斐波那契数是以下整数序列中的数字。
0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55, 89, 144, …..
在数学术语中,斐波那契数列 Fn 由递推关系定义
Fn = Fn-1 + Fn-2带有种子值
F0 = 0 and F1 = 1.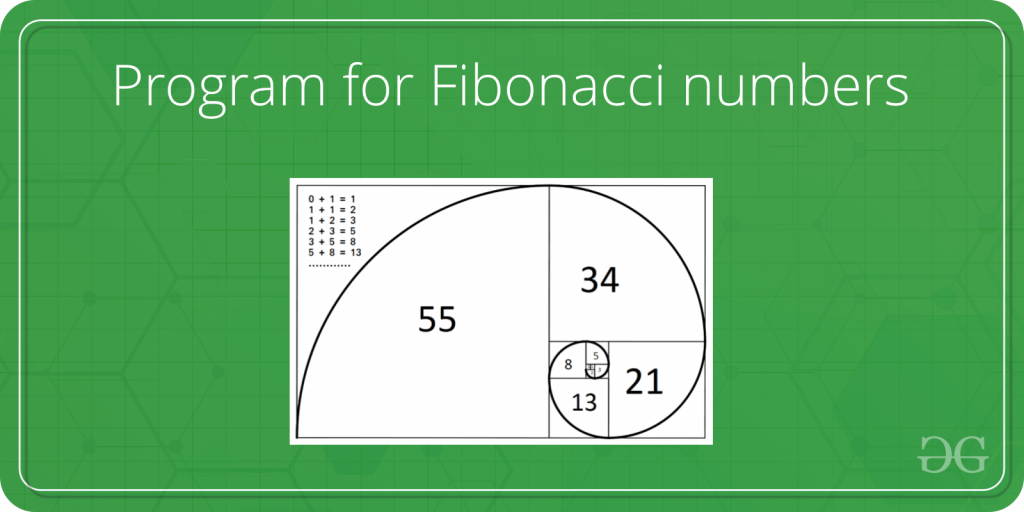
给定一个数 n,打印第 n 个斐波那契数。
例子:
Input : n = 2
Output : 1
Input : n = 9
Output : 34编写一个返回 F n的函数int fib(int n) 。例如,如果n = 0,那么fib()应该返回 0。如果 n = 1,那么它应该返回 1。对于 n > 1,它应该返回 F n-1 + F n-2
For n = 9
Output:34以下是获取第 n 个斐波那契数的不同方法。
方法一(使用递归)
一种简单的方法,即上面给出的直接递归实现数学递推关系。
C++
//Fibonacci Series using Recursion
#include
using namespace std;
int fib(int n)
{
if (n <= 1)
return n;
return fib(n-1) + fib(n-2);
}
int main ()
{
int n = 9;
cout << fib(n);
getchar();
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed
// by Akanksha Rai C
//Fibonacci Series using Recursion
#include
int fib(int n)
{
if (n <= 1)
return n;
return fib(n-1) + fib(n-2);
}
int main ()
{
int n = 9;
printf("%d", fib(n));
getchar();
return 0;
} Java
//Fibonacci Series using Recursion
class fibonacci
{
static int fib(int n)
{
if (n <= 1)
return n;
return fib(n-1) + fib(n-2);
}
public static void main (String args[])
{
int n = 9;
System.out.println(fib(n));
}
}
/* This code is contributed by Rajat Mishra */Python
# Function for nth Fibonacci number
def Fibonacci(n):
if n<0:
print("Incorrect input")
# First Fibonacci number is 0
elif n==0:
return 0
# Second Fibonacci number is 1
elif n==1:
return 1
else:
return Fibonacci(n-1)+Fibonacci(n-2)
# Driver Program
print(Fibonacci(9))
#This code is contributed by Saket ModiC#
// C# program for Fibonacci Series
// using Recursion
using System;
public class GFG
{
public static int Fib(int n)
{
if (n <= 1)
{
return n;
}
else
{
return Fib(n - 1) + Fib(n - 2);
}
}
// driver code
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
int n = 9;
Console.Write(Fib(n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Sam007PHP
Javascript
C++
// C++ program for Fibonacci Series
// using Dynamic Programming
#include
using namespace std;
class GFG{
public:
int fib(int n)
{
// Declare an array to store
// Fibonacci numbers.
