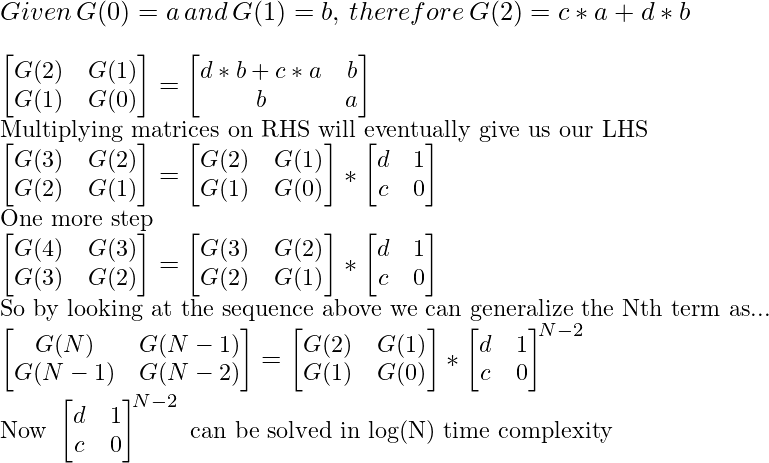我们都知道斐波那契数 (Fn) 是由递推关系定义的
Fibonacci Numbers (Fn) = F(n-1) + F(n-2)
with seed values
F0 = 0 and F1 = 1
同样,我们可以概括这些数字。这样的数列被称为广义斐波那契数 (G) 。
广义斐波那契数 (G)由递推关系定义
Generalized Fibonacci Numbers (Gn) = (c * G(n-1)) + (d * G(n-2))
with seed values
G0 = a and G1 = b
查找第 N 项
给定广义斐波那契数的四个常数值a、b、c和 d以及一个整数N ,任务是找到广义斐波那契数的第 N 项,即Gn 。
例子:
Input: N = 2, a = 0, b = 1, c = 2, d = 3
Output: 2
Explanation:
As a = 0 -> G(0) = 0
b = 1 -> G(1) = 1
So, G(2) = 2 * G(1) + 3 * G(0) = 2
Input: N = 3, a = 0, b = 1, c = 2, d = 3
Output: 7
朴素方法:使用给定的值,找到系列中的每一项,直到第 N 项,然后打印第 N 项。
时间复杂度: O(2 N )
另一种方法:这个想法是使用DP制表来查找所有术语直到第N个术语,然后打印第N个术语。
时间复杂度: O(N)
有效的方法:使用矩阵乘法,我们可以在 log(N) 时间内解决给定的问题。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program to implement the
// Generalised Fibonacci numbers
#include
using namespace std;
// Helper function that multiplies
// 2 matrices F and M of size 2*2,
// and puts the multiplication
// result back to F[][]
void multiply(int F[2][2], int M[2][2]);
// Helper function that calculates F[][]
// raised to the power N
// and puts the result in F[][]
void power(int F[2][2], int N, int m, int n);
// Function to find the Nth term
int F(int N, int a, int b, int m, int n)
{
// m 1
// n 0
int F[2][2] = { { m, 1 }, { n, 0 } };
if (N == 0)
return a;
if (N == 1)
return b;
if (N == 2)
return m * b + n * a;
int initial[2][2]
= { { m * b + n * a, b },
{ b, a } };
power(F, N - 2, m, n);
// Discussed above
multiply(initial, F);
return F[0][0];
}
// Function that multiplies
// 2 matrices F and M of size 2*2,
// and puts the multiplication
// result back to F[][]
void multiply(int F[2][2], int M[2][2])
{
int x = F[0][0] * M[0][0] + F[0][1] * M[1][0];
int y = F[0][0] * M[0][1] + F[0][1] * M[1][1];
int z = F[1][0] * M[0][0] + F[1][1] * M[1][0];
int w = F[1][0] * M[0][1] + F[1][1] * M[1][1];
F[0][0] = x;
F[0][1] = y;
F[1][0] = z;
F[1][1] = w;
}
// Function that calculates F[][]
// raised to the power N
// and puts the result in F[][]
void power(int F[2][2], int N, int m, int n)
{
int i;
int M[2][2] = { { m, 1 }, { n, 0 } };
for (i = 1; i <= N; i++)
multiply(F, M);
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int N = 2, a = 0, b = 1, m = 2, n = 3;
printf("%d\n", F(N, a, b, m, n));
N = 3;
printf("%d\n", F(N, a, b, m, n));
N = 4;
printf("%d\n", F(N, a, b, m, n));
N = 5;
printf("%d\n", F(N, a, b, m, n));
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to implement the
// Generalised Fibonacci numbers
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Function to find the Nth term
static int F(int N, int a, int b,
int m, int n)
{
// m 1
// n 0
int[][] F = { { m, 1 }, { n, 0 } };
if (N == 0)
return a;
if (N == 1)
return b;
if (N == 2)
return m * b + n * a;
int[][] initial = { { m * b + n * a, b },
{ b, a } };
power(F, N - 2, m, n);
// Discussed below
multiply(initial, F);
return F[0][0];
}
// Function that multiplies
// 2 matrices F and M of size 2*2,
// and puts the multiplication
// result back to F[][]
static void multiply(int[][] F, int[][] M)
{
int x = F[0][0] * M[0][0] +
F[0][1] * M[1][0];
int y = F[0][0] * M[0][1] +
F[0][1] * M[1][1];
int z = F[1][0] * M[0][0] +
F[1][1] * M[1][0];
int w = F[1][0] * M[0][1] +
