1. 提取、加载和转换(ELT):
提取、加载和转换 (ELT) 是一种从源中提取原始数据并将其存储在目标服务器的数据仓库中并为终端流用户准备的技术。
ELT 包括对数据执行的 3 种不同操作:
- 提炼:
提取数据是一种从一个或多个来源识别数据的技术。来源可以是数据库、文件、ERP、CRM 或任何其他有用的数据来源。 - 加载:
加载是将提取的原始数据存储在数据仓库或数据湖中的过程。 - 转换:
数据转换是将原始数据源转换为分析所需的目标格式的过程。
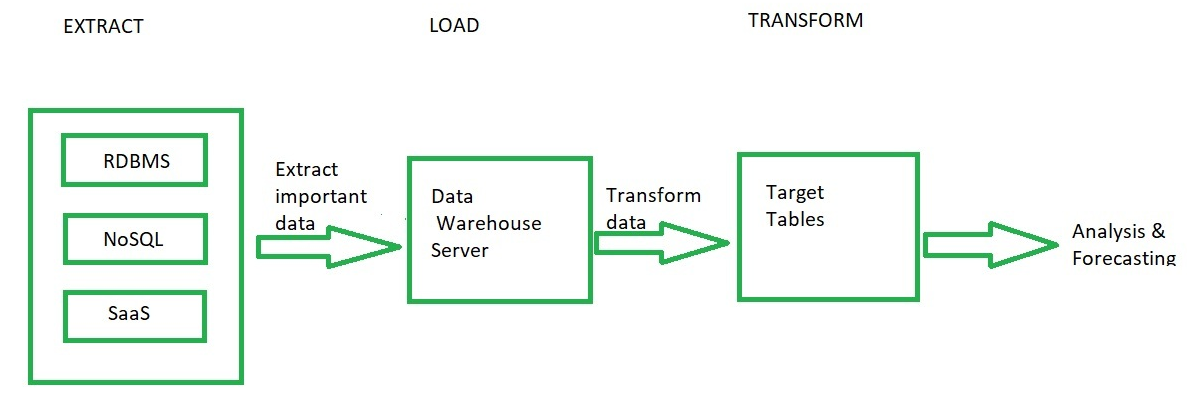
来自源的数据被提取并存储在数据仓库中。不转换整个数据,而仅在必要时完成所需的转换。需要时可以随时从仓库中检索原始数据。然后将根据需要转换的数据发送给分析。当您使用 ELT 时,您将存在于源系统中的整个数据集移动到目标。这意味着与 ETL 方法相比,您可以在数据仓库中使用原始数据。
2. 提取、转换和加载(ETL):
ETL 是提取原始数据,根据需要为用户转换并存储在数据仓库中的传统技术。后来开发了 ELT,以 ETL 为基础。 ETL 和 ELT 中发生的三个操作是相同的,只是它们的处理顺序略有不同。进行这种顺序更改是为了克服一些缺点。
- 提炼:
它是从所有可用数据源(例如数据库、文件、ERP、CRM 或任何其他数据源)中提取原始数据的过程。 - 转换:
提取的数据会根据用户的要求立即进行转换。 - 加载:
然后将转换后的数据加载到用户可以访问的数据仓库中。
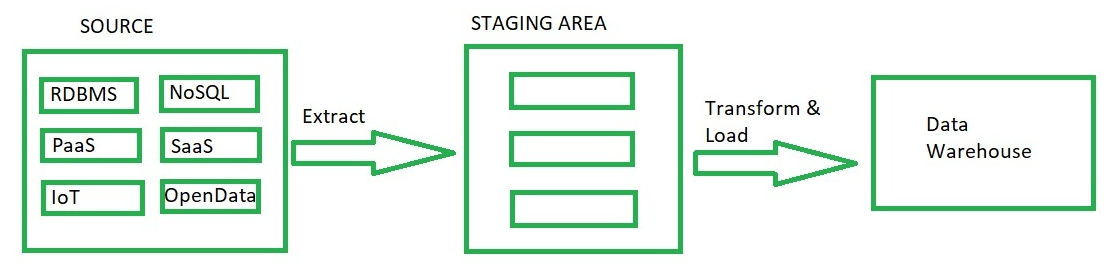
从源收集的数据直接存储在暂存区。对暂存区中的数据执行所需的转换。一旦数据被转换,结果数据就存储在数据仓库中。 ETL 架构的主要缺点是,转换后的数据一旦存储在仓库中,就无法再次修改,而在 ELT 中,原始数据的副本始终在仓库中可用,并且仅在需要时转换所需的数据。
ELT和ETL的区别:
| ELT | ETL |
|---|---|
| ELT tools do not require additional hardware | ETL tools require specific hardware with their own engines to perform transformations |
| Mostly Hadoop or NoSQL database to store data.Rarely RDBMS is used | RDBMS is used exclusively to store data |
| As all components are in one system, loading is done only once | As ETL uses staging area, extra time is required to load the data |
| Time to transform data is independent of the size of data | The system has to wait for large sizes of data. As the size of data increases, transformation time also increases |
| It is cost effective ans available to all business using SaaS solution | Not cost effective for small and medium business |
| The data transformed is used by data scientists and advanced analysts | The data transformed is used by users reading report and SQL coders |
| Creates ad hoc views.Low cost for building and maintaining | Views are created based on multiple scripts.Deleting view means deleting data |
| Best for unstructured and non-relational data. Ideal for data lakes. Suited for very large amounts of data | Best for relational and structured data. Better for small to medium amounts of data |