加密和哈希是密码术中广泛使用的两个术语。在本文中,我们将学习加密和哈希之间的区别。
1.加密:
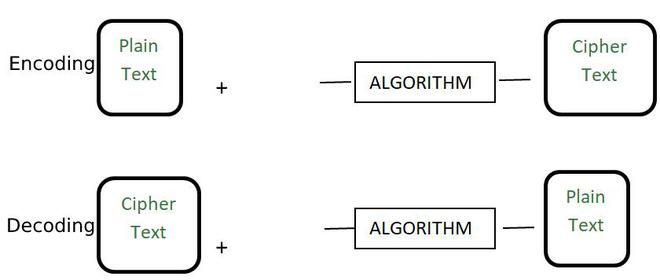
加密是将普通的可读消息(称为纯文本)转换为垃圾消息或非可读消息(称为密文)的过程。从加密获得的密文可以使用加密密钥轻松地转换为纯文本。加密算法的一些示例是RSA,AES和Blowfish。
2.散列:
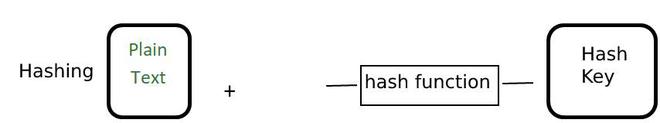
散列是使用散列函数将信息转换为密钥的过程。原始信息无法通过任何方式从哈希键中检索。通常,哈希密钥存储在数据库中,并将它们进行比较以检查原始信息是否匹配。它们通常用于存储登录密码。哈希算法的一些示例是MD5,SHA256。
哈希和加密之间的区别:
| Basis | Hashing | Encryption |
| Definition | It is a process to convert information to a shorter fixed value known as the key that is used to represent the original information. | It is the process to encode data securely such that only the authorized user who knows the key or password is able to retrieve the original data for everyone else it is just garbage. |
| Purpose | The purpose of hashing is indexing and retrieving items from the database. The process is very fast. | The purpose of encryption is to transform data to keep it secret from others. |
| Reverse Process | The hash code or key can not be reversed to the original information by any means. It can only be mapped and the hash code is checked if the hash code is the same the information is the same otherwise not. The original information can not be retrieved. | The original information can be easily retrieved if we know the encryption key and algorithm used for encryption. |
| Secure | It is more secure in comparison to encryption. | It is less secure in comparison to hashing. |
| Creation of file | Generally, it tries to generate a new key for each information passed to the hash function but on rare occasions, it might generate the same key popularly known as a collision. | It will always generate a new key for each information. |
| Example | MD5, SHA256 | RSA, AES and Blowfish |
| Length of information | The hashed information is generally of small and fixed length. It does not grow with the increase in the information length of information. | The encrypted information is not of fixed length. It grows with the increase in length of information. |