LinkedHashMap就像 HashMap 一样,具有维护插入其中的元素顺序的附加功能。 HashMap 提供了快速插入、搜索和删除的优点,但它从未维护 LinkedHashMap 提供的插入轨迹和插入顺序,其中元素可以按插入顺序访问。
例子:
Java
// Java program to demonstrate
// working of LinkedHashMap
import java.util.*;
class LinkedHashMapExample {
public static void main(String args[])
{
// create an instance of LinkedHashMap
LinkedHashMap lhm;
lhm = new LinkedHashMap();
// insert element in LinkedHashMap
lhm.put(100, "Amit");
// inser first null key
lhm.put(null, "Ajay");
lhm.put(101, "Vijay");
lhm.put(102, "Rahul");
// insert second null key
// which replace first null key value
lhm.put(null, "Anuj");
// insert duplicate
// which replace first 102 key value
lhm.put(102, "Saurav");
// iterate and print the key/value pairs
lhm.entrySet().stream().forEach((m) -> {
System.out.println(m.getKey() + " "
+ m.getValue());
});
}
} Java
// Java program to demonstrate
// working of LinkedHashSet
import java.util.*;
class LinkedHashSetExample {
public static void main(String args[])
{
// create an instance of LinkedHashSet
LinkedHashSet lhs
= new LinkedHashSet();
// insert element in LinkedHashMap
lhs.add("Amit");
// insert first null key
lhs.add(null);
lhs.add("Vijay");
lhs.add("Rahul");
// insert second null key
// which replace first null key value
lhs.add(null);
// insert duplicate
lhs.add("Vijay");
// create an iterator
// iterate and print the elements
Iterator itr = lhs.iterator();
while (itr.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(itr.next());
}
}
} 输出
100 Amit
null Anuj
101 Vijay
102 SauravLinkedHashSet是 HashSet 的有序版本,它在所有元素之间维护一个双向链表。当需要维护迭代顺序时,使用这个类。当遍历 HashSet 时,顺序是不可预测的,而 LinkedHashSet 允许我们按照元素插入的顺序遍历元素。当使用迭代器循环遍历 LinkedHashSet 时,元素将按照它们被插入的顺序返回。
例子:
Java
// Java program to demonstrate
// working of LinkedHashSet
import java.util.*;
class LinkedHashSetExample {
public static void main(String args[])
{
// create an instance of LinkedHashSet
LinkedHashSet lhs
= new LinkedHashSet();
// insert element in LinkedHashMap
lhs.add("Amit");
// insert first null key
lhs.add(null);
lhs.add("Vijay");
lhs.add("Rahul");
// insert second null key
// which replace first null key value
lhs.add(null);
// insert duplicate
lhs.add("Vijay");
// create an iterator
// iterate and print the elements
Iterator itr = lhs.iterator();
while (itr.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(itr.next());
}
}
}
输出
Amit
null
Vijay
RahulLinkedHashMap和LinkedHashSet的层次结构
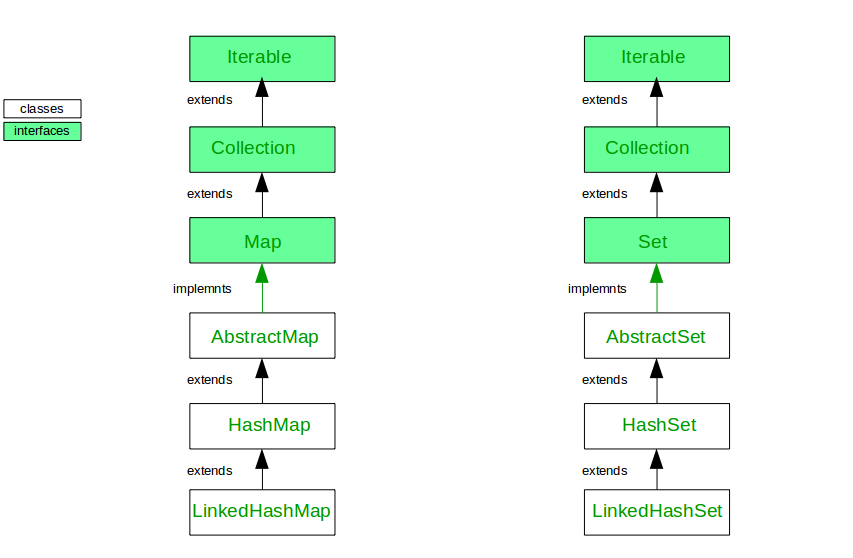
LinkedHashMap 和 LinkedHashSet 之间的相似之处
|
Property |
LinkedHashMap and LinkedHashSet |
|---|---|
| Order | Both LinkedHashMap and LinkedHashSet maintain the insertion order. Elements get sorted in the same sequence in which they have been added. |
| Synchronized | Both are not synchronized and must be synchronized externally. |
| Duplicates | LinkedHashMap does a mapping of keys to values so it doesn’t have duplicates and LinkedHashSet simply stores a collection of things with no duplicates. |
| Memory | Keeping the insertion order in both LinkedHashmap and LinkedHashset have additional associated costs, both in terms of spending additional CPU cycles and needing more memory. |
LinkedHashMap 和 LinkedHashSet 的区别
|
Property |
LinkedHashMap |
LinkedHashSet |
|---|---|---|
| Declaration |
The default constructor declaration is : LinkedHashMap lhm = new LinkedHashMap(); |
The default constructor declaration is : LinkedHashSet hs = new LinkedHashSet(); |
| Class Declaration | public class LinkedHashMap |
public class LinkedHashSet |
| Constructor |
The LinkedHashMap accepts five types of constructors:
|
The LinkedHashSet accepts four types of constructors:
|
| Operation | LinkedHashMap does a mapping of keys to values. | LinkedHashSet simply stores a collection of things. |
| Replacement | LinkedHashMap replaces the value with a duplicate key. | LinkedHashSet not change the original value. |
| Null Object | LinkedHashMap has elements in key-value pairs so have only one null key and multiple null values. | LinkedHashSet simply stores a collection of things with one null value. |