延迟加载是一个概念,我们将对象的加载延迟到我们需要它的时候。
- 延迟加载只是在实际需要时初始化类的过程的一个花哨名称。
- 简单来说,延迟加载是一种软件设计模式,其中对象的初始化仅在实际需要时发生,而不是在之前发生,以保持使用的简单性并提高性能。
- 当对象创建的成本非常高并且对象的使用非常少时,延迟加载是必不可少的。所以这是值得实施延迟加载的场景。延迟加载的基本思想是在需要时加载对象/数据。
例如,假设您正在创建一个应用程序,其中有一个 Company 对象,并且该对象在 ContactList 对象中包含公司员工的列表。一家公司可能有数千名员工。从数据库中加载 Company 对象以及 ContactList 对象中所有员工的列表可能非常耗时。在某些情况下,您甚至不需要员工列表,但您必须等到公司及其员工列表加载到内存中。
节省时间和内存的一种方法是避免在需要之前加载员工对象,这是使用延迟加载设计模式完成的。 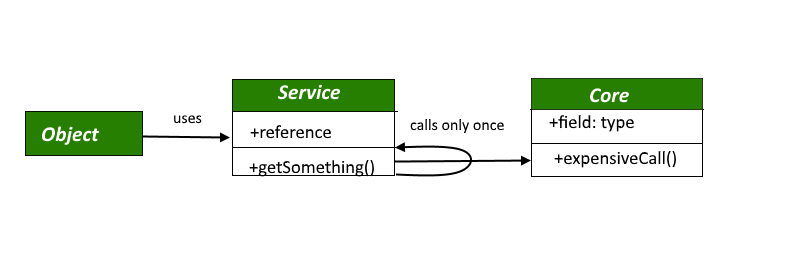
延迟加载模式有四种常见的实现:
- 虚拟代理
- 延迟初始化
- 鬼
- 价值持有者
虚拟代理
虚拟代理模式是一种内存节省技术,建议将对象创建推迟到需要时。它用于创建在内存使用或涉及的处理方面很昂贵的对象。
// Java program to illustrate
// virtual proxy in
// Lazy Loading Design Pattern
import java.util.List;
import java.util.ArrayList;
interface ContactList
{
public List getEmployeeList();
}
class Company {
String companyName;
String companyAddress;
String companyContactNo;
ContactList contactList;
public Company(String companyName, String companyAddress,
String companyContactNo, ContactList contactList)
{
this.companyName = companyName;
this.companyAddress = companyAddress;
this.companyContactNo = companyContactNo;
this.contactList = contactList;
}
public String getCompanyName()
{
return companyName;
}
public String getCompanyAddress()
{
return companyAddress;
}
public String getCompanyContactNo()
{
return companyContactNo;
}
public ContactList getContactList()
{
return contactList;
}
}
class ContactListImpl implements ContactList {
public List getEmployeeList()
{
return getEmpList();
}
private static List getEmpList()
{
List empList = new ArrayList(5);
empList.add(new Employee("Lokesh", 2565.55, "SE"));
empList.add(new Employee("Kushagra", 22574, "Manager"));
empList.add(new Employee("Susmit", 3256.77, "G4"));
empList.add(new Employee("Vikram", 4875.54, "SSE"));
empList.add(new Employee("Achint", 2847.01, "SE"));
return empList;
}
}
class ContactListProxyImpl implements ContactList {
private ContactList contactList;
public List getEmployeeList()
{
if (contactList == null) {
System.out.println("Fetching list of employees");
contactList = new ContactListImpl();
}
return contactList.getEmployeeList();
}
}
class Employee {
private String employeeName;
private double employeeSalary;
private String employeeDesignation;
public Employee(String employeeName,
double employeeSalary, String employeeDesignation)
{
this.employeeName = employeeName;
this.employeeSalary = employeeSalary;
this.employeeDesignation = employeeDesignation;
}
public String getEmployeeName()
{
return employeeName;
}
public double getEmployeeSalary()
{
return employeeSalary;
}
public String getEmployeeDesignation()
{
return employeeDesignation;
}
public String toString()
{
return "Employee Name: " + employeeName + ",
EmployeeDesignation : " + employeeDesignation + ",
Employee Salary : " + employeeSalary;
}
}
class LazyLoading {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
ContactList contactList = new ContactListProxyImpl();
Company company = new Company
("Geeksforgeeks", "India", "+91-011-28458965", contactList);
System.out.println("Company Name: " + company.getCompanyName());
System.out.println("Company Address: " + company.getCompanyAddress());
System.out.println("Company Contact No.: " + company.getCompanyContactNo());
System.out.println("Requesting for contact list");
contactList = company.getContactList();
List empList = contactList.getEmployeeList();
for (Employee emp : empList) {
System.out.println(emp);
