给定一个大小为NXN 的方阵,当矩阵沿其对角线分为四个部分时,任务是找到每个部分的所有元素的总和。对角线上的元素不应计入总和。
例子:
Input: arr[][] = {{1, 2, 3, 4}, {5, 6, 7, 8}, {9, 10, 11, 12}, {13, 14, 15, 16}}
Output: 68
Explanation:
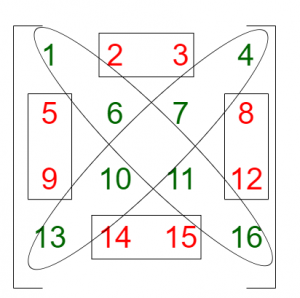
From the above image, (1, 6, 11, 16) and (4, 7, 10, 13) are the diagonals.
The sum of the elements needs to be found are:
Top: (2 + 3) = 5
Left: (5 + 9) = 14
Bottom: (14 + 15) = 29
Right: (8 + 12) = 20
Therefore, sum of all parts = 68.
Input: arr[][] = { {1, 3, 1, 5}, {2, 2, 4, 1}, {5, 0, 2, 3}, {1, 3, 1, 5}}
Output: 19
方法:这个想法是使用索引来识别对角线上的元素。
- 在二维矩阵中,两条对角线的标识方式如下:
- 主对角线:第一个对角线的行索引等于列索引。
Condition for Principal Diagonal:
The row-column condition is row = column.- 二级对角线:第二对角线的行和列的索引之和等于 N(矩阵的大小)。
Condition for Secondary Diagonal:
The row-column condition is row = numberOfRows - column -1- 确定两条对角线后,可以使用穿过最后一行的第一个元素和第一行的最后一个元素的对角线将矩阵进一步分为两部分:
- 左侧部分:
- 如果列索引大于行索引,则该元素属于矩阵的顶部。
- 如果行索引大于列索引,则该元素属于矩阵的左侧部分。
- 正确的部分:
- 如果列索引大于行索引,则该元素属于矩阵的右侧部分。
- 如果行索引大于列索引,则该元素属于矩阵的底部。
- 左侧部分:
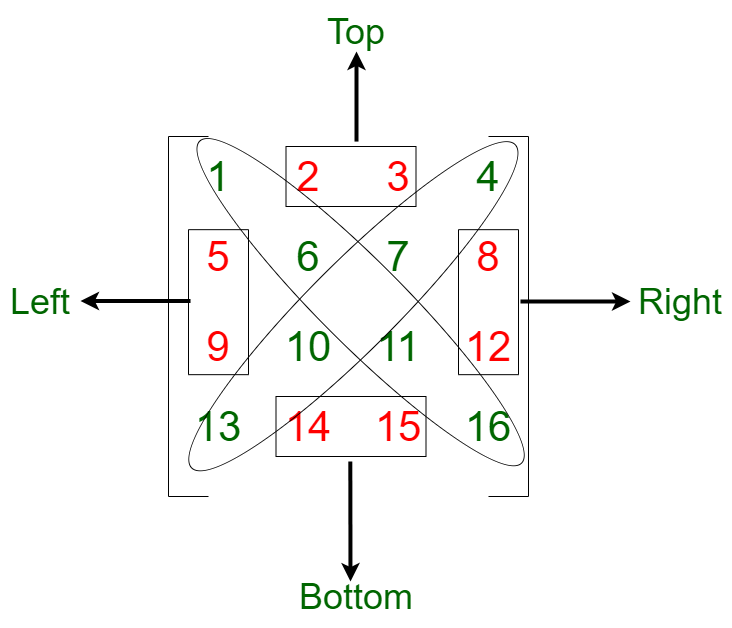
- 所以为了得到矩阵的非对角线部分的总和:
- 按行遍历矩阵
- 如果元素是对角线的一部分,则跳过此元素
- 如果元素是左侧、右侧、底部或顶部(即非对角线部分)的一部分,则在结果总和中添加该元素
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ implementation of the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to return a vector which
// consists the sum of
// four portions of the matrix
int sumOfParts(int* arr, int N)
{
int sum_part1 = 0, sum_part2 = 0,
sum_part3 = 0, sum_part4 = 0;
int totalsum = 0;
// Iterating through the matrix
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
// Condition for selecting all values
// before the second diagonal of metrics
if (i + j < N - 1) {
// Top portion of the matrix
if (i < j and i != j and i + j)
sum_part1 += (arr + i * N)[j];
// Left portion of the matrix
else if (i != j)
sum_part2 += (arr + i * N)[j];
}
else {
// Bottom portion of the matrix
if (i > j and i + j != N - 1)
sum_part3 += (arr + i * N)[j];
// Right portion of the matrix
else {
if (i + j != N - 1 and i != j)
sum_part4 += (arr + i * N)[j];
}
}
}
}
// Adding all the four portions into a vector
totalsum = sum_part1 + sum_part2
+ sum_part3 + sum_part4;
return totalsum;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int N = 4;
int arr[N][N] = { { 1, 2, 3, 4 },
{ 5, 6, 7, 8 },
{ 9, 10, 11, 12 },
{ 13, 14, 15, 16 } };
cout << sumOfParts((int*)arr, N);
} Java
// Java implementation of the above approach
class GFG
{
// Function to return a vector which
// consists the sum of
// four portions of the matrix
static int sumOfParts(int[][] arr, int N)
{
int sum_part1 = 0, sum_part2 = 0,
sum_part3 = 0, sum_part4 = 0;
int totalsum = 0;
// Iterating through the matrix
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
// Condition for selecting all values
// before the second diagonal of metrics
if (i + j < N - 1) {
// Top portion of the matrix
if (i < j && i != j && i + j > 0)
sum_part1 += arr[i][j];
