },
{ 3, 0, 1, 0 },
{ 2, 1, 0, 3 } };
// this function basically generates the key(key1 and
//key2) using P10 and P8 with (1 and 2)left shifts
void key_generation()
{
int key_[] = new int[10];
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
key_[i] = key[P10[i] - 1];
}
int Ls[] = new int[5];
int Rs[] = new int[5];
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
Ls[i] = key_[i];
Rs[i] = key_[i + 5];
}
int[] Ls_1 = shift(Ls, 1);
int[] Rs_1 = shift(Rs, 1);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
key_[i] = Ls_1[i];
key_[i + 5] = Rs_1[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
key1[i] = key_[P8[i] - 1];
}
int[] Ls_2 = shift(Ls, 2);
int[] Rs_2 = shift(Rs, 2);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
key_[i] = Ls_2[i];
key_[i + 5] = Rs_2[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
key2[i] = key_[P8[i] - 1];
}
System.out.println("Your Key-1 :");
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++)
System.out.print(key1[i] + " ");
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Your Key-2 :");
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++)
System.out.print(key2[i] + " ");
}
// this function is use full for shifting(circular) the
//array n position towards left
int[] shift(int[] ar, int n)
{
while (n > 0) {
int temp = ar[0];
for (int i = 0; i < ar.length - 1; i++) {
ar[i] = ar[i + 1];
}
ar[ar.length - 1] = temp;
n--;
}
return ar;
}
// this is main encryption function takes plain text as
//input uses another functions and returns the array of
//cipher text
int[] encryption(int[] plaintext)
{
int[] arr = new int[8];
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
arr[i] = plaintext[IP[i] - 1];
}
int[] arr1 = function_(arr, key1);
int[] after_swap = swap(arr1, arr1.length / 2);
int[] arr2 = function_(after_swap, key2);
int[] ciphertext = new int[8];
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
ciphertext[i] = arr2[IP_inv[i] - 1];
}
return ciphertext;
}
// decimal to binary string 0-3
String binary_(int val)
{
if (val == 0)
return "00";
else if (val == 1)
return "01";
else if (val == 2)
return "10";
else
return "11";
}
// this function is doing core things like expansion
// then xor with desired key then S0 and S1
//substitution P4 permutation and again xor we have used
//this function 2 times(key-1 and key-2) during
//encryption and 2 times(key-2 and key-1) during
//decryption
int[] function_(int[] ar, int[] key_)
{
int[] l = new int[4];
int[] r = new int[4];
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
l[i] = ar[i];
r[i] = ar[i + 4];
}
int[] ep = new int[8];
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
ep[i] = r[EP[i] - 1];
}
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
ar[i] = key_[i] ^ ep[i];
}
int[] l_1 = new int[4];
int[] r_1 = new int[4];
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
l_1[i] = ar[i];
r_1[i] = ar[i + 4];
}
int row, col, val;
row = Integer.parseInt("" + l_1[0] + l_1[3], 2);
col = Integer.parseInt("" + l_1[1] + l_1[2], 2);
val = S0[row][col];
String str_l = binary_(val);
row = Integer.parseInt("" + r_1[0] + r_1[3], 2);
col = Integer.parseInt("" + r_1[1] + r_1[2], 2);
val = S1[row][col];
String str_r = binary_(val);
int[] r_ = new int[4];
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
char c1 = str_l.charAt(i);
char c2 = str_r.charAt(i);
r_[i] = Character.getNumericValue(c1);
r_[i + 2] = Character.getNumericValue(c2);
}
int[] r_p4 = new int[4];
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
r_p4[i] = r_[P4[i] - 1];
}
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
l[i] = l[i] ^ r_p4[i];
}
int[] ouptput = new int[8];
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
ouptput[i] = l[i];
ouptput[i + 4] = r[i];
}
return ouptput;
}
// this function swaps the nibble of size n(4)
int[] swap(int[] aray, int n)
{
int[] l = new int[n];
int[] r = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
l[i] = aray[i];
r[i] = aray[i + n];
}
int[] output = new int[2 * n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
output[i] = r[i];
output[i + n] = l[i];
}
return output;
}
// this is main decryption function
// here we have used all previously defined function
// it takes cipher text as input and returns the array
//of decrypted text
int[] decryption(int[] ar)
{
int[] arr = new int[8];
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
arr[i] = ar[IP[i] - 1];
}
int[] arr1 = function_(arr, key2);
int[] after_swap = swap(arr1, arr1.length / 2);
int[] arr2 = function_(after_swap, key1);
int[] decrypted = new int[8];
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
decrypted[i] = arr2[IP_inv[i] - 1];
}
return decrypted;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
GFG obj = new GFG();
obj.key_generation(); // call to key generation
// function
// int []plaintext= {1,0,1,0,0,1,0,1};
int[] plaintext = {
1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1
}; // extra example for checking perpose
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Your plain Text is :");
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) // printing the
// plaintext
System.out.print(plaintext[i] + " ");
int[] ciphertext = obj.encryption(plaintext);
System.out.println();
System.out.println(
"Your cipher Text is :"); // printing the cipher
// text
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++)
System.out.print(ciphertext[i] + " ");
int[] decrypted = obj.decryption(ciphertext);
System.out.println();
System.out.println(
"Your decrypted Text is :"); // printing the
// decrypted text
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++)
System.out.print(decrypted[i] + " ");
}
}
//Omkar VarhadiYour Key-1 :
1 0 1 0 0 1 0 0
Your Key-2 :
0 1 0 0 0 0 1 1
Your plain Text is :
1 0 0 1 0 1 1 1
Your cipher Text is :
0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0
Your decrypted Text is :
1 0 0 1 0 1 1 1