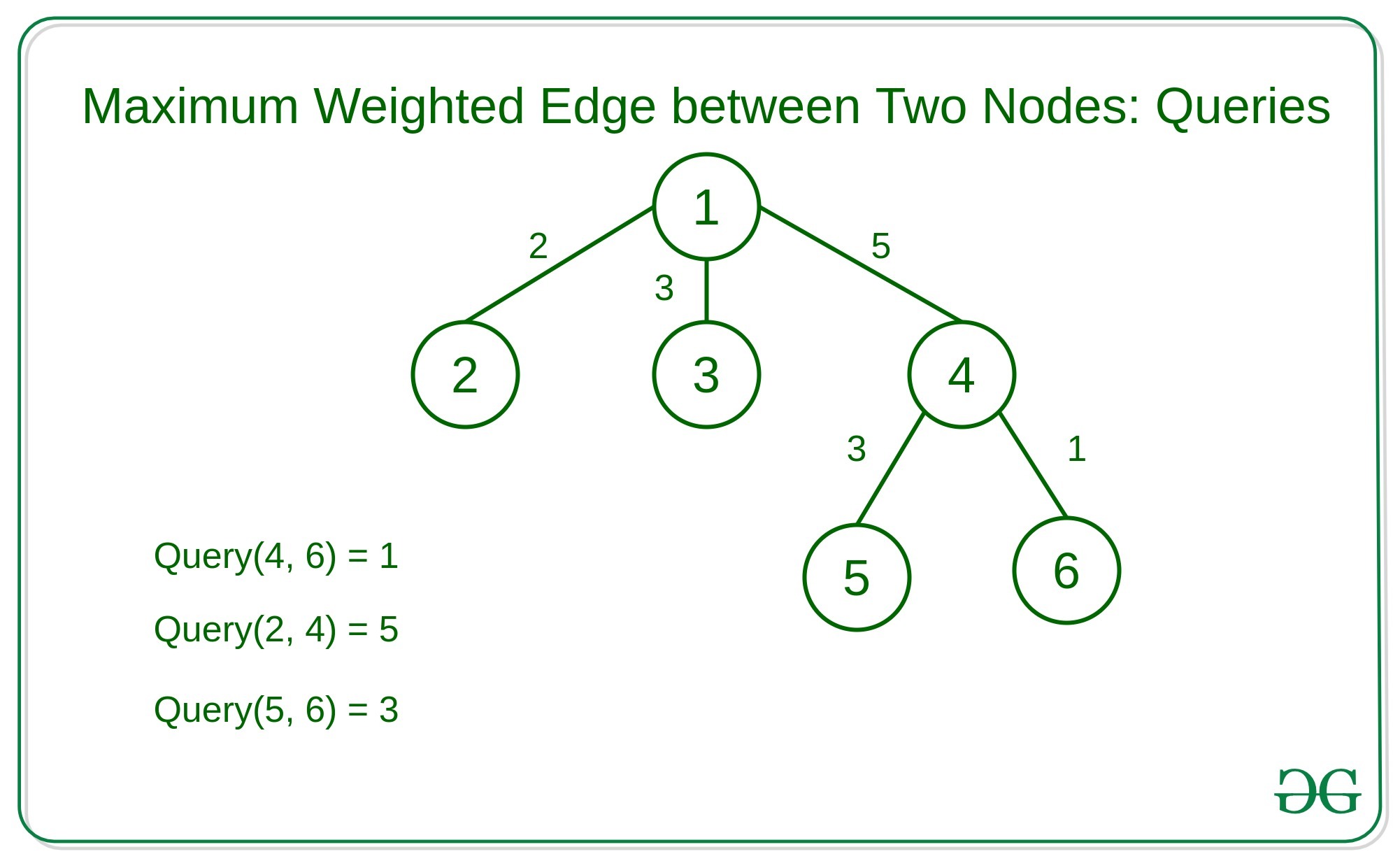
给定一个带有加权边和Q查询的 N 元树,其中每个查询包含树的两个节点。任务是在这两个节点之间的简单路径中找到最大加权边。
例子:
朴素的方法:一个简单的解决方案是为每个查询遍历整个树并找到两个节点之间的路径。
高效的方法:这个想法是使用二进制提升来预先计算从每个节点到某个距离的其他节点的最大加权边
![]()
.我们将存储最大加权边直到
![]()
等级。
![]()
and
![]()
在哪里
- j 是节点并且
- 我是距离
![]()
- dp[i][j] 将 j 的父级存储在
![]()
- 距离如果存在,否则它将存储 0
- mx[i][j] 存储从节点 j 到这个节点的父节点的最大边在
![]()
- 距离。
我们将进行深度优先搜索以找到所有的父母
![]()
距离和它们的权重,然后预先计算父母和最大边缘
![]()
距离。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ implementation to find the
// maximum weighted edge in the simple
// path between two nodes in N-ary Tree
#include
using namespace std;
const int N = 100005;
// Depths of Nodes
vector level(N);
const int LG = 20;
// Parent at every 2^i level
vector > dp(LG, vector(N));
// Maximum node at every 2^i level
vector > mx(LG, vector(N));
// Graph that stores destinations
// and its weight
vector > > v(N);
int n;
// Function to traverse the nodes
// using the Depth-First Search Traversal
void dfs_lca(int a, int par, int lev)
{
dp[0][a] = par;
level[a] = lev;
for (auto i : v[a]) {
// Condition to check if its
// equal to its parent then skip
if (i.first == par)
continue;
mx[0][i.first] = i.second;
// DFS Recursive Call
dfs_lca(i.first, a, lev + 1);
}
}
// Function to find the ansector
void find_ancestor()
{
// Loop to set every 2^i distance
for (int i = 1; i < LG; i++) {
// Loop to calculate for
// each node in the N-ary tree
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
dp[i][j]
= dp[i - 1][dp[i - 1][j]];
// Storing maximum edge
mx[i][j]
= max(mx[i - 1][j],
mx[i - 1][dp[i - 1][j]]);
}
}
}
int getMax(int a, int b)
{
// Swaping if node a is at more depth
// than node b because we will
// always take at more depth
if (level[b] < level[a])
swap(a, b);
int ans = 0;
// Diffeence between the depth of
// the two given nodes
int diff = level[b] - level[a];
while (diff > 0) {
int log = log2(diff);
ans = max(ans, mx[log][b]);
// Changing Node B to its
// parent at 2 ^ i distance
b = dp[log][b];
// Subtracting distance by 2^i
diff -= (1 << log);
}
// Take both a, b to its
// lca and find maximum
while (a != b) {
int i = log2(level[a]);
// Loop to find the maximum 2^ith
// parent the is differnet
// for both a and b
while (i > 0
&& dp[i][a] == dp[i][b])
i--;
// Updating ans
ans = max(ans, mx[i][a]);
ans = max(ans, mx[i][b]);
// Changing value to its parent
a = dp[i][a];
b = dp[i][b];
}
return ans;
}
// Function to compute the Least
// common Ansector
void compute_lca()
{
dfs_lca(1, 0, 0);
find_ancestor();
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Undirected tree
n = 5;
v[1].push_back(make_pair(2, 2));
v[2].push_back(make_pair(1, 2));
v[1].push_back(make_pair(3, 5));
v[3].push_back(make_pair(1, 5));
v[3].push_back(make_pair(4, 3));
v[4].push_back(make_pair(3, 4));
