- 数组 - TypeScript (1)
- TypeScript数组(1)
- TypeScript-数组(1)
- TypeScript数组
- TypeScript 数组
- typescript 数组 - TypeScript (1)
- typescript 数组 - TypeScript 代码示例
- 数组 - TypeScript 代码示例
- typescript 对象数组 - TypeScript (1)
- typescript 对象到数组 - TypeScript (1)
- 空对象的 typescript 数组 - TypeScript (1)
- typescript 数组计数 - TypeScript (1)
- typescript 对象数组 - TypeScript 代码示例
- 空对象的 typescript 数组 - TypeScript 代码示例
- typescript 对象到数组 - TypeScript 代码示例
- typescript 从数组中删除元素 - TypeScript (1)
- typescript 数组插入 - TypeScript (1)
- c++ 数组中的元素数 - TypeScript (1)
- typescript 数组计数 - TypeScript 代码示例
- typescript 数组字符串到数组文字 - TypeScript (1)
- typescript 从数组中删除元素 - TypeScript 代码示例
- typescript 数组插入 - TypeScript 代码示例
- 反应元素的 typescript 数组 - TypeScript (1)
- typescript 枚举到数组 - TypeScript (1)
- typescript 数组字符串到数组文字 - TypeScript 代码示例
- TypeScript 中的类
- 1, - TypeScript (1)
- 好的 - TypeScript (1)
- TypeScript-类(1)
📅 最后修改于: 2020-10-19 03:53:27 🧑 作者: Mango
使用变量存储值存在以下限制-
-
变量本质上是标量。换句话说,变量声明一次只能包含一个。这意味着要在程序中存储n个值,将需要n个变量声明。因此,当需要存储更大的值集合时,使用变量是不可行的。
-
程序中的变量按随机顺序分配给内存,因此很难按声明的顺序检索/读取值。
TypeScript引入了数组的概念来解决这一问题。数组是值的同质集合。为简化起见,数组是相同数据类型的值的集合。它是用户定义的类型。
阵列的特征
这是数组功能的列表-
-
数组声明分配顺序的内存块。
-
数组是静态的。这意味着数组一旦初始化就无法调整大小。
-
每个存储块代表一个数组元素。
-
数组元素由唯一的整数(称为元素的下标/索引)标识。
-
像变量一样,数组也应在使用前声明。使用var关键字声明一个数组。
-
数组初始化是指填充数组元素。
-
数组元素值可以更新或修改,但不能删除。
声明和初始化数组
要在Typescript中声明一个初始化数组,请使用以下语法-
句法
var array_name[:datatype]; //declaration
array_name = [val1,val2,valn..] //initialization
没有数据类型的数组声明被视为任何类型。这种数组的类型是从初始化期间数组的第一个元素的数据类型推断出来的。
例如,像-var numlist:number [] = [2,4,6,8]这样的声明将创建一个数组,如下所示-
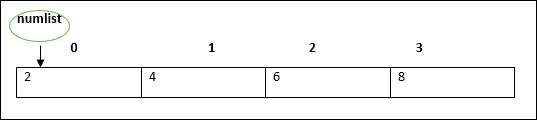
默认情况下,数组指针指向第一个元素。
可以在单个语句中声明和初始化数组。相同的语法是-
var array_name[:data type] = [val1,val2…valn]
注意-[]对称为数组的维数。
访问数组元素
数组名称后跟下标用于引用数组元素。它的语法如下-
array_name[subscript] = value
示例:简单数组
var alphas:string[];
alphas = ["1","2","3","4"]
console.log(alphas[0]);
console.log(alphas[1]);
在编译时,它将生成以下JavaScript代码-
//Generated by typescript 1.8.10
var alphas;
alphas = ["1", "2", "3", "4"];
console.log(alphas[0]);
console.log(alphas[1]);
上面代码的输出如下-
1
2
示例:单条语句声明和初始化
var nums:number[] = [1,2,3,3]
console.log(nums[0]);
console.log(nums[1]);
console.log(nums[2]);
console.log(nums[3]);
在编译时,它将生成以下JavaScript代码-
//Generated by typescript 1.8.10
var nums = [1, 2, 3, 3];
console.log(nums[0]);
console.log(nums[1]);
console.log(nums[2]);
console.log(nums[3]);
其输出如下-
1
2
3
3
数组对象
也可以使用Array对象创建一个数组。可以传递Array构造函数。
-
一个数字值,表示数组的大小或
-
逗号分隔值的列表。
下面的示例演示如何使用此方法创建数组。
例
var arr_names:number[] = new Array(4)
for(var i = 0;i编译时,它将生成以下JavaScript代码。
//Generated by typescript 1.8.10
var arr_names = new Array(4);
for (var i = 0; i < arr_names.length; i++) {
arr_names[i] = i * 2;
console.log(arr_names[i]);
}
其输出如下-
0
2
4
6
示例:数组构造函数接受逗号分隔的值
var names:string[] = new Array("Mary","Tom","Jack","Jill")
for(var i = 0;i在编译时,它将生成以下JavaScript代码-
//Generated by typescript 1.8.10
var names = new Array("Mary", "Tom", "Jack", "Jill");
for (var i = 0; i < names.length; i++) {
console.log(names[i]);
}
其输出如下-
Mary
Tom
Jack
Jill
数组方法
下面列出了Array对象的方法及其说明。
| S.No. | Method & Description |
|---|---|
