- C++中的delete和free()(1)
- C++中的delete和free()
- C++中的delete和free()(1)
- C++中的delete和free()
- C++ 中的 delete 和 free()(1)
- C++ 中的 delete 和 free()
- C++中的new vs malloc()和free()vs delete(1)
- C++中的new vs malloc()和free()vs delete
- C++中的new vs malloc()和free()vs delete(1)
- C++ 中的 new vs malloc() 和 free() vs delete(1)
- C++中的new vs malloc()和free()vs delete
- C++ 中的 new vs malloc() 和 free() vs delete
- C++ free()(1)
- C++ free()
- delete # (1)
- matlab free (1)
- delete # - 任何代码示例
- matlab free - 任何代码示例
- c++ vs c# - C++ (1)
- c vs c++ vs c# - C++ (1)
- c vs c++ vs c#(1)
- c# vs c++ (1)
- ++i vs i++ (1)
- c vs c++ (1)
- c++ vs g++ - C++ (1)
- robux free - C# (1)
- robux free (1)
- c vs c++ vs c# - C++ 代码示例
- c vs c++ vs c#代码示例
📅 最后修改于: 2020-10-16 06:52:46 🧑 作者: Mango
Free vs Delete in C++
在本主题中,我们将学习free()函数和C++中的delete运算符。
free()函数
free()函数在C++中用于动态取消分配内存。它基本上是C++中使用的库函数,并且在stdlib.h头文件中定义。当指针指向使用malloc()函数分配的内存或Null指针时,将使用此库函数。
free()函数的语法
假设我们已经声明了一个指针“ ptr”,现在,我们想取消分配它的内存:
free(ptr);
上面的语法将取消分配指针变量“ ptr”的内存。
free()参数
在以上语法中,ptr是free()函数内部的参数。 ptr是指向使用malloc(),calloc()或realloc函数分配的内存块的指针。该指针也可以为null或使用malloc分配但不指向任何其他内存块的指针。
- 如果指针为空,则free()函数将不执行任何操作。
- 如果使用malloc,calloc或realloc分配了指针,但未指向任何内存块,则此函数将导致未定义的行为。
free()返回值
free()函数不返回任何值。它的主要函数是释放内存。
让我们通过一个例子来理解。
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int *ptr;
ptr = (int*) malloc(5*sizeof(int));
cout << "Enter 5 integer" << endl;
for (int i=0; i<5; i++)
{
// *(ptr+i) can be replaced by ptr[i]
cin >>ptr[i];
}
cout << endl << "User entered value"<< endl;
for (int i=0; i<5; i++)
{
cout <<*(ptr+i) << " ";
}
free(ptr);
/* prints a garbage value after ptr is free */
cout << "Garbage Value" << endl;
for (int i=0; i<5; i++)
{
cout << *(ptr+i)<< " ";
}
return 0;
}
上面的代码展示了free()函数如何与malloc()一起工作。首先,我们声明整数指针* ptr,然后使用malloc()函数将内存分配给该指针变量。现在,ptr指向5个整数的未初始化存储块。分配内存后,我们使用free()函数销毁分配的内存。当我们尝试print由ptr指向的值时,我们得到一个垃圾值,这意味着内存已被取消分配。
输出量

让我们看看free()函数如何与calloc一起工作。
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
float *ptr; // float pointer declaration
ptr=(float*)calloc(1,sizeof(float));
*ptr=6.7;
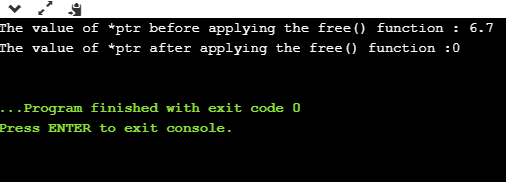
std::cout << "The value of *ptr before applying the free() function : " <<*ptr<< std::endl;
free(ptr);
std::cout << "The value of *ptr after applying the free() function :" <<*ptr<< std::endl;
return 0;
}
在上面的示例中,我们可以观察到free()函数与calloc()一起工作。我们使用calloc()函数将内存块分配给浮点指针ptr。我们为ptr分配了一个内存块,该内存块可以具有单个浮点类型值。
输出:
让我们看另一个例子。
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int *ptr1=NULL;
int *ptr2;
int x=9;
ptr2=&x;
if(ptr1)
{
std::cout << "Pointer is not Null" << std::endl;
}
else
{
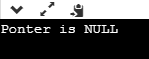
cout<<"Ponter is NULL";
}
free(ptr1);
//free(ptr2); // If this statement is executed, then it gives a runtime error.
return 0;
}
上面的代码显示了free()函数如何与NULL指针一起工作。我们声明了两个指针,即ptr1和ptr2。我们为指针ptr1分配NULL值,为指针ptr2分配x变量的地址。当将free(ptr1)函数应用于ptr1时,分配给ptr的内存块将成功释放。语句free(ptr2)显示运行时错误,因为未使用malloc或calloc函数分配分配给ptr2的内存块。
输出量
删除运算符
它是C++编程语言中使用的运算符,用于动态取消分配内存。该运算符主要用于使用新运算符分配的那些指针或NULL指针。
句法
delete pointer_name
例如,如果我们使用new运算符将内存分配给指针,现在我们要删除它。要删除指针,我们使用以下语句:
delete p;
要删除数组,我们使用以下语句:
delete [] p;
与删除运算符有关的一些重要点是:
- 它用于删除使用new关键字分配的数组或非数组对象。
- 要删除数组或非数组对象,我们分别使用delete []和delete运算符。
- new关键字在堆中分配了内存;因此,可以说delete运算符总是从堆中取消分配内存
- 它不会破坏指针,但是指针所指向的值或存储块将被破坏。
让我们看一下delete运算符的简单示例。
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int *ptr;
ptr=new int;
*ptr=68;
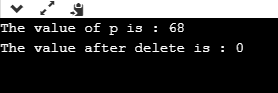
std::cout << "The value of p is : " <<*ptr<< std::endl;
delete ptr;
std::cout <<"The value after delete is : " <<*ptr<< std::endl;
return 0;
}
在上面的代码中,我们使用new运算符分配内存,因此我们使用delete ptr运算符销毁由指针ptr指向的内存块。
输出量
让我们看看删除是如何与对象数组一起工作的。
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int *ptr=new int[5]; // memory allocation using new operator.
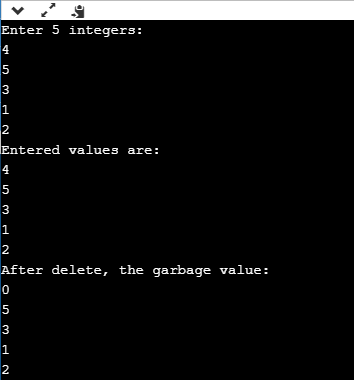
std::cout << "Enter 5 integers:" << std::endl;
for(int i=1;i<=5;i++)
{
cin>>ptr[i];
}
std::cout << "Entered values are:" << std::endl;
for(int i=1;i<=5;i++)
{
cout<<*(ptr+i)< 输出量
delete和free()之间的区别
以下是C++中delete和free()之间的区别:
- delete是一个运算符,它动态地取消分配内存,而free()是一个在运行时破坏内存的函数。
- delete运算符用于删除使用new运算符或NULL指针分配的指针,而free()函数用于删除使用malloc(),calloc()或realloc()分配的指针。函数或NULL指针。
- 当delete运算符销毁分配的内存时,它将在C++中调用该类的析构函数,而free()函数不会调用该析构函数。它只会从堆中释放内存。
- delete()运算符比free()函数要快。