分析是将复杂的数据块分解成更小的部分以便更好地理解它的过程。分析是对过去已经发生的事情进行的。另一方面,分析通常指的是未来。它不是解释过去的事件,而是探索潜在的未来事件。分析是以系统的方式对数据进行计算分析,用于发现和解释新趋势以及数据中有意义模式的交流。它还包括将这些数据模式应用于未来的有效决策。
高级分析有多种类别,如下所示:
- 商业分析
- 商业智能
- 数据分析
- 数据科学
- 机器学习
- 人工智能
分析进一步分为两个领域:
- 定性分析:除了计划下一个决定之外,它还涉及使用直觉和经验。
- 定量分析:它是指将公式和算法应用于从分析中收集的数据。
如今,许多专业人士将分析视为分析和分析的结合。
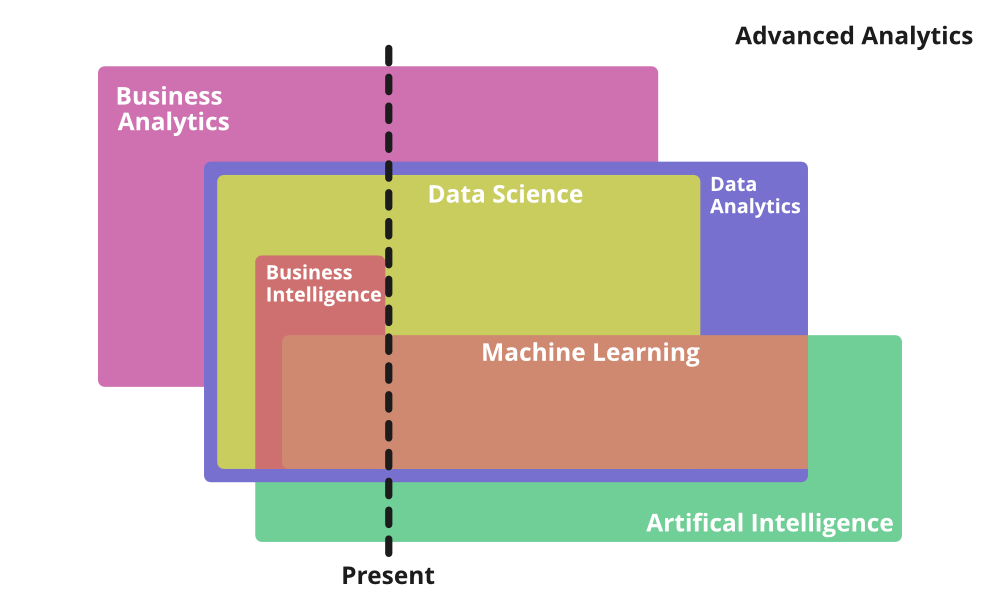
上图显示了数据科学和商业相关领域中最受欢迎的学科以及它们之间的关系。
虚线左边的部分是指对过去数据的活动,右边的部分是对未来规划和预测的决策。
业务分析:在业务领域,有业务案例研究、定性分析、初步数据报告、创建仪表板和销售预测等操作术语。其中,业务案例研究等活动是业务分析的一部分,而定性分析是业务分析的一部分。这两个是纯粹的业务相关活动,而创建初步数据报告和仪表板以及销售预测是数据驱动的业务活动。因此,这两个活动都将位于图表的蓝色部分。
数据分析:通过数据驱动的业务活动,如创建初步数据报告和仪表板以及销售预测,数据分析进入了画面。现在创建初步数据报告和仪表板是对过去数据的反映,因此它们将位于业务和数据分析的公共区域,但位于虚线的左侧,即“数据分析”和销售预测之间在右侧,因为预测本身是一项面向未来的活动。
数据科学:这是一个跨学科领域,其中使用科学方法、计算过程以及数学和统计算法从结构化和非结构化数据中提取知识并获得未来洞察力。数据科学是一门高度依赖数据可用性的学科,而业务分析不依赖于数据,尽管它包含了使用复杂数学、统计和编程工具的数据分析的一部分。创建初步数据报告和仪表板以及销售预测等活动在业务分析、数据分析和数据科学中很常见。
商业智能:它是指分析和报告历史业务数据的过程。商业智能的目的是在评估业务数据后解释过去的事件。它必须位于时间线的左侧,因为它只处理过去的事件,并且必须作为子领域位于数据科学部分,因为它是预测分析的初步步骤。
人工智能:是指在机器中模拟人类思维及其智能,使其像人类一样思考并模仿他们的行为。
机器学习:它是人工智能 (AI) 的一个子集,它为系统提供了无需明确编程即可自行学习和从经验中改进的能力。机器学习矩形的放置有点争议,因为监督机器学习将标记数据作为输入,而无监督机器学习算法不使用标记数据。
商业分析和商业智能之间的区别:
|
Based On |
Business Analytics |
Business Intelligence |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Business Analytics is repeated exploration and investigation of past business performances to gain insights and trends | Business Intelligence(BI) refers to the process of analyzing and reporting historical and present business data. |
| Need | Needed for future business operations and investments | Needed for current business operation. |
| Tools | SAP Business Objects, QlikSense, PowerBI, etc. | Word processing, Google docs, MS Visio, MS Office Tools, etc. |
| Example | Studying business case studies of other companies and business personalities and learning from their mistakes and ideas. | Reporting data with visuals and creating dashboards. |
数据分析和数据科学之间的区别:
|
Based On |
Data Analytics |
Data Science |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Data Analytics refers to cleaning, structuring, transforming, and modeling data in order to gain useful information and reach a conclusion that can help in decision making. | Data science is an interdisciplinary field in which scientific methods, computational processes, and mathematical and statistical algorithms are used to extract knowledge and gain future insights from structured and unstructured data. |
| Reliability On Data | Rely on data completely. | Partially rely on data. |
| Scope | Mirco | Macro |
| Data TYpe | Deals with structured data | Deals with unstructured data |
| Skill | Statistical and Programming skills are not much needed. | Statistical and Programming skills are needed. |
| Example | Digital Signal Processing uses Data Analytics to produce a higher quality signal. | Optimizing the accuracy of predictions based on data extracted from various activities typical drilling operations in the oil and gas industry. |
人工智能和机器学习的区别:
|
Based On |
Artificial Intelligence |
Machine Learning |
| Definition | Artificial intelligence (AI) refers to the simulation of the human mind and its intelligence in machines to think like humans and mimic their actions. | Machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence (AI) that provides systems the ability to learn by themselves and improve from experience without being explicitly programmed. |
| Optimal Solution | Finds optimal solution. | Finds a solution whether it is optimal or not. |
| Reliability On Data | Deals with Structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data. | Deals with Structured and semi-structured data only |
| Example | Siri, customer support using catboats, Expert System, Online game playing, Intelligent humanoid robot | Online recommender system, Google search algorithms, Facebook auto friend tagging suggestions |