树是分层数据结构。二叉树是最多有两个孩子的树。二叉树左边的节点称为“Left-Child”,右边的节点称为“Right-Child”。此外,较小的树或根节点左侧的子树称为“左子树”,右侧的称为“右子树”。
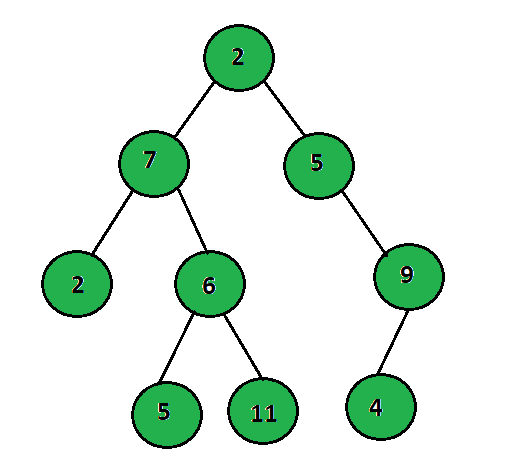
以下是可以在二叉树上执行的各种操作:
二叉树的创建:
这个想法是首先创建给定树的根节点,然后递归地为每个父节点创建左子节点和右子节点。下面是说明相同的程序:
C++
// C++ program to illustrate how to
// create a tree
#include
using namespace std;
// Structure of the Binary Tree
struct treenode {
int info;
struct treenode *left,
*right;
};
// Function to create the Binary Tree
struct treenode* create()
{
int data;
struct treenode* tree;
// Dynamically allocating memory
// for the tree-node
tree = new treenode;
cout << "\nEnter data to be inserted "
<< "or type -1 for no insertion : ";
// Input from the user
cin >> data;
// Termination Condition
if (data == -1)
return 0;
// Assign value from user into tree
tree->info = data;
// Recursively Call to create the
// left and the right sub tree
cout << "Enter left child of : "
<< data;
tree->left = create();
cout << "Enter right child of : "
<< data;
tree->right = create();
// Return the created Tree
return tree;
};
// Function to perform the inorder
// traversal of the given Tree
void inorder(struct treenode* root)
{
// If root is NULL
if (root == NULL)
return;
// Recursively call for the left
// and the right subtree
inorder(root->left);
cout << root->info << " ";
inorder(root->right);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Root Node
struct treenode* root = NULL;
// Function Call
root = create();
// Perform Inorder Traversal
inorder(root);
return 0;
}
/* Will be creating tree:
2
/ \
7 5
/ \ \
2 6 9
*/ C++
// C++ program to demonstrate the
// pre-order traversal
#include "bits/stdc++.h"
using namespace std;
// Structure of the Binary Tree
struct treenode {
int info;
struct treenode *left,
*right;
};
// Function to create the Binary Tree
struct treenode* create()
{
int data;
struct treenode* tree;
// Dynamically allocating memory
// for the tree-node
tree = new treenode;
cout << "\nEnter data to be inserted "
<< "or type -1 for no insertion : ";
// Input from the user
cin >> data;
// Termination Condition
if (data == -1)
return 0;
// Assign value from user into tree
tree->info = data;
// Recursively Call to create the
// left and the right sub tree
cout << "Enter left child of : "
<< data;
tree->left = create();
cout << "Enter right child of : "
<< data;
tree->right = create();
// Return the created Tree
return tree;
};
// Function to perform the pre-order
// traversal for the given tree
void preorder(struct treenode* root)
{
// If the root is NULL
if (root == NULL)
return;
// Using tree-node type stack STL
stack s;
while ((root != NULL) || (!s.empty())) {
if (root != NULL) {
// Print the root
cout << root->info << " ";
// Push the node in the stack
s.push(root);
// Move to left subtree
root = root->left;
}
else {
// Remove the top of stack
root = s.top();
s.pop();
root = root->right;
}
}
cout << endl;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Root Node
struct treenode* root = NULL;
// Function Call
root = create();
// Perform Inorder Traversal
preorder(root);
return 0;
}
/* Will be creating tree:
2
/ \
7 5
/ \ \
2 6 9
*/ C++
// C++ program to illustrate how to
// create a tree
#include "bits/stdc++.h"
using namespace std;
// Structure of the Binary Tree
struct treenode {
int info;
struct treenode *left,
*right;
};
// Function to create the Binary Tree
struct treenode* create()
{
int data;
struct treenode* tree;
// Dynamically allocating memory
// for the tree-node
tree = new treenode;
cout << "\nEnter data to be inserted "
<< "or type -1 for no insertion : ";
// Input from the user
cin >> data;
// Termination Condition
if (data == -1)
return 0;
// Assign value from user into tree
tree->info = data;
// Recursively Call to create the
// left and the right sub tree
cout << "Enter left child of : "
<< data;
tree->left = create();
cout << "Enter right child of : "
<< data;
tree->right = create();
// Return the created Tree
return tree;
};
// Function to perform the inorder
// traversal of the given Tree
void inorder(struct treenode* root)
{
// If root is NULL
if (root == NULL)
return;
// Recursively call for the left
// and the right subtree
inorder(root->left);
cout << root->info << " ";
inorder(root->right);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Root Node
struct treenode* root = NULL;
// Function Call
root = create();
// Perform Inorder Traversal
inorder(root);
return 0;
}
/* Will be creating tree:
2
/ \
7 5
/ \ \
2 6 9
*/C++
// C++ program to implement the
// post-order traversal
#include "bits/stdc++.h"
using namespace std;
// Structure of the Binary Tree
struct treenode {
int info;
struct treenode *left,
*right;
};
// Function to create the Binary Tree
struct treenode* create()
{
int data;
struct treenode* tree;
// Dynamically allocating memory
// for the tree-node
tree = new treenode;
cout << "\nEnter data to be inserted "
<< "or type -1 for no insertion : ";
// Input from the user
cin >> data;
// Termination Condition
if (data == -1)
return 0;
// Assign value from user into tree
tree->info = data;
// Recursively Call to create the
// left and the right sub tree
cout << "Enter left child of : "
<< data;
tree->left = create();
cout << "Enter right child of : "
<< data;
tree->right = create();
// Return the created Tree
return tree;
};
// Function to perform the post-order
// traversal of the given tree
void postorder(struct treenode* root)
{
// If the root is NULL
return;
stack s3;
struct treenode* previous = NULL;
do {
// Iterate until root is present
while (root != NULL) {
s3.push(root);
root = root->left;
}
while (root == NULL && (!s3.empty())) {
root = s3.top();
// If the right subtree is NULL
if (root->right == NULL
|| root->right == previous) {
// Print the root information
cout << root->info << " ";
s3.pop();
// Update the previous
previous = root;
root = NULL;
}
// Otherwise
else
root = root->right;
}
} while (!s3.empty());
cout << endl;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Root Node
struct treenode* root = NULL;
// Function Call
root = create();
// Perform Inorder Traversal
postorder(root);
return 0;
}
/* Will be creating tree:
2
/ \
7 5
/ \ \
2 6 9
*/ C++
// C++ program to illustrate the
// level order traversal#include "bits/stdc++.h"
using namespace std;
// Structure of the Binary Tree
struct treenode {
int info;
struct treenode *left,
*right;
};
// Function to create the Binary Tree
struct treenode* create()
{
int data;
struct treenode* tree;
// Dynamically allocating memory
// for the tree-node
tree = new treenode;
cout << "\nEnter data to be inserted "
<< "or type -1 for no insertion : ";
// Input from the user
cin >> data;
// Termination Condition
if (data == -1)
return 0;
// Assign value from user into tree
tree->info = data;
// Recursively Call to create the
// left and the right sub tree
cout << "Enter left child of : "
<< data;
tree->left = create();
cout << "Enter right child of : "
<< data;
tree->right = create();
// Return the created Tree
return tree;
};
// Function to perform the level-order
// traversal
void levelorder(struct treenode* root)
{
// If the root is NULL
if (root == NULL)
return;
// Use queue for traversal
queue q;
// Print the root's value and
// push it into the queue
cout << root->info << " ";
q.push(root);
// Iterate until queue is non-empty
while (!q.empty()) {
// Get the front node
root = q.front();
q.pop();
// If the root has the left child
if (root->left) {
cout << root->left->info
<< " ";
q.push(root->left);
}
// If the root has the right child
if (root->right) {
cout << root->right->info
<< " ";
q.push(root->right);
}
}
cout << endl;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Root Node
struct treenode* root = NULL;
// Function Call
root = create();
// Perform Inorder Traversal
levelorder(root);
return 0;
}
/* Will be creating tree:
2
/ \
7 5
/ \ \
2 6 9
*/ C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include "bits/stdc++.h"