F[1][1] * M[1][1];
F[0][0] = x;
F[0][1] = y;
F[1][0] = z;
F[1][1] = w;
}
// Function that calculates F[][]
// raised to the power N
// and puts the result in F[][]
static void power(int[][] F, int N,
int m, int n)
{
int i;
int[][] M = { { m, 1 }, { n, 0 } };
for(i = 1; i <= N; i++)
multiply(F, M);
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int N = 2, a = 0, b = 1, m = 2, n = 3;
System.out.println(F(N, a, b, m, n));
N = 3;
System.out.println(F(N, a, b, m, n));
N = 4;
System.out.println(F(N, a, b, m, n));
N = 5;
System.out.println(F(N, a, b, m, n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by offbeatPython3
# Python3 program to implement the
# Generalised Fibonacci numbers
# Function to find the Nth term
def F(N, a, b, m, n):
# m 1
# n 0
F = [[ m, 1 ], [ n, 0 ]]
if(N == 0):
return a
if(N == 1):
return b
if(N == 2):
return m * b + n * a
initial = [[ m * b + n * b, b ],
[ b, a ]]
power(F, N - 2, m, n)
multiply(initial, F)
return F[0][0]
# Function that multiplies
# 2 matrices F and M of size 2*2,
# and puts the multiplication
# result back to F[][]
def multiply(F, M):
x = (F[0][0] * M[0][0] +
F[0][1] * M[1][0])
y = (F[0][0] * M[0][1] +
F[0][1] * M[1][1])
z = (F[1][0] * M[0][0] +
F[1][1] * M[1][0])
w = (F[1][0] * M[0][1] +
F[1][1] * M[1][1])
F[0][0] = x
F[0][1] = y
F[1][0] = z
F[1][1] = w
# Function that calculates F[][]
# raised to the power N
# and puts the result in F[][]
def power(F, N, m, n):
M = [[ m, 1 ], [ n, 0 ]]
for i in range(1, N + 1):
multiply(F, M)
# Driver code
if __name__ == '__main__':
N, a, b, m, n = 2, 0, 1, 2, 3
print(F(N, a, b, m, n))
N = 3
print(F(N, a, b, m, n))
N = 4
print(F(N, a, b, m, n))
N = 5
print(F(N, a, b, m, n))
# This code is contributed by Shivam SinghC#
// C# program to implement the
// Generalised Fibonacci numbers
using System;
class GFG{
// Function to find the Nth term
static int F(int N, int a, int b,
int m, int n)
{
// m 1
// n 0
int[,] F = { { m, 1 }, { n, 0 } };
if (N == 0)
return a;
if (N == 1)
return b;
if (N == 2)
return m * b + n * a;
int[,] initial = { { m * b + n * a, b },
{ b, a } };
power(F, N - 2, m, n);
// Discussed below
multiply(initial, F);
return F[0, 0];
}
// Function that multiplies
// 2 matrices F and M of size 2*2,
// and puts the multiplication
// result back to F[,]
static void multiply(int[,] F, int[,] M)
{
int x = F[0, 0] * M[0, 0] +
F[0, 1] * M[1, 0];
int y = F[0, 0] * M[0, 1] +
F[0, 1] * M[1, 1];
int z = F[1, 0] * M[0, 0] +
F[1, 1] * M[1, 0];
int w = F[1, 0] * M[0, 1] +
F[1, 1] * M[1, 1];
F[0, 0] = x;
F[0, 1] = y;
F[1, 0] = z;
F[1, 1] = w;
}
// Function that calculates F[,]
// raised to the power N
// and puts the result in F[,]
static void power(int[,] F, int N,
int m, int n)
{
int i;
int[,] M = { { m, 1 }, { n, 0 } };
for(i = 1; i <= N; i++)
multiply(F, M);
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int N = 2, a = 0, b = 1, m = 2, n = 3;
Console.WriteLine(F(N, a, b, m, n));
N = 3;
Console.WriteLine(F(N, a, b, m, n));
N = 4;
Console.WriteLine(F(N, a, b, m, n));
N = 5;
Console.WriteLine(F(N, a, b, m, n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by shikhasingrajputJavascript
2
7
20
61如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。