迭代器模式是一种相对简单且经常使用的设计模式。每种语言都有很多可用的数据结构/集合。每个集合都必须提供一个迭代器,让它遍历它的对象。然而,在这样做时,它应该确保它不会暴露其实现。
假设我们正在构建一个需要我们维护通知列表的应用程序。最终,您的代码的某些部分将需要遍历所有通知。如果我们将您的通知集合实现为数组,您可以将它们迭代为:
// If a simple array is used to store notifications
for (int i = 0; i < notificationList.length; i++)
Notification notification = notificationList[i]);
// If ArrayList is Java is used, then we would iterate
// over them as:
for (int i = 0; i < notificationList.size(); i++)
Notification notification = (Notification)notificationList.get(i);
如果它是其他一些集合,如集合、树等,迭代方式会略有变化。现在,如果我们构建一个迭代器,它提供了一种通用的方法来迭代一个独立于其类型的集合。
// Create an iterator
Iterator iterator = notificationList.createIterator();
// It wouldn’t matter if list is Array or ArrayList or
// anything else.
while (iterator.hasNext())
{
Notification notification = iterator.next());
}
迭代器模式让我们可以做到这一点。正式定义如下:
迭代器模式提供了一种访问聚合对象元素而不暴露其底层表示的方法。
类图: 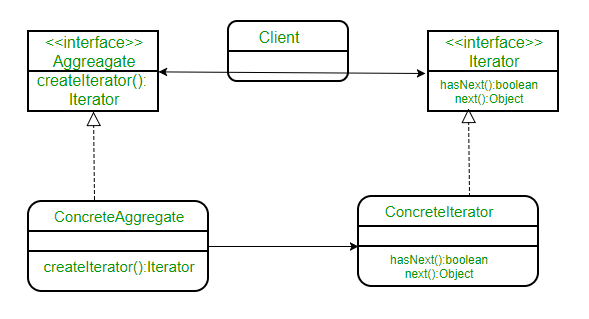
这里我们有一个用于客户端的公共接口 Aggregate,因为它将它与您的对象集合的实现分离。 ConcreteAggregate 实现了 createIterator(),它为其集合返回迭代器。每个 ConcreteAggregate 的职责是实例化一个 ConcreteIterator,它可以迭代它的对象集合。迭代器接口提供了一组遍历或修改集合的方法,除了 next()/hasNext() 它还可以提供搜索、删除等功能。
让我们通过一个例子来理解这一点。假设我们正在我们的应用程序中创建一个通知栏,它显示了一个通知集合中保存的所有通知。 NotificationCollection 提供了一个迭代器来迭代它的元素,而不会将它如何实现集合(在这种情况下为数组)暴露给客户端(NotificationBar)。
类图将是:
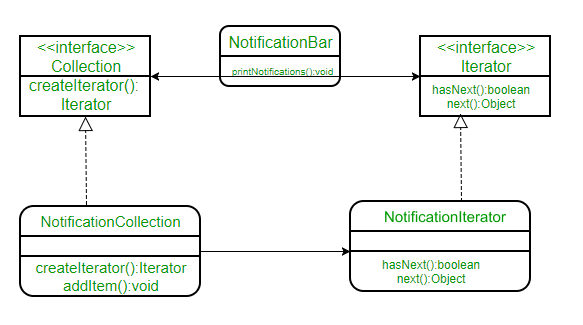
下面是相同的Java实现:
// A Java program to demonstrate implementation
// of iterator pattern with the example of
// notifications
// A simple Notification class
class Notification
{
// To store notification message
String notification;
public Notification(String notification)
{
this.notification = notification;
}
public String getNotification()
{
return notification;
}
}
// Collection interface
interface Collection
{
public Iterator createIterator();
}
// Collection of notifications
class NotificationCollection implements Collection
{
static final int MAX_ITEMS = 6;
int numberOfItems = 0;
Notification[] notificationList;
public NotificationCollection()
{
notificationList = new Notification[MAX_ITEMS];
// Let us add some dummy notifications
addItem("Notification 1");
addItem("Notification 2");
addItem("Notification 3");
}
public void addItem(String str)
{
Notification notification = new Notification(str);
if (numberOfItems >= MAX_ITEMS)
System.err.println("Full");
else
{
notificationList[numberOfItems] = notification;
numberOfItems = numberOfItems + 1;
}
}
public Iterator createIterator()
{
return new NotificationIterator(notificationList);
}
}
// We could also use Java.Util.Iterator
interface Iterator
{
// indicates whether there are more elements to
// iterate over
boolean hasNext();
// returns the next element
Object next();
}
// Notification iterator
class NotificationIterator implements Iterator
{
Notification[] notificationList;
// maintains curr pos of iterator over the array
int pos = 0;
// Constructor takes the array of notifiactionList are
// going to iterate over.
public NotificationIterator (Notification[] notificationList)
{
this.notificationList = notificationList;
}
public Object next()
{
// return next element in the array and increment pos
Notification notification = notificationList[pos];
pos += 1;
return notification;
}
public boolean hasNext()
{
if (pos >= notificationList.length ||
notificationList[pos] == null)
return false;
else
return true;
}
}
// Contains collection of notifications as an object of
// NotificationCollection
class NotificationBar
{
NotificationCollection notifications;
public NotificationBar(NotificationCollection notifications)
{
this.notifications = notifications;
}
public void printNotifications()
{
Iterator iterator = notifications.createIterator();
System.out.println("-------NOTIFICATION BAR------------");
while (iterator.hasNext())
{
Notification n = (Notification)iterator.next();
System.out.println(n.getNotification());
}
}
}
// Driver class
class Main
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
NotificationCollection nc = new NotificationCollection();
NotificationBar nb = new NotificationBar(nc);
nb.printNotifications();
}
}
输出:
-------NOTIFICATION BAR------------
Notification 1
Notification 2
Notification 3请注意,如果我们使用 ArrayList 而不是 Array,由于使用迭代器接口实现了解耦,因此客户端(通知栏)代码不会有任何变化。
参考:
Head First 设计模式