using namespace std;
// Structure of the Binary Tree
struct treenode {
int info;
struct treenode *left, *right;
};
// Function to create the Binary Tree
struct treenode* create()
{
int data;
struct treenode* tree;
// Dynamically allocating memory
// for the tree-node
tree = new treenode;
cout << "\nEnter data to be inserted "
<< "or type -1 for no insertion : ";
// Input from the user
cin >> data;
// Termination Condition
if (data == -1)
return 0;
// Assign value from user into tree
tree->info = data;
// Recursively Call to create the
// left and the right sub tree
cout << "Enter left child of : " << data;
tree->left = create();
cout << "Enter right child of : " << data;
tree->right = create();
// Return the created Tree
return tree;
};
// Function to find the maximum element
// in the given Binary Tree
int FindMax(struct treenode* root)
{
// If the tree is empty
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
queue q;
int max;
struct treenode* temp;
max = root->info;
// Push the root in the queue
q.push(root);
// Iterate until queue is non-empty
while (!q.empty()) {
// Get the front node of
// the tree
root = q.front();
temp = root;
q.pop();
// Update the maximum value
// of the Tree
if (max < temp->info)
max = temp->info;
if (root->left) {
q.push(root->left);
}
if (root->right) {
q.push(root->right);
}
}
// Return the maximum value
return max;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Root Node
struct treenode* root = NULL;
// Function Call
root = create();
// Perform Inorder Traversal
FindMax(root);
return 0;
}
/* Will be creating tree:
2
/ \
7 5
/ \ \
2 6 9
*/ C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include "bits/stdc++.h"
using namespace std;
// Structure of the Binary Tree
struct treenode {
int info;
struct treenode *left, *right;
};
// Function to create the Binary Tree
struct treenode* create()
{
int data;
struct treenode* tree;
// Dynamically allocating memory
// for the tree-node
tree = new treenode;
cout << "\nEnter data to be inserted "
<< "or type -1 for no insertion : ";
// Input from the user
cin >> data;
// Termination Condition
if (data == -1)
return 0;
// Assign value from user into tree
tree->info = data;
// Recursively Call to create the
// left and the right sub tree
cout << "Enter left child of : " << data;
tree->left = create();
cout << "Enter right child of : " << data;
tree->right = create();
// Return the created Tree
return tree;
};
// Function to search an element in the
// given Binary Tree
int FindElement(struct treenode* root,
int data)
{
// If the root is NULL
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
queue q;
struct treenode* temp;
if (!root)
return 0;
else {
// Push the root
q.push(root);
// Perform the level-order traversal
while (!q.empty()) {
// Get the root
root = q.front();
temp = root;
q.pop();
// If the node with value data
// exists then return 1
if (data == temp->info)
return 1;
// Recursively push the left and
// the right child of the node
if (root->left) {
q.push(root->left);
}
if (root->right) {
q.push(root->right);
}
}
// Otherwise, not found
return 0;
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int data;
// Root of the tree
struct treenode* root = NULL;
// Create the Tree
root = create();
cout << "\nEnter element to searched : ";
cin >> data;
// Function Call
if (FindElement(root, data) == 1)
cout << "\nElement is found";
else
cout << "Element is not found";
return 0;
}
/* Will be creating tree:
2
/ \
7 5
/ \ \
2 6 9
*/ C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include "bits/stdc++.h"
using namespace std;
// Structure of the Binary Tree
struct treenode {
int info;
struct treenode *left, *right;
};
// Function to create the Binary Tree
struct treenode* create()
{
int data;
struct treenode* tree;
// Dynamically allocating memory
// for the tree-node
tree = new treenode;
cout << "\nEnter data to be inserted "
<< "or type -1 for no insertion : ";
// Input from the user
cin >> data;
// Termination Condition
if (data == -1)
return 0;
// Assign value from user into tree
tree->info = data;
// Recursively Call to create the
// left and the right sub tree
cout << "Enter left child of : " << data;
tree->left = create();
cout << "Enter right child of : " << data;
tree->right = create();
// Return the created Tree
return tree;
};
// Function to print the reverse level
// order traversal of the given tree
void reversetree(struct treenode* root)
{
// If the root is NULL
if (root == NULL)
return;
queue q;
stack s;
struct treenode* temp;
q.push(root);
// Until queue is empty
while (!q.empty()) {
// Get the front node
temp = q.front();
q.pop();
// Push every countered node
// data into stack
s.push(temp->info);
// Check for the left subtree
if (temp->left)
q.push(temp->left);
// Check for the right subtree
if (temp->right)
q.push(temp->right);
}
// While S is non-empty, print
// all the nodes
while (!s.empty()) {
cout << s.top() << " ";
s.pop();
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Create root node
struct treenode* root = NULL;
// Create a tree
root = create();
cout << "\nReversed tree is : ";
reversetree(root);
return 0;
}
/* Will be creating tree:
2
/ \
7 5
/ \ \
2 6 9
*/ C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include "bits/stdc++.h"
using namespace std;
// Structure of the Binary Tree
struct treenode {
int info;
struct treenode *left, *right;
};
// Function to create the Binary Tree
struct treenode* create()
{
int data;
struct treenode* tree;
// Dynamically allocating memory
// for the tree-node
tree = new treenode;
cout << "\nEnter data to be inserted "
<< "or type -1 for no insertion : ";
// Input from the user
cin >> data;
// Termination Condition
if (data == -1)
return 0;
// Assign value from user into
// the tree
tree->info = data;
// Recursively Call to create the
// left and the right sub tree
cout << "Enter left child of : "
<< data;
tree->left = create();
cout << "Enter right child of : "
<< data;
tree->right = create();
// Return the created Tree
return tree;
};
// Function to find the height of
// the given Binary tree
int height(struct treenode* root)
{
int x, y;
// If root is NOT NULL
if (root != NULL) {
// x will contain the height
// of left subtree
x = height(root->left);
// y will contain the height
// of right subtree
y = height(root->right);
if (x > y)
// Leaf node has one height
// so x or y + 1
return x + 1;
else
return y + 1;
}
return 0;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Root Node
struct treenode* root = NULL;
// Create the tree
root = create();
cout << "\nHeight of the tree is : "
<< height(root);
return 0;
}
/* Will be creating tree:
2
/ \
7 5
/ \ \
2 6 9
*/C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include "bits/stdc++.h"
using namespace std;
// Structure of the Binary Tree
struct treenode {
int info;
struct treenode *left, *right;
};
// Function to create the Binary Tree
struct treenode* create()
{
int data;
struct treenode* tree;
// Dynamically allocating memory
// for the tree-node
tree = new treenode;
cout << "\nEnter data to be inserted "
<< "or type -1 for no insertion : ";
// Input from the user
cin >> data;
// Termination Condition
if (data == -1)
return 0;
// Assign value from user into tree
tree->info = data;
// Recursively Call to create the
// left and the right sub tree
cout << "Enter left child of : " << data;
tree->left = create();
cout << "Enter right child of : " << data;
tree->right = create();
// Return the created Tree
return tree;
};
// Function to find the deepest node
// of the given Binary Tree
int deepest(struct treenode* root)
{
// If the root is NULL
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
queue q;
q.push(root);
// While queue is non-empty
while (!q.empty()) {
// Get the front node of queue
root = q.front();
q.pop();
// Check for the left and
// the right subtree
if (root->left)
q.push(root->left);
if (root->right)
q.push(root->right);
}