v[3].push_back(make_pair(5, 1));
v[5].push_back(make_pair(3, 1));
// Computing LCA
compute_lca();
int queries[][2]
= { { 3, 5 },
{ 2, 3 },
{ 2, 4 } };
int q = 3;
for (int i = 0; i < q; i++) {
int max_edge = getMax(queries[i][0],
queries[i][1]);
cout << max_edge << endl;
}
return 0;
} Python3
# Python3 implementation to
# find the maximum weighted
# edge in the simple path
# between two nodes in N-ary Tree
import math
N = 100005;
# Depths of Nodes
level = [0 for i in range(N)]
LG = 20;
# Parent at every 2^i level
dp = [[0 for j in range(N)]
for i in range(LG)]
# Maximum node at every 2^i level
mx = [[0 for j in range(N)]
for i in range(LG)]
# Graph that stores destinations
# and its weight
v = [[] for i in range(N)]
n = 0
# Function to traverse the
# nodes using the Depth-First
# Search Traversal
def dfs_lca(a, par, lev):
dp[0][a] = par;
level[a] = lev;
for i in v[a]:
# Condition to check
# if its equal to its
# parent then skip
if (i[0] == par):
continue;
mx[0][i[0]] = i[1];
# DFS Recursive Call
dfs_lca(i[0], a, lev + 1);
# Function to find the ansector
def find_ancestor():
# Loop to set every 2^i distance
for i in range(1, 16):
# Loop to calculate for
# each node in the N-ary tree
for j in range(1, n + 1):
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][dp[i - 1][j]];
# Storing maximum edge
mx[i][j] = max(mx[i - 1][j],
mx[i - 1][dp[i - 1][j]]);
def getMax(a, b):
# Swaping if node a is at more depth
# than node b because we will
# always take at more depth
if (level[b] < level[a]):
a, b = b, a
ans = 0;
# Diffeence between the
# depth of the two given
# nodes
diff = level[b] - level[a];
while (diff > 0):
log = int(math.log2(diff));
ans = max(ans, mx[log][b]);
# Changing Node B to its
# parent at 2 ^ i distance
b = dp[log][b];
# Subtracting distance by 2^i
diff -= (1 << log);
# Take both a, b to its
# lca and find maximum
while (a != b):
i = int(math.log2(level[a]));
# Loop to find the maximum 2^ith
# parent the is differnet
# for both a and b
while (i > 0 and
dp[i][a] == dp[i][b]):
i-=1
# Updating ans
ans = max(ans, mx[i][a]);
ans = max(ans, mx[i][b]);
# Changing value to
# its parent
a = dp[i][a];
b = dp[i][b];
return ans;
# Function to compute the Least
# common Ansector
def compute_lca():
dfs_lca(1, 0, 0);
find_ancestor();
# Driver code
if __name__=="__main__":
# Undirected tree
n = 5;
v[1].append([2, 2]);
v[2].append([1, 2]);
v[1].append([3, 5]);
v[3].append([1, 5]);
v[3].append([4, 3]);
v[4].append([3, 4]);
v[3].append([5, 1]);
v[5].append([3, 1]);
# Computing LCA
compute_lca();
queries= [[3, 5], [2, 3], [2,4]]
q = 3;
for i in range(q):
max_edge = getMax(queries[i][0],
queries[i][1]);
print(max_edge)
# This code is contributed by Rutvik_56输出:
1
5
5
时间复杂度:
如果您想与行业专家一起参加直播课程,请参阅Geeks Classes Live