加密和编码是经常互换和错误使用的术语。这两个术语之间有很多区别,了解这些区别非常重要。在本文中,我们将了解加密和编码这两个术语之间的区别。
1. 加密:
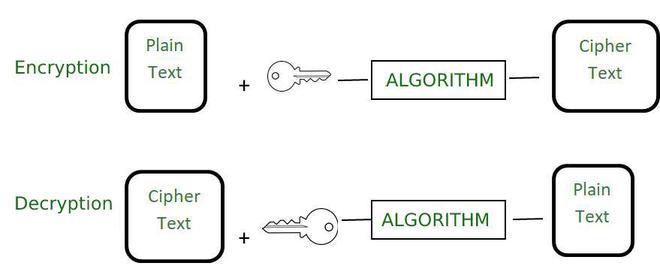
这是一个用于将简单的可读数据(称为纯文本)转换为不可读数据(称为密文)的过程,密文只有在用户知道加密密钥的情况下才能转换为纯文本。它主要用于确保我们的数据安全。加密的主要目的是将我们的数据转换成这样的形式,即对于不知道加密密钥的人来说是垃圾。它用于防止未经授权的 ace。加密的逆过程是解密,它用于从密文中取回明文。对于解密,我们必须知道加密密钥和加密算法。
加密的数据就像其他数据一样被处理。我们还可以对同一数据使用一种以上的加密算法。现实生活中的例子是向某人发送只有他们应该能够阅读的秘密消息,或者通过 Internet 安全地发送密码。目标是数据保密。
加密算法示例: AES、RSA 和 Blowfish。
2. 编码:
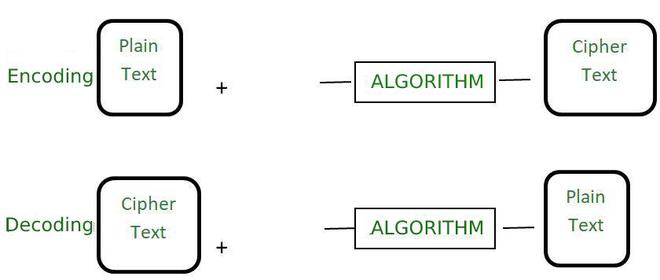
它是将数据转换为易于被不同类型系统使用的格式的过程。用于对数据进行编码的算法是公开可用的,如果人们知道该算法,则可以轻松地以可读形式对其进行解码。它不需要任何密钥来解码信息。主要目的是数据可用性而不是机密性。编码的主要目的是转换数据,以便它可以被不同类型的系统正确使用。它不用于保护数据,因为与加密相比,它很容易逆转。
此过程用于确保数据的完整性和可用性。现实生活中的例子就像通过电子邮件发送的二进制数据或查看网页上的特殊字符。主要目标是数据可用性。
编码算法示例:ASCII、UNICODE、URL 编码、Base64
加密和编码的区别:
| Basis | Encryption | Encoding |
| Definition | It is the process to encode data securely such that only the authorized user who knows the key or password is able to retrieve the original data for everyone else it is just garbage. | It is the process of transforming data into such a format that it can be by a different type of system using publically available algorithms. |
| Purpose | The purpose of encryption is to transform data to keep it secret from others. | The main purpose is the protection of the integrity of data. |
| Used for | It is used to maintain data confidentiality. | It is used to maintain data usability. |
| Reverse Process | The original data can be retrieved using decryption. | The original data can be retrieved using decoding. The algorithm used to encode the data is publicly available. |
| Key requirement | The encryption key is required to decrypt the data and get the original data. | The encryption key is not required to decrypt the data and get the original data. |
| Secure | The encrypted data is more secure. | The encoded data is less secure. It can easily be decoded. |
| Example of Algorithm | AES, RSA, and Blowfish. | ASCII, UNICODE, URL encoding, Base64. |
| Real-life example | Securely sending a password over the internet. | viewing special characters on the web page. |