// Return the value for the
// deepest node
return (root->info);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Root Node
struct treenode* root = NULL;
// Create the tree
root = create();
cout << "\nDeepest node of the tree is : " << deepest(root);
return 0;
}
/* Will be creating tree:
2
/ \
7 5
/ \ \
2 6 9
*/ C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include "bits/stdc++.h"
using namespace std;
// Structure of the Binary Tree
struct treenode {
int info;
struct treenode *left, *right;
};
// Function to create the Binary Tree
struct treenode* create()
{
int data;
struct treenode* tree;
// Dynamically allocating memory
// for the tree-node
tree = new treenode;
cout << "\nEnter data to be inserted "
<< "or type -1 for no insertion : ";
// Input from the user
cin >> data;
// Termination Condition
if (data == -1)
return 0;
// Assign value from user into tree
tree->info = data;
// Recursively Call to create the
// left and the right sub tree
cout << "Enter left child of : " << data;
tree->left = create();
cout << "Enter right child of : " << data;
tree->right = create();
// Return the created Tree
return tree;
};
// Stores the maximum left size
int maxlevelleft = 0;
// Function to print the left view of
// the tree
void leftview(struct treenode* root,
int level)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
// If current level is at least
// the maximum left level
if (level >= maxlevelleft) {
// Print the data
cout << root->info << " ";
maxlevelleft++;
}
// Left and Right Subtree
// recursive calls
leftview(root->left, level + 1);
leftview(root->right, level + 1);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Root Node
struct treenode* root = NULL;
// Create the tree
root = create();
cout << "\nLeft view of the tree is : ";
// Function Call
leftview(root, 0);
return 0;
}
/* Will be creating tree:
2
/ \
7 5
/ \ \
2 6 9
*/C++
// C++ program to demonstrate the
// above concepts
#include "bits/stdc++.h"
using namespace std;
// Structure of the Binary Tree
struct treenode {
int info;
struct treenode *left,
*right;
};
// Function to create the Binary Tree
struct treenode* create()
{
int data;
struct treenode* tree;
// Dynamically allocating memory
// for the tree-node
tree = new treenode;
cout << "\nEnter data to be inserted "
<< "or type -1 for no insertion : ";
// Input from the user
cin >> data;
// Termination Condition
if (data == -1)
return 0;
// Assign value from user into tree
tree->info = data;
// Recursively Call to create the
// left and the right sub tree
cout << "Enter left child of : "
<< data;
tree->left = create();
cout << "Enter right child of : "
<< data;
tree->right = create();
// Return the created Tree
return tree;
};
// Stores the maximum right level
int maxlevelright = 0;
// Function to print the right view of
// the given Binary tree
void rightview(struct treenode* root,
int level)
{
// If the root is NULL
if (root == NULL)
return;
// If the current level is greater
// than the maximum right level
if (level >= maxlevelright) {
// Print the data
cout << root->info << " ";
maxlevelright++;
}
// Recursively call for the right
// and the left subtree
rightview(root->right, level + 1);
rightview(root->left, level + 1);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Root Node
struct treenode* root = NULL;
// Create the tree
root = create();
cout << "\nRight view of the tree is : ";
rightview(root, 0);
return 0;
}
/* Will be creating tree:
2
/ \
7 5
/ \ \
2 6 9
*/C++
// C++ program to demonstrate the
// above concepts
#include "bits/stdc++.h"
using namespace std;
// Structure of the Binary Tree
struct treenode {
int info;
struct treenode *left,
*right;
};
// Function to create the Binary Tree
struct treenode* create()
{
int data;
struct treenode* tree;
// Dynamically allocating memory
// for the tree-node
tree = new treenode;
cout << "\nEnter data to be inserted "
<< "or type -1 for no insertion : ";
// Input from the user
cin >> data;
// Termination Condition
if (data == -1)
return 0;
// Assign value from user into tree
tree->info = data;
// Recursively Call to create the
// left and the right sub tree
cout << "Enter left child of : "
<< data;
tree->left = create();
cout << "Enter right child of : "
<< data;
tree->right = create();
// Return the created Tree
return tree;
};
// Initialize an ordered map
map HashMap;
// Iterator for the map
map::iterator it;
// Function to print the top view
// of the given Binary Tree
void topview(struct treenode* root,
int level)
{
// If the root is NULL
if (root == NULL)
return;
// Get the level
int i = HashMap.count(level);
// Update the root information
if (i == 0)
HashMap[level] = root->info;
// Left and Right recursive calls
topview(root->left, level - 1);
topview(root->right, level + 1);
// Update the current level
// with the root's value
HashMap[level] = root->info;
return;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Root Node
struct treenode* root = NULL;
// Create a tree
root = create();
topview(root, 0);
cout << "\nTop view of the tree is : ";
for (it = HashMap.begin();
it != HashMap.end(); it++) {
cout << it->second << " ";
}
return 0;
}
/* Will be creating tree:
2
/ \
7 5
/ \ \
2 6 9
*/ C++
// C++ program to demonstrate the
// above concepts
#include "bits/stdc++.h"
using namespace std;
// Structure of the Binary Tree
struct treenode {
int info;
struct treenode *left,
*right;
};
// Function to create the Binary Tree
struct treenode* create()
{
int data;
struct treenode* tree;
// Dynamically allocating memory
// for the tree-node
tree = new treenode;
cout << "\nEnter data to be inserted "
<< "or type -1 for no insertion : ";
// Input from the user
cin >> data;
// Termination Condition
if (data == -1)
return 0;
// Assign value from user into tree
tree->info = data;
// Recursively Call to create the
// left and the right sub tree
cout << "Enter left child of : "
<< data;
tree->left = create();
cout << "Enter right child of : "
<< data;
tree->right = create();
// Return the created Tree
return tree;
};
// Initialize an ordered Map
map > HashMap;
// Iterator for the map
map >::iterator it;
// Function to print the bottom view
// of the given binary tree
void bottomview(struct treenode* root,
int level, int height)
{
// If root is NULL
if (root == NULL)
return;
// If the height of the level is
// greater than the current
// stored height of the level
if (height >= HashMap[level].second) {
HashMap[level] = { root->info,
height };
}
// Left and right recursive calls
bottomview(root->left, level - 1,
height + 1);
bottomview(root->right, level + 1,
height + 1);
return;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Root Node
struct treenode* root = NULL;
// Create the tree
root = create();
bottomview(root, 0, 0);
cout << "\nBottom view of the tree is : ";
for (it = HashMap.begin();
it != HashMap.end(); it++) {
cout << it->second.first << " ";
}
return 0;
}
/* Will be creating tree:
2
/ \
7 5
/ \ \
2 6 9
*/ C++
// C++ program to implement
// the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// structure of the binary tree
struct treenode {
// data part
int info;
// left and right node
struct treenode *left, *right;
};
// create function for binary
// tree creation
struct treenode* create()
{
int data;
// variable of the structure
struct treenode* tree;
// dynamically allocating
// memory for tree-node
tree = new treenode;
cout << "\nEnter data to be inserted or type -1 for no insertion : ";
// input from the user
cin >> data;
// condition for termination
if (data == -1)
return 0;
// assigning value from user
// into tree.
tree->info = data;
// recursively calling create function
// for left and right sub tree
cout << "Enter left child of : " << data;
tree->left = create();
cout << "Enter right child of : " << data;
tree->right = create();
// returning the created tree
return tree;
};
/*
With the simple logic of recursion and
swapping, we can create mirror tree.
