先决条件:磁盘调度算法
给定一组磁盘磁道号和初始磁头位置,如果使用LOOK磁盘调度算法,我们的任务是找到为访问所有请求的磁道而执行的寻道操作总数。另外,编写一个程序来使用LOOK磁盘调度算法查找查找序列。
看看磁盘调度算法:
LOOK 是 SCAN(电梯)磁盘调度算法的高级版本,它比层次结构中的任何其他算法(FCFS->SRTF->SCAN->C-SCAN->LOOK) 提供稍好的寻道时间。 LOOK 算法服务请求类似于 SCAN 算法,同时它也“向前看”,好像有更多的轨道需要在同一个方向上服务。如果在移动方向上没有未决请求,则头部反转方向并开始为相反方向的请求提供服务。
与 SCAN 相比,LOOK 算法性能更好的主要原因是因为在该算法中,磁头不允许移动到磁盘末尾。
算法:
- 让 Request 数组表示一个数组,存储已按到达时间升序请求的曲目的索引。 ‘head’ 是磁盘磁头的位置。
- 头部运动的初始方向是给定的,它以相同的方向服务。
- 头部在头部移动的方向上一一服务所有的请求。
- 头部继续向同一个方向移动,直到这个方向的所有请求都没有完成。
- 在此方向上移动时,计算轨道与磁头的绝对距离。
- 使用此距离增加总寻道计数。
- 当前服务的轨道位置现在成为新的磁头位置。
- 转到第 5 步,直到我们到达此方向的最后一个请求。
- 如果我们到达不需要在这个方向上服务的请求的地方,则反转方向并转到步骤 3,直到请求数组中的所有轨道都没有得到服务。
例子:
Input:
Request sequence = {176, 79, 34, 60, 92, 11, 41, 114}
Initial head position = 50
Direction = right (We are moving from left to right)
Output:
Initial position of head: 50
Total number of seek operations = 291
Seek Sequence is
60
79
92
114
176
41
34
11下图显示了使用 LOOK 服务请求的轨道的顺序。
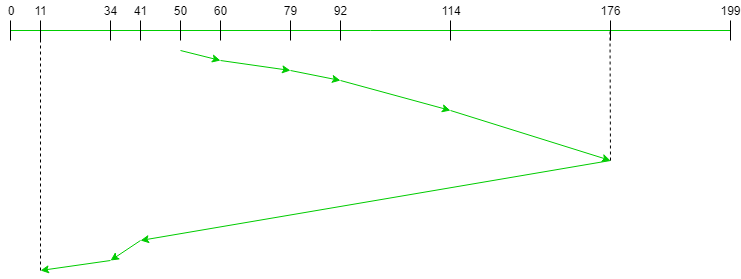
因此,总寻道计数计算如下:
= (60-50)+(79-60)+(92-79)
+(114-92)+(176-114)
+(176-41)+(41-34)+(34-11)执行:
下面给出LOOK算法的实现。
注意: distance 变量用于存储磁头与当前磁道位置之间的绝对距离。 disk_size 是磁盘的大小。 Vectors left 和 right 分别存储初始头部位置左侧和右侧的所有请求轨迹。
C++
// C++ program to demonstrate
// LOOK Disk Scheduling algorithm
int size = 8;
#include
using namespace std;
// Code by Vikram Chaurasia
int disk_size = 200;
void LOOK(int arr[], int head, string direction)
{
int seek_count = 0;
int distance, cur_track;
vector left, right;
vector seek_sequence;
// appending values which are
// currently at left and right
// direction from the head.
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (arr[i] < head)
left.push_back(arr[i]);
if (arr[i] > head)
right.push_back(arr[i]);
}
// sorting left and right vectors
// for servicing tracks in the
// correct sequence.
std::sort(left.begin(), left.end());
std::sort(right.begin(), right.end());
// run the while loop two times.
// one by one scanning right
// and left side of the head
int run = 2;
while (run--) {
if (direction == "left") {
for (int i = left.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
cur_track = left[i];
// appending current track to seek sequence
seek_sequence.push_back(cur_track);
// calculate absolute distance
distance = abs(cur_track - head);
// increase the total count
seek_count += distance;
// accessed track is now the new head
head = cur_track;
}
// reversing the direction
direction = "right";
}
else if (direction == "right") {
for (int i = 0; i < right.size(); i++) {
cur_track = right[i];
// appending current track to seek sequence
seek_sequence.push_back(cur_track);
// calculate absolute distance
distance = abs(cur_track - head);
// increase the total count
seek_count += distance;
// accessed track is now new head
head = cur_track;
}
// reversing the direction
direction = "left";
}
}
cout << "Total number of seek operations = "
<< seek_count << endl;
cout << "Seek Sequence is" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < seek_sequence.size(); i++) {
cout << seek_sequence[i] << endl;
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// request array
int arr[size] = { 176, 79, 34, 60,
92, 11, 41, 114 };
int head = 50;
string direction = "right";
cout << "Initial position of head: "
<< head << endl;
LOOK(arr, head, direction);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to demonstrate
// LOOK Disk Scheduling algorithm
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static int size = 8;
static int disk_size = 200;
public static void LOOK(int arr[], int head,
String direction)
{
int seek_count = 0;
int distance, cur_track;
Vector left = new Vector();
Vector right = new Vector();
Vector seek_sequence = new Vector();
// Appending values which are
// currently at left and right
// direction from the head.
