Python Tkinter – 文本小部件
Tkinter 是Python中用于制作用户友好 GUI 的 GUI 工具包。Tkinter 是Python中最常用和最基本的 GUI 框架。 Tkinter 使用面向对象的方法来制作 GUI。
注意:更多信息请参考Python GUI – tkinter
文本小部件
文本小部件用于用户想要插入多行文本字段的地方。此小部件可用于需要多行文本的各种应用程序,例如消息传递、发送信息或显示信息以及许多其他任务。我们也可以在 Textwidget 中插入媒体文件,例如图像和链接。
句法:
T = Text(root, bg, fg, bd, height, width, font, ..)可选参数
- root - 根窗口。
- bg – 背景颜色
- fg——前景色
- bd - 小部件的边框。
- height - 小部件的高度。
- width - 小部件的宽度。
- font - 文本的字体类型。
- cursor - 要使用的光标类型。
- insetofftime – 光标闪烁关闭的时间(以毫秒为单位)。
- insertontime – 光标闪烁的时间(以毫秒为单位)。
- padx - 水平填充。
- pady - 垂直填充。
- state – 定义小部件是否响应鼠标或键盘的移动。
- highlightthickness - 定义焦点高光的厚度。
- insertwidth – 定义插入字符的宽度。
- 浮雕- 可以是 SUNKEN、RAISED、GROOVE 和 RIDGE 的边界类型。
- yscrollcommand – 使小部件可以垂直滚动。
- xscrollcommand – 使小部件水平滚动。
一些常用方法
- index(index) -- 获取指定的索引。
- insert(index) – 在指定索引处插入字符串。
- see(index) – 检查字符串在给定索引处是否可见。
- get(startindex, endindex) – 获取给定范围内的字符。
- delete(startindex, endindex) – 删除指定范围内的字符。
标签处理方法
- tag_delete(tagname) – 删除给定的标签。
- tag_add(tagname, startindex, endindex) – 标记指定范围内的字符串
- tag_remove(tagname, startindex, endindex) – 从指定范围删除标签
标记处理方法
- mark_names() – 获取给定范围内的所有标记。
- index(mark) - 获取标记的索引。
- mark_gravity() – 获取给定标记的重力。
示例 1:
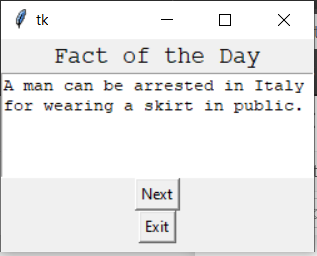
Python3
import tkinter as tk
root = Tk()
# specify size of window.
root.geometry("250x170")
# Create text widget and specify size.
T = Text(root, height = 5, width = 52)
# Create label
l = Label(root, text = "Fact of the Day")
l.config(font =("Courier", 14))
Fact = """A man can be arrested in
Italy for wearing a skirt in public."""
# Create button for next text.
b1 = Button(root, text = "Next", )
# Create an Exit button.
b2 = Button(root, text = "Exit",
command = root.destroy)
l.pack()
T.pack()
b1.pack()
b2.pack()
# Insert The Fact.
T.insert(tk.END, Fact)
tk.mainloop()Python3
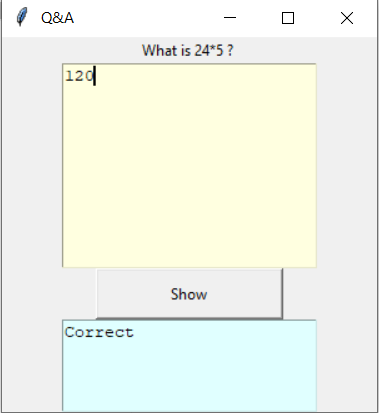
from tkinter import *
root = Tk()
root.geometry("300x300")
root.title(" Q&A ")
def Take_input():
INPUT = inputtxt.get("1.0", "end-1c")
print(INPUT)
if(INPUT == "120"):
Output.insert(END, 'Correct')
else:
Output.insert(END, "Wrong answer")
l = Label(text = "What is 24 * 5 ? ")
inputtxt = Text(root, height = 10,
width = 25,
bg = "light yellow")
Output = Text(root, height = 5,
width = 25,
bg = "light cyan")
Display = Button(root, height = 2,
width = 20,
text ="Show",
command = lambda:Take_input())
l.pack()
inputtxt.pack()
Display.pack()
Output.pack()
mainloop()输出
示例 2:保存文本并执行操作
Python3
from tkinter import *
root = Tk()
root.geometry("300x300")
root.title(" Q&A ")
def Take_input():
INPUT = inputtxt.get("1.0", "end-1c")
print(INPUT)
if(INPUT == "120"):
Output.insert(END, 'Correct')
else:
Output.insert(END, "Wrong answer")
l = Label(text = "What is 24 * 5 ? ")
inputtxt = Text(root, height = 10,
width = 25,
bg = "light yellow")
Output = Text(root, height = 5,
width = 25,
bg = "light cyan")
Display = Button(root, height = 2,
width = 20,
text ="Show",
command = lambda:Take_input())
l.pack()
inputtxt.pack()
Display.pack()
Output.pack()
mainloop()
输出