We will swap the the left-node and
right-node of root node. We will use
recursion and start swapping from the
bottom of the tree.
*/
// function to form mirror image a tree
void mirrortree(struct treenode* root)
{
if (root != NULL) {
mirrortree(root->left);
mirrortree(root->right);
struct treenode* temp;
temp = root->left;
root->left = root->right;
root->right = temp;
}
return;
}
// function for the inorder traversal
void inorder(struct treenode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
inorder(root->left);
cout << root->info << " ";
inorder(root->right);
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// creating variable of the
// structure
struct treenode* root = NULL;
// calling create function to
// create tree
root = create();
mirrortree(root);
cout << "\nInorder of the mirror tree is = ";
inorder(root);
return 0;
}
/* Will be creating tree:
2
/ \
7 5
/ \ \
2 6 9
*/ C++
// C++ program to implement
// the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// structure of the binary tree
struct treenode {
// data part
int info;
// left and right node
struct treenode *left, *right;
};
// create function for binary
// tree creation
struct treenode* create()
{
int data;
// variable of the structure
struct treenode* tree;
// dynamically allocating
// memory for tree-node
tree = new treenode;
cout << "\nEnter data to be inserted or type -1 for no insertion : ";
// input from the user
cin >> data;
// condition for termination
if (data == -1)
return 0;
// assigning value from user
// into tree.
tree->info = data;
// recursively calling create function
// for left and right sub tree
cout << "Enter left child of : " << data;
tree->left = create();
cout << "Enter right child of : " << data;
tree->right = create();
// returning the created tree
return tree;
};
// Function to serialize the given
// Binary Tree
void serialize(struct treenode* root,
vector& v)
{
// If the root is NULL, then
// push -1 and return
if (root == NULL) {
v.push_back(-1);
return;
}
// Otherwise, push the data part
v.push_back(root->info);
// Recursively Call for the left
// and the right Subtree
serialize(root->left, v);
serialize(root->right, v);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Root Node
struct treenode* root = NULL;
// Create a tree
root = create();
vector v;
serialize(root, v);
cout << "\nSerialize form of the tree is = ";
for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++)
cout << v[i] << " ";
return 0;
}
/* Will be creating tree:
2
/ \
7 5
/ \ \
2 6 9
*/ 输出:
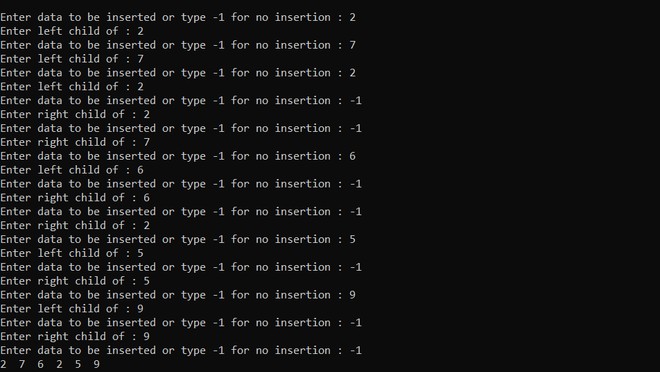
时间复杂度: O(N)
辅助空间: O(1)
预购遍历:
在这个遍历中,首先访问根,然后是左子树和右子树。下面是说明相同的程序:
C++
// C++ program to demonstrate the
// pre-order traversal
#include "bits/stdc++.h"
using namespace std;
// Structure of the Binary Tree
struct treenode {
int info;
struct treenode *left,
*right;
};
// Function to create the Binary Tree
struct treenode* create()
{
int data;
struct treenode* tree;
// Dynamically allocating memory
// for the tree-node
tree = new treenode;
cout << "\nEnter data to be inserted "
<< "or type -1 for no insertion : ";
// Input from the user
cin >> data;
// Termination Condition
if (data == -1)
return 0;
// Assign value from user into tree
tree->info = data;
// Recursively Call to create the
// left and the right sub tree
cout << "Enter left child of : "
<< data;
tree->left = create();
cout << "Enter right child of : "
<< data;
tree->right = create();
// Return the created Tree
return tree;
};
// Function to perform the pre-order
// traversal for the given tree
void preorder(struct treenode* root)
{
// If the root is NULL
if (root == NULL)
return;
// Using tree-node type stack STL
stack s;
while ((root != NULL) || (!s.empty())) {
if (root != NULL) {
// Print the root
cout << root->info << " ";
// Push the node in the stack
s.push(root);
// Move to left subtree
root = root->left;
}
else {
// Remove the top of stack
root = s.top();
s.pop();
root = root->right;
}
}
cout << endl;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Root Node
struct treenode* root = NULL;
// Function Call
root = create();
// Perform Inorder Traversal
preorder(root);
return 0;
}
/* Will be creating tree:
2
/ \
7 5
/ \ \
2 6 9
*/
输出:

时间复杂度: O(N)
辅助空间: O(N)
有序遍历:
在这个遍历中,首先访问左子树,然后是根和右子树。下面是说明相同的程序:
C++
// C++ program to illustrate how to
// create a tree
#include "bits/stdc++.h"
using namespace std;
// Structure of the Binary Tree
struct treenode {
int info;
struct treenode *left,
*right;
};
// Function to create the Binary Tree
struct treenode* create()
{
int data;
struct treenode* tree;
// Dynamically allocating memory
// for the tree-node
tree = new treenode;
cout << "\nEnter data to be inserted "
<< "or type -1 for no insertion : ";
// Input from the user
cin >> data;
// Termination Condition
if (data == -1)
return 0;
// Assign value from user into tree
tree->info = data;
// Recursively Call to create the
// left and the right sub tree
cout << "Enter left child of : "
<< data;
tree->left = create();
cout << "Enter right child of : "
<< data;
tree->right = create();
// Return the created Tree
return tree;
};
// Function to perform the inorder
// traversal of the given Tree
void inorder(struct treenode* root)
{
// If root is NULL
if (root == NULL)
return;
// Recursively call for the left
// and the right subtree
inorder(root->left);
cout << root->info << " ";
inorder(root->right);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Root Node
struct treenode* root = NULL;
// Function Call
root = create();
// Perform Inorder Traversal
inorder(root);
return 0;
}
/* Will be creating tree:
2
/ \
7 5
/ \ \
2 6 9
*/
输出:
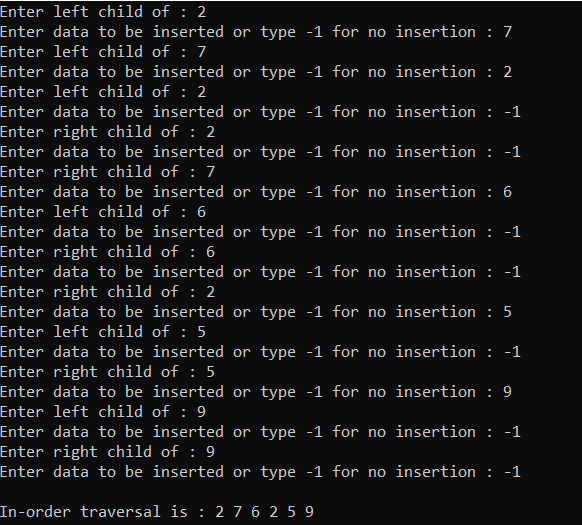
时间复杂度: O(N)
辅助空间: O(N)
后序遍历:
在这个遍历中,首先访问左子树,然后是右子树和根节点。下面是说明相同的程序:
C++
// C++ program to implement the