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
if (arr[i] < head)
left.add(arr[i]);
if (arr[i] > head)
right.add(arr[i]);
}
// Sorting left and right vectors
// for servicing tracks in the
// correct sequence.
Collections.sort(left);
Collections.sort(right);
// Run the while loop two times.
// one by one scanning right
// and left side of the head
int run = 2;
while (run-- > 0)
{
if (direction == "left")
{
for(int i = left.size() - 1;
i >= 0; i--)
{
cur_track = left.get(i);
// Appending current track to
// seek sequence
seek_sequence.add(cur_track);
// Calculate absolute distance
distance = Math.abs(cur_track - head);
// Increase the total count
seek_count += distance;
// Accessed track is now the new head
head = cur_track;
}
// Reversing the direction
direction = "right";
}
else if (direction == "right")
{
for(int i = 0; i < right.size(); i++)
{
cur_track = right.get(i);
// Appending current track to
// seek sequence
seek_sequence.add(cur_track);
// Calculate absolute distance
distance = Math.abs(cur_track - head);
// Increase the total count
seek_count += distance;
// Accessed track is now new head
head = cur_track;
}
// Reversing the direction
direction = "left";
}
}
System.out.println("Total number of seek " +
"operations = " + seek_count);
System.out.println("Seek Sequence is");
for(int i = 0; i < seek_sequence.size(); i++)
{
System.out.println(seek_sequence.get(i));
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
// Request array
int arr[] = { 176, 79, 34, 60,
92, 11, 41, 114 };
int head = 50;
String direction = "right";
System.out.println("Initial position of head: " +
head);
LOOK(arr, head, direction);
}
}
// This code is contributed by divyesh072019 Python3
# Python3 program to demonstrate
# LOOK Disk Scheduling algorithm
size = 8
disk_size = 200
def LOOK(arr, head, direction):
seek_count = 0
distance = 0
cur_track = 0
left = []
right = []
seek_sequence = []
# Appending values which are
# currently at left and right
# direction from the head.
for i in range(size):
if (arr[i] < head):
left.append(arr[i])
if (arr[i] > head):
right.append(arr[i])
# Sorting left and right vectors
# for servicing tracks in the
# correct sequence.
left.sort()
right.sort()
# Run the while loop two times.
# one by one scanning right
# and left side of the head
run = 2
while (run):
if (direction == "left"):
for i in range(len(left) - 1, -1, -1):
cur_track = left[i]
# Appending current track to
# seek sequence
seek_sequence.append(cur_track)
# Calculate absolute distance
distance = abs(cur_track - head)
# Increase the total count
seek_count += distance
# Accessed track is now the new head
head = cur_track
# Reversing the direction
direction = "right"
elif (direction == "right"):
for i in range(len(right)):
cur_track = right[i]
# Appending current track to
# seek sequence
seek_sequence.append(cur_track)
# Calculate absolute distance
distance = abs(cur_track - head)
# Increase the total count
seek_count += distance
# Accessed track is now new head
head = cur_track
# Reversing the direction
direction = "left"
run -= 1
print("Total number of seek operations =",
seek_count)
print("Seek Sequence is")
for i in range(len(seek_sequence)):
print(seek_sequence[i])
# Driver code
# Request array
arr = [ 176, 79, 34, 60, 92, 11, 41, 114 ]
head = 50
direction = "right"
print("Initial position of head:", head)
LOOK(arr, head, direction)
# This code is contributed by rag2127C#
// C# program to demonstrate
// LOOK Disk Scheduling algorithm
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
static int size = 8;
static void LOOK(int[] arr, int head,
string direction)
{
int seek_count = 0;
int distance, cur_track;
List left = new List();
List right = new List();
List seek_sequence = new List();
// Appending values which are
// currently at left and right
// direction from the head.
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
if (arr[i] < head)
left.Add(arr[i]);
if (arr[i] > head)
right.Add(arr[i]);
}
// Sorting left and right vectors
// for servicing tracks in the
// correct sequence.
left.Sort();
right.Sort();
// Run the while loop two times.
// one by one scanning right
// and left side of the head
int run = 2;
while (run-- > 0)
{
if (direction == "left")
{
for(int i = left.Count - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
cur_track = left[i];
// Appending current track to
// seek sequence
seek_sequence.Add(cur_track);
// Calculate absolute distance
distance = Math.Abs(cur_track - head);
// Increase the total count
seek_count += distance;
// Accessed track is now the new head
head = cur_track;
}
// Reversing the direction
direction = "right";
}
else if (direction == "right")
{
for(int i = 0; i < right.Count; i++)
{
cur_track = right[i];
// Appending current track to
// seek sequence
seek_sequence.Add(cur_track);
// Calculate absolute distance
distance = Math.Abs(cur_track - head);
// Increase the total count
seek_count += distance;
// Accessed track is now new head
head = cur_track;
}
// Reversing the direction
direction = "left";
}
}
Console.WriteLine("Total number of seek " +
"operations = " + seek_count);
Console.WriteLine("Seek Sequence is");
for(int i = 0; i < seek_sequence.Count; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(seek_sequence[i]);
}
}
// Driver code
static void Main()
{
// Request array
int[] arr = { 176, 79, 34, 60,
92, 11, 41, 114 };
int head = 50;
string direction = "right";
Console.WriteLine("Initial position of head: " +
head);
LOOK(arr, head, direction);
}
}
// This code is contributed by divyeshrabadiya07 Javascript
输出:
Initial position of head: 50
Total number of seek operations = 291
Seek Sequence is
60
79
92
114
176
41
34
11