1.分层数据模型:
分层数据模型是最早的数据模型类型。它由IBM在1968年开发。它以树状结构组织数据。层次模型包括以下内容:
- 它包含通过分支连接的节点。
- 最顶层的节点称为根节点。
- 如果在顶层出现多个节点,则可以将这些节点称为根段。
- 每个节点只有一个父节点。
- 一位父母可能有很多孩子。

在上图中,电子是根节点,它有两个子节点,即电视和便携式电子设备。这两个人还有更多的孩子,他们将其作为父母。例如:电视有孩子,例如电子管,液晶显示器和等离子,这三台电视作为父级。它遵循一对多的关系。
2.关系数据模型:
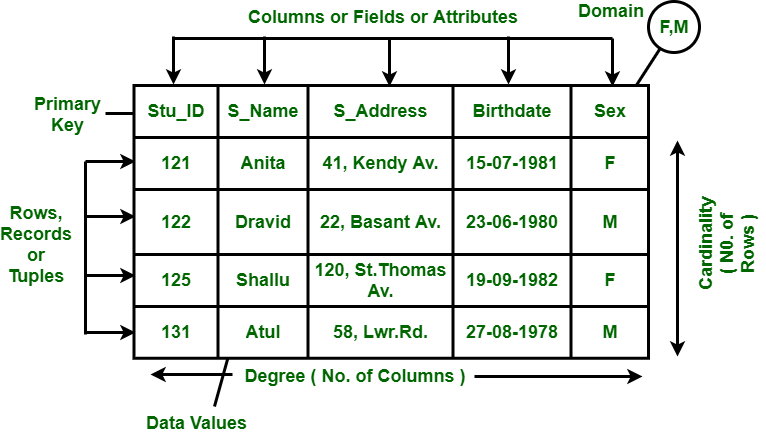
关系数据模型是由EF Codd在1970年开发的。与分层数据模型中的关系不同,它们并不是物理链接。以下是关系数据模型的属性:
- 数据仅以表的形式表示。
- 它仅处理数据,而不处理物理结构。
- 它提供有关元数据的信息。
- 在行和列的交集处,元组只有一个值。
- 它提供了一种轻松处理查询的方法。
层次数据模型和关系数据模型之间的区别:
| Hierarchical Data Model | Relational Data Model |
|---|---|
| In this model, to store data hierarchy method is used. It is oldest method and not in use today. | It is the most flexible and efficient database model. It is most used database in today. |
| It implements 1:1 and 1:n. | In addition to 1:1 and 1:n it also implements many to many relationships. |
| To organize records, it uses tree structure. | To organize records, it uses table. |
| More chances of complexity. | No chance of complexity. |
| There is lack of declarative query facility. | It provides facility of declarative query facility using SQL. |
| Records are linked with help of pointers. | Records are linked with help of rows and columns. |
| Insertion anomaly exits in this model i.e. child node cannot be inserted without parent node. | There is no insertion anomaly. |
| Deletion anomaly exists in this model i.e. it is difficult to delete parent node. | There is no deletion anomaly. |
| It is used to access data which is complex and asymmetric. | It is used to access data which is complex and symmetric. |
| This model lacks data independence. | This model provides data independence. |