// post-order traversal
#include "bits/stdc++.h"
using namespace std;
// Structure of the Binary Tree
struct treenode {
int info;
struct treenode *left,
*right;
};
// Function to create the Binary Tree
struct treenode* create()
{
int data;
struct treenode* tree;
// Dynamically allocating memory
// for the tree-node
tree = new treenode;
cout << "\nEnter data to be inserted "
<< "or type -1 for no insertion : ";
// Input from the user
cin >> data;
// Termination Condition
if (data == -1)
return 0;
// Assign value from user into tree
tree->info = data;
// Recursively Call to create the
// left and the right sub tree
cout << "Enter left child of : "
<< data;
tree->left = create();
cout << "Enter right child of : "
<< data;
tree->right = create();
// Return the created Tree
return tree;
};
// Function to perform the post-order
// traversal of the given tree
void postorder(struct treenode* root)
{
// If the root is NULL
return;
stack s3;
struct treenode* previous = NULL;
do {
// Iterate until root is present
while (root != NULL) {
s3.push(root);
root = root->left;
}
while (root == NULL && (!s3.empty())) {
root = s3.top();
// If the right subtree is NULL
if (root->right == NULL
|| root->right == previous) {
// Print the root information
cout << root->info << " ";
s3.pop();
// Update the previous
previous = root;
root = NULL;
}
// Otherwise
else
root = root->right;
}
} while (!s3.empty());
cout << endl;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Root Node
struct treenode* root = NULL;
// Function Call
root = create();
// Perform Inorder Traversal
postorder(root);
return 0;
}
/* Will be creating tree:
2
/ \
7 5
/ \ \
2 6 9
*/
输出:

时间复杂度: O(N)
辅助空间: O(N)
层序遍历:
在这个遍历中,给定的树是逐级遍历的。下面是说明相同的程序:
C++
// C++ program to illustrate the
// level order traversal#include "bits/stdc++.h"
using namespace std;
// Structure of the Binary Tree
struct treenode {
int info;
struct treenode *left,
*right;
};
// Function to create the Binary Tree
struct treenode* create()
{
int data;
struct treenode* tree;
// Dynamically allocating memory
// for the tree-node
tree = new treenode;
cout << "\nEnter data to be inserted "
<< "or type -1 for no insertion : ";
// Input from the user
cin >> data;
// Termination Condition
if (data == -1)
return 0;
// Assign value from user into tree
tree->info = data;
// Recursively Call to create the
// left and the right sub tree
cout << "Enter left child of : "
<< data;
tree->left = create();
cout << "Enter right child of : "
<< data;
tree->right = create();
// Return the created Tree
return tree;
};
// Function to perform the level-order
// traversal
void levelorder(struct treenode* root)
{
// If the root is NULL
if (root == NULL)
return;
// Use queue for traversal
queue q;
// Print the root's value and
// push it into the queue
cout << root->info << " ";
q.push(root);
// Iterate until queue is non-empty
while (!q.empty()) {
// Get the front node
root = q.front();
q.pop();
// If the root has the left child
if (root->left) {
cout << root->left->info
<< " ";
q.push(root->left);
}
// If the root has the right child
if (root->right) {
cout << root->right->info
<< " ";
q.push(root->right);
}
}
cout << endl;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Root Node
struct treenode* root = NULL;
// Function Call
root = create();
// Perform Inorder Traversal
levelorder(root);
return 0;
}
/* Will be creating tree:
2
/ \
7 5
/ \ \
2 6 9
*/
输出:
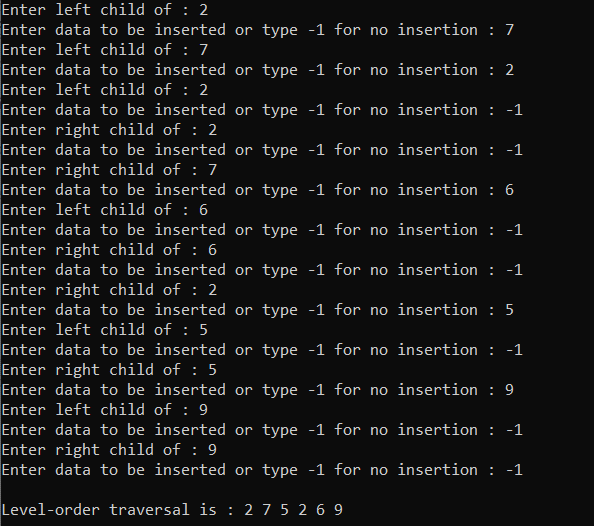
时间复杂度: O(N)
辅助空间: O(N)
二叉树的最大元素:
二叉树所有元素中最大的元素称为最大元素。下面是说明相同的程序:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include "bits/stdc++.h"
using namespace std;
// Structure of the Binary Tree
struct treenode {
int info;
struct treenode *left, *right;
};
// Function to create the Binary Tree
struct treenode* create()
{
int data;
struct treenode* tree;
// Dynamically allocating memory
// for the tree-node
tree = new treenode;
cout << "\nEnter data to be inserted "
<< "or type -1 for no insertion : ";
// Input from the user
cin >> data;
// Termination Condition
if (data == -1)
return 0;
// Assign value from user into tree
tree->info = data;
// Recursively Call to create the
// left and the right sub tree
cout << "Enter left child of : " << data;
tree->left = create();
cout << "Enter right child of : " << data;
tree->right = create();
// Return the created Tree
return tree;
};
// Function to find the maximum element
// in the given Binary Tree
int FindMax(struct treenode* root)
{
// If the tree is empty
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
queue q;
int max;
struct treenode* temp;
max = root->info;
// Push the root in the queue
q.push(root);
// Iterate until queue is non-empty
while (!q.empty()) {
// Get the front node of
// the tree
root = q.front();
temp = root;
q.pop();
// Update the maximum value
// of the Tree
if (max < temp->info)
max = temp->info;
if (root->left) {
q.push(root->left);
}
if (root->right) {
q.push(root->right);
}
}
// Return the maximum value
return max;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Root Node
struct treenode* root = NULL;
// Function Call
root = create();
// Perform Inorder Traversal
FindMax(root);
return 0;
}
/* Will be creating tree:
2
/ \
7 5
/ \ \
2 6 9
*/
输出:
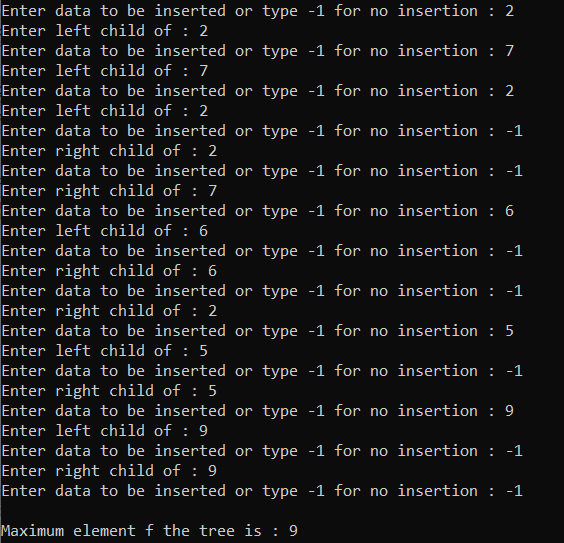
时间复杂度: O(N)
辅助空间: O(N)
搜索元素:
在树节点中搜索任何特定元素的方法是对给定的树执行任何树遍历并检查是否存在具有给定搜索值的任何节点。如果发现为真,则打印“Element is Found” 。否则,打印“Element Not Found” 。
下面是说明相同的程序:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include "bits/stdc++.h"
using namespace std;
// Structure of the Binary Tree
struct treenode {
int info;
struct treenode *left, *right;
};
// Function to create the Binary Tree
struct treenode* create()
{
int data;
struct treenode* tree;
// Dynamically allocating memory
// for the tree-node
tree = new treenode;