| 1. | concat()
Returns a new array comprised of this array joined with other array(s) and/or value(s). |
| 2. | every()
Returns true if every element in this array satisfies the provided testing function. |
| 3. | filter()
Creates a new array with all of the elements of this array for which the provided filtering function returns true. |
| 4. | forEach()
Calls a function for each element in the array. |
| 5. | indexOf()
Returns the first (least) index of an element within the array equal to the specified value, or -1 if none is found. |
| 6. | join()
Joins all elements of an array into a string. |
| 7. | lastIndexOf()
Returns the last (greatest) index of an element within the array equal to the specified value, or -1 if none is found. |
| 8. | map()
Creates a new array with the results of calling a provided function on every element in this array. |
| 9. | pop()
Removes the last element from an array and returns that element. |
| 10. | push()
Adds one or more elements to the end of an array and returns the new length of the array. |
| 11. | reduce()
Apply a function simultaneously against two values of the array (from left-to-right) as to reduce it to a single value. |
| 12. | reduceRight()
Apply a function simultaneously against two values of the array (from right-to-left) as to reduce it to a single value. |
| 13. | reverse()
Reverses the order of the elements of an array — the first becomes the last, and the last becomes the first. |
| 14. | shift()
Removes the first element from an array and returns that element. |
| 15. | slice()
Extracts a section of an array and returns a new array. |
| 16. | some()
Returns true if at least one element in this array satisfies the provided testing function. |
| 17. | sort()
Sorts the elements of an array. |
| 18. | splice()
Adds and/or removes elements from an array. |
| 19. | toString()
Returns a string representing the array and its elements. |
| 20. | unshift()
Adds one or more elements to the front of an array and returns the new length of the array. |
阵列解构
指分解实体的结构。当在数组的上下文中使用时,TypeScript支持解构。
例
var arr:number[] = [12,13]
var[x,y] = arr
console.log(x)
console.log(y)
编译时,它将生成以下JavaScript代码。
//Generated by typescript 1.8.10
var arr = [12, 13];
var x = arr[0], y = arr[1];
console.log(x);
console.log(y);
其输出如下-
12
13
使用for…in循环进行数组遍历
可以使用for…in循环遍历数组。
var j:any;
var nums:number[] = [1001,1002,1003,1004]
for(j in nums) {
console.log(nums[j])
}
该循环执行基于索引的数组遍历。
编译时,它将生成以下JavaScript代码。
//Generated by typescript 1.8.10
var j;
var nums = [1001, 1002, 1003, 1004];
for (j in nums) {
console.log(nums[j]);
}
上面代码的输出如下-
1001
1002
1003
1004
TypeScript中的数组
TypeScript在数组中支持以下概念-
| S.No. | Concept & Description |
|---|---|
| 1. | Multi-dimensional arrays
TypeScript supports multidimensional arrays. The simplest form of the multidimensional array is the twodimensional array. |
| 2. | Passing arrays to functions
You can pass to the function a pointer to an array by specifying the array’s name without an index. |
| 3. | Return array from functions
Allows a function to return an array |