先决条件: C 中的数组
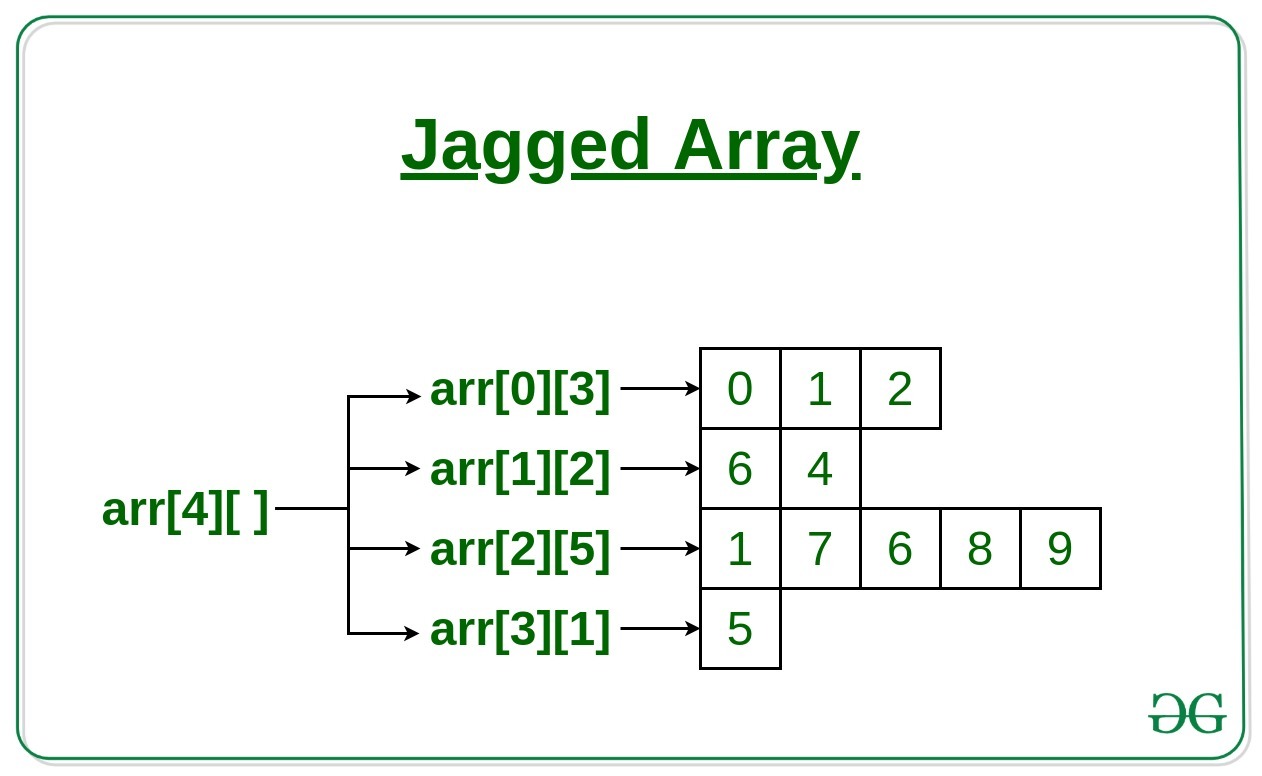
锯齿状数组是数组的数组,这样成员数组可以具有不同的大小,即我们可以创建一个二维数组,但每行的列数是可变的。这些类型的数组也称为锯齿形数组。
例子:
arr[][] = { {0, 1, 2},
{6, 4},
{1, 7, 6, 8, 9},
{5}
};
下面是在 C 中实现锯齿状数组的方法:
- 使用数组和指针(静态锯齿状数组)
- 首先声明具有您需要的行数的一维数组,
- 每个数组(行中元素的数组)的大小将是行中的列数(或元素),
- 然后声明一个一维指针数组,用于保存行的地址,
- 一维数组的大小是您想要在锯齿状数组中的行数。
下面是上述方法的实现:
例子:// C program to show the // implementation of Jagged Arrays #include#include int main() { int row0[4] = { 1, 2, 3, 4 }; int row1[2] = { 5, 6 }; int* jagged[2] = { row0, row1 }; // Array to hold the size of each row int Size[2] = { 4, 2 }, k = 0; // To display elements of Jagged array for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) { // pointer to hold the address of the row int* ptr = jagged[i]; for (int j = 0; j < Size[k]; j++) { printf("%d ", *ptr); // move the pointer to the // next element in the row ptr++; } printf("\n"); k++; // move the pointer to the next row jagged[i]++; } return 0; } 输出:1 2 3 4 5 6 - 使用指针数组(Dynamic Jagged Array)
- 声明一个指针数组(锯齿状数组),
- 此数组的大小将是 Jagged 数组中所需的行数
- 然后,对于数组中的每个指针,为该行中所需的元素数分配内存。
下面是上述方法的实现:
例子:// C program to show the // implementation of Jagged Arrays #include#include int main() { // 2 Rows int* jagged[2]; // Allocate memory for elements in row 0 jagged[0] = malloc(sizeof(int) * 1); // Allocate memory for elements in row 1 jagged[1] = malloc(sizeof(int) * 3); // Array to hold the size of each row int Size[2] = { 1, 3 }, k = 0, number = 100; // User enters the numbers for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) { int* p = jagged[i]; for (int j = 0; j < Size[k]; j++) { *p = number++; // move the pointer p++; } k++; } k = 0; // Display elements in Jagged array for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) { int* p = jagged[i]; for (int j = 0; j < Size[k]; j++) { printf("%d ", *p); // move the pointer to the next element p++; } printf("\n"); k++; // move the pointer to the next row jagged[i]++; } return 0; } 输出:100 101 102 103
如果您想与行业专家一起参加直播课程,请参阅Geeks Classes Live