cout << "\nEnter data to be inserted "
<< "or type -1 for no insertion : ";
// Input from the user
cin >> data;
// Termination Condition
if (data == -1)
return 0;
// Assign value from user into tree
tree->info = data;
// Recursively Call to create the
// left and the right sub tree
cout << "Enter left child of : " << data;
tree->left = create();
cout << "Enter right child of : " << data;
tree->right = create();
// Return the created Tree
return tree;
};
// Function to search an element in the
// given Binary Tree
int FindElement(struct treenode* root,
int data)
{
// If the root is NULL
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
queue q;
struct treenode* temp;
if (!root)
return 0;
else {
// Push the root
q.push(root);
// Perform the level-order traversal
while (!q.empty()) {
// Get the root
root = q.front();
temp = root;
q.pop();
// If the node with value data
// exists then return 1
if (data == temp->info)
return 1;
// Recursively push the left and
// the right child of the node
if (root->left) {
q.push(root->left);
}
if (root->right) {
q.push(root->right);
}
}
// Otherwise, not found
return 0;
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int data;
// Root of the tree
struct treenode* root = NULL;
// Create the Tree
root = create();
cout << "\nEnter element to searched : ";
cin >> data;
// Function Call
if (FindElement(root, data) == 1)
cout << "\nElement is found";
else
cout << "Element is not found";
return 0;
}
/* Will be creating tree:
2
/ \
7 5
/ \ \
2 6 9
*/
输出:

时间复杂度: O(log N)
辅助空间: O(N)
反向水平顺序遍历:
下面是说明相同的程序:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include "bits/stdc++.h"
using namespace std;
// Structure of the Binary Tree
struct treenode {
int info;
struct treenode *left, *right;
};
// Function to create the Binary Tree
struct treenode* create()
{
int data;
struct treenode* tree;
// Dynamically allocating memory
// for the tree-node
tree = new treenode;
cout << "\nEnter data to be inserted "
<< "or type -1 for no insertion : ";
// Input from the user
cin >> data;
// Termination Condition
if (data == -1)
return 0;
// Assign value from user into tree
tree->info = data;
// Recursively Call to create the
// left and the right sub tree
cout << "Enter left child of : " << data;
tree->left = create();
cout << "Enter right child of : " << data;
tree->right = create();
// Return the created Tree
return tree;
};
// Function to print the reverse level
// order traversal of the given tree
void reversetree(struct treenode* root)
{
// If the root is NULL
if (root == NULL)
return;
queue q;
stack s;
struct treenode* temp;
q.push(root);
// Until queue is empty
while (!q.empty()) {
// Get the front node
temp = q.front();
q.pop();
// Push every countered node
// data into stack
s.push(temp->info);
// Check for the left subtree
if (temp->left)
q.push(temp->left);
// Check for the right subtree
if (temp->right)
q.push(temp->right);
}
// While S is non-empty, print
// all the nodes
while (!s.empty()) {
cout << s.top() << " ";
s.pop();
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Create root node
struct treenode* root = NULL;
// Create a tree
root = create();
cout << "\nReversed tree is : ";
reversetree(root);
return 0;
}
/* Will be creating tree:
2
/ \
7 5
/ \ \
2 6 9
*/
输出:
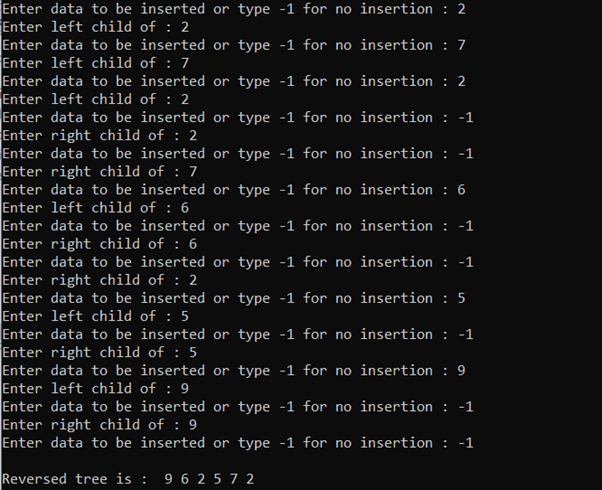
时间复杂度: O(N)
辅助空间: O(N)
树的高度:
二叉树的高度是从根节点到树中任何叶节点的最长路径。下面是说明相同的程序:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include "bits/stdc++.h"
using namespace std;
// Structure of the Binary Tree
struct treenode {
int info;
struct treenode *left, *right;
};
// Function to create the Binary Tree
struct treenode* create()
{
int data;
struct treenode* tree;
// Dynamically allocating memory
// for the tree-node
tree = new treenode;
cout << "\nEnter data to be inserted "
<< "or type -1 for no insertion : ";
// Input from the user
cin >> data;
// Termination Condition
if (data == -1)
return 0;
// Assign value from user into
// the tree
tree->info = data;
// Recursively Call to create the
// left and the right sub tree
cout << "Enter left child of : "
<< data;
tree->left = create();
cout << "Enter right child of : "
<< data;
tree->right = create();
// Return the created Tree
return tree;
};
// Function to find the height of
// the given Binary tree
int height(struct treenode* root)
{
int x, y;
// If root is NOT NULL
if (root != NULL) {
// x will contain the height
// of left subtree
x = height(root->left);
// y will contain the height
// of right subtree
y = height(root->right);
if (x > y)
// Leaf node has one height
// so x or y + 1
return x + 1;
else
return y + 1;
}
return 0;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Root Node
struct treenode* root = NULL;
// Create the tree
root = create();
cout << "\nHeight of the tree is : "
<< height(root);
return 0;
}
/* Will be creating tree:
2
/ \
7 5
/ \ \
2 6 9
*/
输出:

时间复杂度: O(N)
辅助空间: O(1)
树的最深节点:
出现在最大或最后一层的节点称为最深节点。以下是实现上述方法的程序:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include "bits/stdc++.h"
using namespace std;
// Structure of the Binary Tree
struct treenode {
int info;
struct treenode *left, *right;
};
// Function to create the Binary Tree
struct treenode* create()
{
int data;
struct treenode* tree;
// Dynamically allocating memory
// for the tree-node
tree = new treenode;
cout << "\nEnter data to be inserted "
<< "or type -1 for no insertion : ";
// Input from the user
cin >> data;
// Termination Condition
if (data == -1)
return 0;
// Assign value from user into tree
tree->info = data;
// Recursively Call to create the
// left and the right sub tree
cout << "Enter left child of : " << data;
tree->left = create();
cout << "Enter right child of : " << data;
tree->right = create();
// Return the created Tree
return tree;
};
// Function to find the deepest node