// Left portion of the matrix
else if (i != j)
sum_part2 += arr[i][j];
}
else {
// Bottom portion of the matrix
if (i > j && i + j != N - 1)
sum_part3 += arr[i][j];
// Right portion of the matrix
else {
if (i + j != N - 1 && i != j)
sum_part4 += arr[i][j];
}
}
}
}
// Adding all the four portions into a vector
totalsum = sum_part1 + sum_part2
+ sum_part3 + sum_part4;
return totalsum;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int N = 4;
int arr[][] = { { 1, 2, 3, 4 },
{ 5, 6, 7, 8 },
{ 9, 10, 11, 12 },
{ 13, 14, 15, 16 } };
System.out.print(sumOfParts(arr, N));
}
}
// This code is contributed by PrinciRaj1992Python3
# Python3 implementation of the above approach
# Function to return a vector which
# consists the sum of
# four portions of the matrix
def sumOfParts(arr,N):
sum_part1, sum_part2, sum_part3, \
sum_part4 = 0, 0, 0, 0
totalsum = 0
# Iterating through the matrix
for i in range(N):
for j in range(N):
# Condition for selecting all values
# before the second diagonal of metrics
if i + j < N - 1:
# Top portion of the matrix
if(i < j and i != j and i + j):
sum_part1 += arr[i][j]
# Left portion of the matrix
elif i != j:
sum_part2 += arr[i][j]
else:
# Bottom portion of the matrix
if i > j and i + j != N - 1:
sum_part3 += arr[i][j]
else:
# Right portion of the matrix
if i + j != N - 1 and i != j:
sum_part4 += arr[i][j]
# Adding all the four portions into a vecto
return sum_part1 + sum_part2 + sum_part3 + sum_part4
# Driver code
N = 4
arr = [[ 1, 2, 3, 4 ],
[ 5, 6, 7, 8 ],
[ 9, 10, 11, 12 ],
[ 13, 14, 15, 16 ]]
print(sumOfParts(arr, N))
# This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29C#
// C# implementation of the above approach
using System;
class GFG
{
// Function to return a vector which
// consists the sum of
// four portions of the matrix
static int sumOfParts(int[,] arr, int N)
{
int sum_part1 = 0, sum_part2 = 0,
sum_part3 = 0, sum_part4 = 0;
int totalsum = 0;
// Iterating through the matrix
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
// Condition for selecting all values
// before the second diagonal of metrics
if (i + j < N - 1) {
// Top portion of the matrix
if (i < j && i != j && i + j > 0)
sum_part1 += arr[i, j];
// Left portion of the matrix
else if (i != j)
sum_part2 += arr[i, j];
}
else {
// Bottom portion of the matrix
if (i > j && i + j != N - 1)
sum_part3 += arr[i, j];
// Right portion of the matrix
else {
if (i + j != N - 1 && i != j)
sum_part4 += arr[i, j];
}
}
}
}
// Adding all the four portions into a vector
totalsum = sum_part1 + sum_part2
+ sum_part3 + sum_part4;
return totalsum;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
int N = 4;
int [,]arr = { { 1, 2, 3, 4 },
{ 5, 6, 7, 8 },
{ 9, 10, 11, 12 },
{ 13, 14, 15, 16 } };
Console.WriteLine(sumOfParts(arr, N));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Yash_RJavascript
输出:
68时间复杂度: O(N 2 ),因为我们正在逐行遍历完整矩阵。
如果您想与行业专家一起参加直播课程,请参阅Geeks Classes Live