}
}
}
输出:
Company Name: ABC Company
Company Address: India
Company Contact No.: +91-011-28458965
Requesting for contact list
Fetching list of employees
Employee Name: Lokesh, EmployeeDesignation: SE, Employee Salary: 2565.55
Employee Name: Kushagra, EmployeeDesignation: Manager, Employee Salary: 22574.0
Employee Name: Susmit, EmployeeDesignation: G4, Employee Salary: 3256.77
Employee Name: Vikram, EmployeeDesignation: SSE, Employee Salary: 4875.54
Employee Name: Achint, EmployeeDesignation: SE, Employee Salary: 2847.01
现在,在上面的代码中,使用代理 ContactList 对象创建了一个 Company 对象。此时,公司对象持有的是代理引用,而不是真正的 ContactList 对象的引用,因此没有员工列表加载到内存中。
延迟初始化
延迟初始化技术包括在使用时检查类字段的值。如果该值等于 null,则该字段在返回之前会加载正确的值。
这是示例:
// Java program to illustrate
// Lazy Initialization in
// Lazy Loading Design Pattern
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
enum CarType {
none,
Audi,
BMW,
}
class Car {
private static Map types = new HashMap<>();
private Car(CarType type) {}
public static Car getCarByTypeName(CarType type)
{
Car Car;
if (!types.containsKey(type)) {
// Lazy initialisation
Car = new Car(type);
types.put(type, Car);
} else {
// It's available currently
Car = types.get(type);
}
return Car;
}
public static Car getCarByTypeNameHighConcurrentVersion(CarType type)
{
if (!types.containsKey(type)) {
synchronized(types)
{
// Check again, after having acquired the lock to make sure
// the instance was not created meanwhile by another thread
if (!types.containsKey(type)) {
// Lazy initialisation
types.put(type, new Car(type));
}
}
}
return types.get(type);
}
public static void showAll()
{
if (types.size() > 0) {
System.out.println("Number of instances made = " + types.size());
for (Entry entry : types.entrySet()) {
String Car = entry.getKey().toString();
Car = Character.toUpperCase(Car.charAt(0)) + Car.substring(1);
System.out.println(Car);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
class Program {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Car.getCarByTypeName(CarType.BMW);
Car.showAll();
Car.getCarByTypeName(CarType.Audi);
Car.showAll();
Car.getCarByTypeName(CarType.BMW);
Car.showAll();
}
}
输出 :
Number of instances made = 1
BMW
Number of instances made = 2
BMW
Audi
Number of instances made = 2
BMW
Audi
价值持有者
基本上,值持有者是处理延迟加载行为并出现在对象数据字段位置的通用对象。当用户需要访问它时,他们只需通过调用 GetValue 方法向值持有者询问其值。那时(并且只有那时),该值从数据库或服务加载。(这并不总是需要)。
// Java function to illustrate
// Lazy Initialization in
// Lazy Loading Design Pattern
public class ValueHolder {
private T value;
private readonly Func valueRetrieval;
// Constructor
public ValueHolder(Func valueRetrieval)
{
valueRetrieval = this.valueRetrieval;
}
// We'll use the signature "GetValue" for convention
public T GetValue(object parameter)
{
if (value == null)
value = valueRetrieval(parameter);
return value;
}
}
注意:这种方法的主要缺点是用户必须知道期望值持有者。
鬼
幽灵是要在部分状态下加载的对象。它对应于真实对象,但并非处于其完整状态。它可能是空的,也可能只包含一些字段(例如 ID)。当用户尝试访问一些尚未加载的字段时,ghost 对象会完全初始化自己(这并不总是需要)。
例如,让我们考虑一个开发人员添加了一个在线表单,以便任何用户都可以通过该在线表单请求内容。在创建时,我们只知道内容将被访问,但用户不知道哪些操作或内容。
$userData = array(
"UID" = > uniqid(),
"requestTime" = > microtime(true),
"dataType" = > "",
"request" = > "");
if (isset($_POST['data']) && $userData) {
//...
}
在上面的PHP示例中,用户可以以文本文件或任何来源的形式访问来自在线表单的内容。
- UID是每个特定用户的唯一 ID。
- requestTime是用户从在线表单请求内容的时间。
- dataType是数据的类型。主要是文本,但取决于形式。
- request是一个布尔函数,用于通知用户请求是否完成。
好处
- 这种方法是更快的应用程序启动时间,因为它不需要创建和加载所有的应用程序对象。
缺点
- 代码变得复杂,因为我们需要检查是否需要加载。所以这可能会导致性能变慢。