// of the given Binary Tree
int deepest(struct treenode* root)
{
// If the root is NULL
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
queue q;
q.push(root);
// While queue is non-empty
while (!q.empty()) {
// Get the front node of queue
root = q.front();
q.pop();
// Check for the left and
// the right subtree
if (root->left)
q.push(root->left);
if (root->right)
q.push(root->right);
}
// Return the value for the
// deepest node
return (root->info);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Root Node
struct treenode* root = NULL;
// Create the tree
root = create();
cout << "\nDeepest node of the tree is : " << deepest(root);
return 0;
}
/* Will be creating tree:
2
/ \
7 5
/ \ \
2 6 9
*/
输出:
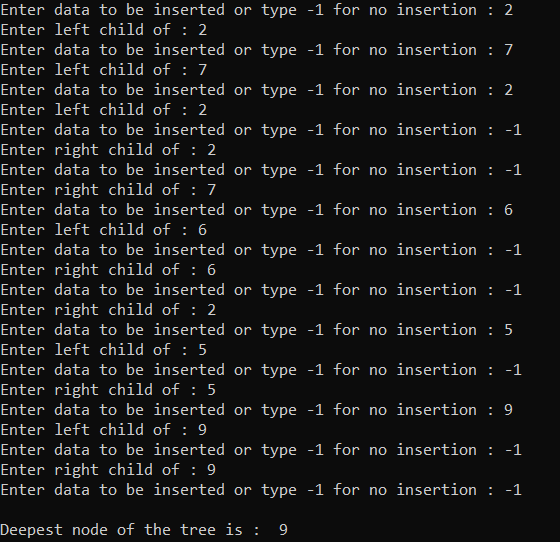
时间复杂度: O(N)
辅助空间: O(N)
树的左视图:
下面是实现相同的程序:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include "bits/stdc++.h"
using namespace std;
// Structure of the Binary Tree
struct treenode {
int info;
struct treenode *left, *right;
};
// Function to create the Binary Tree
struct treenode* create()
{
int data;
struct treenode* tree;
// Dynamically allocating memory
// for the tree-node
tree = new treenode;
cout << "\nEnter data to be inserted "
<< "or type -1 for no insertion : ";
// Input from the user
cin >> data;
// Termination Condition
if (data == -1)
return 0;
// Assign value from user into tree
tree->info = data;
// Recursively Call to create the
// left and the right sub tree
cout << "Enter left child of : " << data;
tree->left = create();
cout << "Enter right child of : " << data;
tree->right = create();
// Return the created Tree
return tree;
};
// Stores the maximum left size
int maxlevelleft = 0;
// Function to print the left view of
// the tree
void leftview(struct treenode* root,
int level)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
// If current level is at least
// the maximum left level
if (level >= maxlevelleft) {
// Print the data
cout << root->info << " ";
maxlevelleft++;
}
// Left and Right Subtree
// recursive calls
leftview(root->left, level + 1);
leftview(root->right, level + 1);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Root Node
struct treenode* root = NULL;
// Create the tree
root = create();
cout << "\nLeft view of the tree is : ";
// Function Call
leftview(root, 0);
return 0;
}
/* Will be creating tree:
2
/ \
7 5
/ \ \
2 6 9
*/
输出:

时间复杂度: O(N)
辅助空间: O(1)
树的右视图:
下面是说明相同的程序:
C++
// C++ program to demonstrate the
// above concepts
#include "bits/stdc++.h"
using namespace std;
// Structure of the Binary Tree
struct treenode {
int info;
struct treenode *left,
*right;
};
// Function to create the Binary Tree
struct treenode* create()
{
int data;
struct treenode* tree;
// Dynamically allocating memory
// for the tree-node
tree = new treenode;
cout << "\nEnter data to be inserted "
<< "or type -1 for no insertion : ";
// Input from the user
cin >> data;
// Termination Condition
if (data == -1)
return 0;
// Assign value from user into tree
tree->info = data;
// Recursively Call to create the
// left and the right sub tree
cout << "Enter left child of : "
<< data;
tree->left = create();
cout << "Enter right child of : "
<< data;
tree->right = create();
// Return the created Tree
return tree;
};
// Stores the maximum right level
int maxlevelright = 0;
// Function to print the right view of
// the given Binary tree
void rightview(struct treenode* root,
int level)
{
// If the root is NULL
if (root == NULL)
return;
// If the current level is greater
// than the maximum right level
if (level >= maxlevelright) {
// Print the data
cout << root->info << " ";
maxlevelright++;
}
// Recursively call for the right
// and the left subtree
rightview(root->right, level + 1);
rightview(root->left, level + 1);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Root Node
struct treenode* root = NULL;
// Create the tree
root = create();
cout << "\nRight view of the tree is : ";
rightview(root, 0);
return 0;
}
/* Will be creating tree:
2
/ \
7 5
/ \ \
2 6 9
*/
输出:
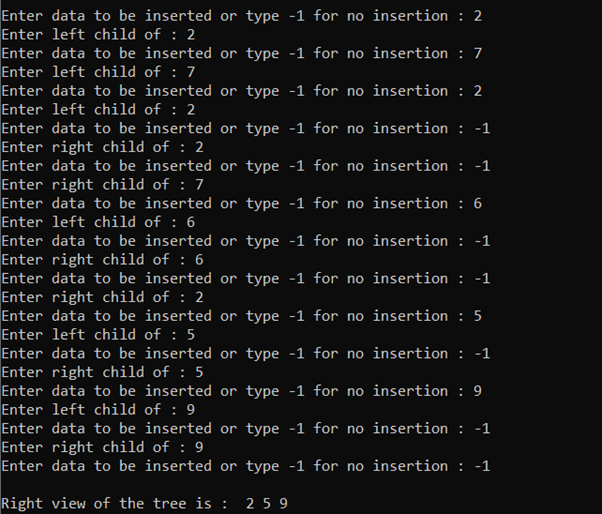
时间复杂度: O(N)
辅助空间: O(1)
树的顶视图:
下面是说明相同的程序:
C++
// C++ program to demonstrate the
// above concepts
#include "bits/stdc++.h"
using namespace std;
// Structure of the Binary Tree
struct treenode {
int info;
struct treenode *left,
*right;
};
// Function to create the Binary Tree
struct treenode* create()
{
int data;
struct treenode* tree;
// Dynamically allocating memory
// for the tree-node
tree = new treenode;
cout << "\nEnter data to be inserted "
<< "or type -1 for no insertion : ";
// Input from the user
cin >> data;
// Termination Condition
if (data == -1)
return 0;
// Assign value from user into tree
tree->info = data;
// Recursively Call to create the
// left and the right sub tree
cout << "Enter left child of : "
<< data;
tree->left = create();
cout << "Enter right child of : "
<< data;
tree->right = create();
// Return the created Tree
return tree;
};
// Initialize an ordered map
map HashMap;
// Iterator for the map
map::iterator it;
// Function to print the top view
// of the given Binary Tree
void topview(struct treenode* root,
int level)
{
// If the root is NULL
if (root == NULL)
return;
// Get the level
int i = HashMap.count(level);
// Update the root information
if (i == 0)
HashMap[level] = root->info;
// Left and Right recursive calls
topview(root->left, level - 1);
topview(root->right, level + 1);
// Update the current level
// with the root's value
HashMap[level] = root->info;
return;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Root Node
struct treenode* root = NULL;
// Create a tree
root = create();
topview(root, 0);
cout << "\nTop view of the tree is : ";
for (it = HashMap.begin();
it != HashMap.end(); it++) {
cout << it->second << " ";
}
