先决条件–实时系统中的时序约束
1.延迟约束:
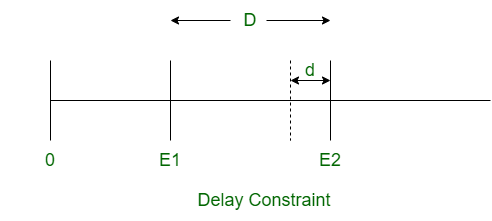
延迟约束是实时系统中两个连续事件发生之间的最小时间间隔。如果事件在延迟约束之前发生,则称为延迟违例。两个事件发生之间的时间间隔应大于或等于延迟约束。
如果D是两个事件发生之间的实际时间间隔,并且d是延迟约束,则D> = d 。
2.截止日期限制:
截止时间约束是实时系统中两个连续事件发生之间的最大时间间隔。如果事件在截止期限约束之后发生,则事件的结果被认为是不正确的。两个事件发生之间的时间间隔应小于或等于截止期限约束。
如果D是两个事件发生之间的实际时间间隔,而d是截止期限约束,则D <= d 。

延迟约束与期限约束之间的区别:
| DELAY CONSTRAINT | DEADLINE CONSTRAINT |
|---|---|
| It is the minimum time interval between occurrence of two consecutive events. | It is the maximum time interval between occurrence of two consecutive events. |
| It implies that after the occurrence of event E1, event E2 can occur only after the time elapsed is equal to delay constraint. | It implies that after the occurrence of event E1, event E2 must occur only before the time elapsed is equal to deadline constraint. |
| If D is the actual time interval between occurrence of two events and d is the delay constraint, then D >= d. | If D is the actual time interval between occurrence of two events and d is the deadline constraint, then D <= d. |
| Delay violation occurs here if an event occurs before delay constraint. | There is no such term as deadline violation if an event occurs after deadline constraint. |
| The result is not considered incorrect if event occurs before delay constraint. | The result is considered incorrect if event occurs after deadline constraint. |
| Delay Constraint under performance is classified as Response-Response (RR) and Stimulus-Response (SR). | Deadline Constraint under performance is classified as Stimulus-Response (SR) and Response-Response (RR). |
| Delay Constraint under performance is classified as Response-Stimulus (RS) and Stimulus-Stimulus (SS). | Deadline Constraint under performance is classified as Stimulus-Stimulus (SS) and Response-Stimulus (RS). |