1. LOOK磁盘调度算法:
外观算法实际上是SCAN算法的改进版本。在这种算法中,磁头从磁盘一侧的第一个请求开始,并通过为磁盘之间的所有请求提供服务而朝另一端移动。到达一端的最后一个请求后,头部反转其方向并返回到第一个请求,为这两个请求之间的所有请求提供服务。与SCAN不同,在这种情况下,磁头不是一直走到最后一个轨道,而是一直走到最后一个请求,然后改变方向。
例子 –
考虑一个具有200个磁道(0-199)的磁盘和具有I / O请求的磁盘队列,其顺序如下:98、183、40、122、10、124、65。读/写的当前磁头位置头是53并且将向右移动。使用LOOK算法计算读/写磁头的磁道移动总数。
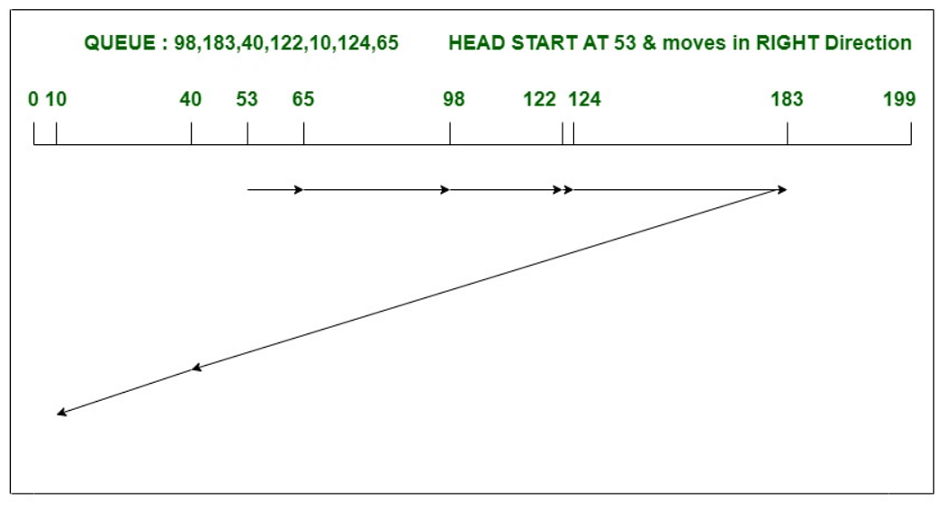
头部总动作
= (65-53)+(98-65)+(122-98)
+(124-122)+(183-124)+(183-40)+(40-10)
= 303 2. C-LOOK磁盘调度算法:
C-LOOK是LOOK和SCAN算法的修改版本。在这种算法中,头部从一个方向上的第一个请求开始,然后在另一端朝向最后一个请求移动,从而服务于两者之间的所有请求。在一端达到最后一个请求后,头部向另一个方向跳动,朝剩余的请求移动,然后在与以前相同的方向上满足它们。与LOOK不同,它仅在一个方向上满足请求。
例子 –
考虑一个具有200个磁道(0-199)的磁盘和具有I / O请求的磁盘队列,其顺序如下:98、183、40、122、10、124、65。读/写的当前磁头位置头是53并且将向右移动。使用C-LOOK算法计算读/写磁头的磁道移动总数。

头部总动作
= (65-53)+(98-65)+(122-98)
+(124-122)+(183-124)+(183-10)+(40-10)
= 333 LOOK和C-LOOK磁盘调度算法之间的区别:
| LOOK DISK SCHEDULING ALGORITHM | C-LOOK SCHEDULING ALGORITHM | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | In LOOK, the head can serve the requests in both the directions. | In C-LOOK algorithm, head can serves the requests only in one direction. |
| 2. | It lags in performance as compared to C-LOOK. | C-LOOK algorithm has the best performance in all disk scheduling algorithms. |
| 3. | In above example of LOOK algorithm, the head moves from 53, serves all requests in right direction till it reaches the last request in one end. Then it reverses the direction and serves the remaining requests in left direction. | In above example of C-LOOK algorithm, the head moves from 53, serves all requests in right direction till it reaches the last request in one end. Then it jumps to the remaining requests and serve them in right direction only. |
| 4. | Here handling of request is not so good as compared to C-LOOK algorithm. | C-LOOK algorithm can handle requests more effectively than LOOK. |
| 5. | LOOK has higher throughput and provides low variance response time. | C-LOOK provides uniform waiting time and response time. |