return 0;
}
/* Will be creating tree:
2
/ \
7 5
/ \ \
2 6 9
*/
输出:
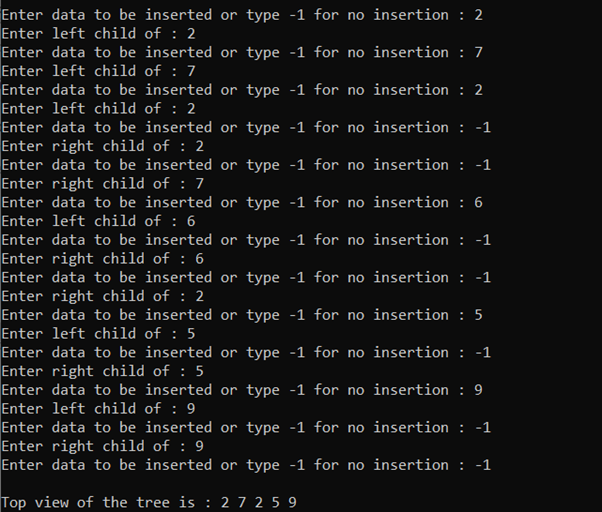
时间复杂度: O(N)
辅助空间: O(N)
树的底视图:
下面是说明相同的程序:
C++
// C++ program to demonstrate the
// above concepts
#include "bits/stdc++.h"
using namespace std;
// Structure of the Binary Tree
struct treenode {
int info;
struct treenode *left,
*right;
};
// Function to create the Binary Tree
struct treenode* create()
{
int data;
struct treenode* tree;
// Dynamically allocating memory
// for the tree-node
tree = new treenode;
cout << "\nEnter data to be inserted "
<< "or type -1 for no insertion : ";
// Input from the user
cin >> data;
// Termination Condition
if (data == -1)
return 0;
// Assign value from user into tree
tree->info = data;
// Recursively Call to create the
// left and the right sub tree
cout << "Enter left child of : "
<< data;
tree->left = create();
cout << "Enter right child of : "
<< data;
tree->right = create();
// Return the created Tree
return tree;
};
// Initialize an ordered Map
map > HashMap;
// Iterator for the map
map >::iterator it;
// Function to print the bottom view
// of the given binary tree
void bottomview(struct treenode* root,
int level, int height)
{
// If root is NULL
if (root == NULL)
return;
// If the height of the level is
// greater than the current
// stored height of the level
if (height >= HashMap[level].second) {
HashMap[level] = { root->info,
height };
}
// Left and right recursive calls
bottomview(root->left, level - 1,
height + 1);
bottomview(root->right, level + 1,
height + 1);
return;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Root Node
struct treenode* root = NULL;
// Create the tree
root = create();
bottomview(root, 0, 0);
cout << "\nBottom view of the tree is : ";
for (it = HashMap.begin();
it != HashMap.end(); it++) {
cout << it->second.first << " ";
}
return 0;
}
/* Will be creating tree:
2
/ \
7 5
/ \ \
2 6 9
*/
输出:

时间复杂度: O(N)
辅助空间: O(N)
树的镜像:
下面是说明相同的程序:
C++
// C++ program to implement
// the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// structure of the binary tree
struct treenode {
// data part
int info;
// left and right node
struct treenode *left, *right;
};
// create function for binary
// tree creation
struct treenode* create()
{
int data;
// variable of the structure
struct treenode* tree;
// dynamically allocating
// memory for tree-node
tree = new treenode;
cout << "\nEnter data to be inserted or type -1 for no insertion : ";
// input from the user
cin >> data;
// condition for termination
if (data == -1)
return 0;
// assigning value from user
// into tree.
tree->info = data;
// recursively calling create function
// for left and right sub tree
cout << "Enter left child of : " << data;
tree->left = create();
cout << "Enter right child of : " << data;
tree->right = create();
// returning the created tree
return tree;
};
/*
With the simple logic of recursion and
swapping, we can create mirror tree.
We will swap the the left-node and
right-node of root node. We will use
recursion and start swapping from the
bottom of the tree.
*/
// function to form mirror image a tree
void mirrortree(struct treenode* root)
{
if (root != NULL) {
mirrortree(root->left);
mirrortree(root->right);
struct treenode* temp;
temp = root->left;
root->left = root->right;
root->right = temp;
}
return;
}
// function for the inorder traversal
void inorder(struct treenode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
inorder(root->left);
cout << root->info << " ";
inorder(root->right);
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// creating variable of the
// structure
struct treenode* root = NULL;
// calling create function to
// create tree
root = create();
mirrortree(root);
cout << "\nInorder of the mirror tree is = ";
inorder(root);
return 0;
}
/* Will be creating tree:
2
/ \
7 5
/ \ \
2 6 9
*/
输出:
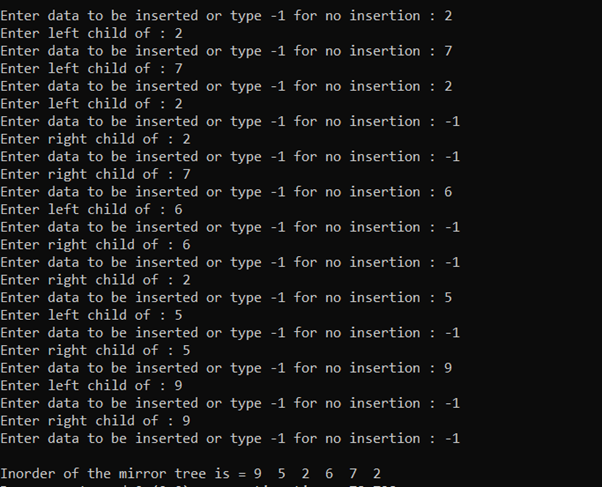
时间复杂度: O(N)
辅助空间: O(1)
序列化一棵树:
树的序列化定义为将给定的树转换为可以在以后恢复的数据格式,并且必须维护树的结构。以下是实现上述方法的程序:
C++
// C++ program to implement
// the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// structure of the binary tree
struct treenode {
// data part
int info;
// left and right node
struct treenode *left, *right;
};
// create function for binary
// tree creation
struct treenode* create()
{
int data;
// variable of the structure
struct treenode* tree;
// dynamically allocating
// memory for tree-node
tree = new treenode;
cout << "\nEnter data to be inserted or type -1 for no insertion : ";
// input from the user
cin >> data;
// condition for termination
if (data == -1)
return 0;
// assigning value from user
// into tree.
tree->info = data;
// recursively calling create function
// for left and right sub tree
cout << "Enter left child of : " << data;
tree->left = create();
cout << "Enter right child of : " << data;
tree->right = create();
// returning the created tree
return tree;
};
// Function to serialize the given
// Binary Tree
void serialize(struct treenode* root,
vector& v)
{
// If the root is NULL, then
// push -1 and return
if (root == NULL) {
v.push_back(-1);
return;
}
// Otherwise, push the data part
v.push_back(root->info);
// Recursively Call for the left
// and the right Subtree
serialize(root->left, v);
serialize(root->right, v);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Root Node
struct treenode* root = NULL;
// Create a tree
root = create();
vector v;
serialize(root, v);
cout << "\nSerialize form of the tree is = ";
for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++)
cout << v[i] << " ";
return 0;
}
/* Will be creating tree:
2
/ \
7 5
/ \ \
2 6 9
*/
输出:
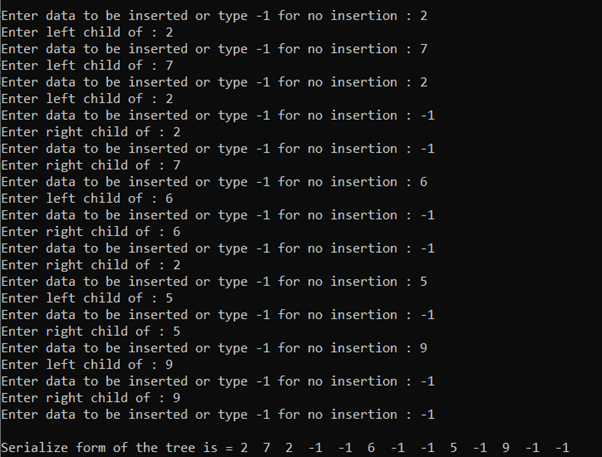
时间复杂度: O(N)
辅助空间: O(N)
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度: O(n)。
- 辅助空间: O(1)。
如果您想与行业专家一起参加直播课程,请参阅Geeks Classes Live