📌 相关文章
- TypeScript类型
- TypeScript-类型(1)
- typescript 获取类型 - TypeScript (1)
- 仅 typescript 类型检查 - TypeScript (1)
- typescript 检查类型 - TypeScript (1)
- typescript 对象键类型 - TypeScript (1)
- typescript 获取类型 - TypeScript 代码示例
- typescript 检查类型 - TypeScript 代码示例
- 仅 typescript 类型检查 - TypeScript 代码示例
- typescript 循环类型 - TypeScript (1)
- typescript 对象键类型 - TypeScript 代码示例
- typescript 循环类型 - TypeScript 代码示例
- typescript 类型加一个属性 - TypeScript (1)
- typescript 动态类型 - TypeScript (1)
- typescript 类型加一个属性 - TypeScript 代码示例
- typescript 参数函数类型 - TypeScript (1)
- typescript 动态类型 - TypeScript 代码示例
- typescript 检查变量的类型 - TypeScript (1)
- typescript 设置参数类型 - TypeScript (1)
- 测试类型 - TypeScript (1)
- typescript 参数函数类型 - TypeScript 代码示例
- typescript 类型特定数字 - TypeScript (1)
- 来自数组的 typescript 类型 - TypeScript (1)
- typescript 检查变量的类型 - TypeScript 代码示例
- 类型脚本 - TypeScript (1)
- typescript 设置参数类型 - TypeScript 代码示例
- typescript 类型特定数字 - TypeScript 代码示例
- 来自数组的 typescript 类型 - TypeScript 代码示例
- 具有类型的对象的 typescript 数组 - TypeScript (1)
📜 TypeScript-类型
📅 最后修改于: 2020-10-19 03:48:36 🧑 作者: Mango
类型系统表示语言支持的不同类型的值。类型系统在提供的值被程序存储或操纵之前检查其有效性。这样可以确保代码的行为符合预期。类型系统还允许更丰富的代码提示和自动化文档。
TypeScript将数据类型作为其可选类型系统的一部分提供。数据类型分类如下-
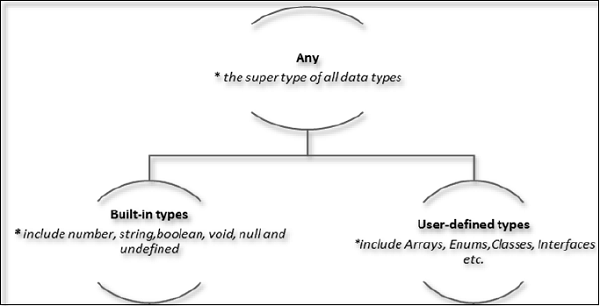
任何类型
any数据类型是TypeScript中所有类型的超级类型。它表示动态类型。使用any类型等效于选择退出变量类型检查。
内置类型
下表说明了TypeScript中的所有内置类型-
| Data type | Keyword | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Number | number | Double precision 64-bit floating point values. It can be used to represent both, integers and fractions. |
| String | string | Represents a sequence of Unicode characters |
| Boolean | boolean | Represents logical values, true and false |
| Void | void | Used on function return types to represent non-returning functions |
| Null | null | Represents an intentional absence of an object value. |
| Undefined | undefined | Denotes value given to all uninitialized variables |
注意-TypeScript和JavaScript中没有整数类型。
空和未定义─它们是否相同?
null和未定义的数据类型通常是造成混乱的原因。 null和undefined不能用于引用变量的数据类型。它们只能作为值分配给变量。
但是, null和undefined不相同。用undefined初始化的变量表示未为其分配值或对象,而null表示已将变量设置为未定义值的对象。
用户定义类型
用户定义的类型包括枚举(枚举),类,接口,数组和元组。这些将在后面的章节中详细讨论。