// 1 extra to handle
// case, n = 0
int f[n + 2];
int i;
// 0th and 1st number of the
// series are 0 and 1
f[0] = 0;
f[1] = 1;
for(i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
//Add the previous 2 numbers
// in the series and store it
f[i] = f[i - 1] + f[i - 2];
}
return f[n];
}
};
// Driver code
int main ()
{
GFG g;
int n = 9;
cout << g.fib(n);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by SoumikMondal C
//Fibonacci Series using Dynamic Programming
#include
int fib(int n)
{
/* Declare an array to store Fibonacci numbers. */
int f[n+2]; // 1 extra to handle case, n = 0
int i;
/* 0th and 1st number of the series are 0 and 1*/
f[0] = 0;
f[1] = 1;
for (i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
/* Add the previous 2 numbers in the series
and store it */
f[i] = f[i-1] + f[i-2];
}
return f[n];
}
int main ()
{
int n = 9;
printf("%d", fib(n));
getchar();
return 0;
} Java
// Fibonacci Series using Dynamic Programming
class fibonacci
{
static int fib(int n)
{
/* Declare an array to store Fibonacci numbers. */
int f[] = new int[n+2]; // 1 extra to handle case, n = 0
int i;
/* 0th and 1st number of the series are 0 and 1*/
f[0] = 0;
f[1] = 1;
for (i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
/* Add the previous 2 numbers in the series
and store it */
f[i] = f[i-1] + f[i-2];
}
return f[n];
}
public static void main (String args[])
{
int n = 9;
System.out.println(fib(n));
}
}
/* This code is contributed by Rajat Mishra */Python
# Fibonacci Series using Dynamic Programming
def fibonacci(n):
# Taking 1st two fibonacci numbers as 0 and 1
f = [0, 1]
for i in range(2, n+1):
f.append(f[i-1] + f[i-2])
return f[n]
print(fibonacci(9))C#
// C# program for Fibonacci Series
// using Dynamic Programming
using System;
class fibonacci {
static int fib(int n)
{
// Declare an array to
// store Fibonacci numbers.
// 1 extra to handle
// case, n = 0
int []f = new int[n + 2];
int i;
/* 0th and 1st number of the
series are 0 and 1 */
f[0] = 0;
f[1] = 1;
for (i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
/* Add the previous 2 numbers
in the series and store it */
f[i] = f[i - 1] + f[i - 2];
}
return f[n];
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main ()
{
int n = 9;
Console.WriteLine(fib(n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by anuj_67.PHP
Javascript
C++
// Fibonacci Series using Space Optimized Method
#include
using namespace std;
int fib(int n)
{
int a = 0, b = 1, c, i;
if( n == 0)
return a;
for(i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
c = a + b;
a = b;
b = c;
}
return b;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int n = 9;
cout << fib(n);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by Code_Mech C
// Fibonacci Series using Space Optimized Method
#include
int fib(int n)
{
int a = 0, b = 1, c, i;
if( n == 0)
return a;
for (i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
c = a + b;
a = b;
b = c;
}
return b;
}
int main ()
{
int n = 9;
printf("%d", fib(n));
getchar();
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for Fibonacci Series using Space
// Optimized Method
class fibonacci
{
static int fib(int n)
{
int a = 0, b = 1, c;
if (n == 0)
return a;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
c = a + b;
a = b;
b = c;
}
return b;
}
public static void main (String args[])
{
int n = 9;
System.out.println(fib(n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Mihir JoshiPython
# Function for nth fibonacci number - Space Optimisation
# Taking 1st two fibonacci numbers as 0 and 1
def fibonacci(n):
a = 0
b = 1
if n < 0:
print("Incorrect input")
elif n == 0:
return a
elif n == 1:
return b
else:
for i in range(2,n+1):
c = a + b
a = b
b = c
return b
# Driver Program
print(fibonacci(9))
#This code is contributed by Saket ModiC#
// C# program for Fibonacci Series
// using Space Optimized Method
using System;
namespace Fib
{
public class GFG
{
static int Fib(int n)
{
int a = 0, b = 1, c = 0;
// To return the first Fibonacci number
if (n == 0) return a;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
c = a + b;
a = b;
b = c;
}
return b;
}
// Driver function
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
int n = 9;
Console.Write("{0} ", Fib(n));
}
}
}
// This code is contributed by Sam007.PHP
Javascript
C++
#include
using namespace std;
// Helper function that multiplies 2
// matrices F and M of size 2*2, and
// puts the multiplication result
// back to F[][]
void multiply(int F[2][2], int M[2][2]);
// Helper function that calculates F[][]
// raise to the power n and puts the
// result in F[][]
// Note that this function is designed
// only for fib() and won't work as
// general power function
void power(int F[2][2], int n);
int fib(int n)
{
int F[2][2] = { { 1, 1 }, { 1, 0 } };
if (n == 0)
return 0;
power(F, n - 1);
return F[0][0];
}
void multiply(int F[2][2], int M[2][2])
{
int x = F[0][0] * M[0][0] +
F[0][1] * M[1][0];
int y = F[0][0] * M[0][1] +
F[0][1] * M[1][1];
int z = F[1][0] * M[0][0] +
F[1][1] * M[1][0];
int w = F[1][0] * M[0][1] +
F[1][1] * M[1][1];
F[0][0] = x;
F[0][1] = y;
F[1][0] = z;
F[1][1] = w;
}
void power(int F[2][2], int n)
{
int i;
int M[2][2] = { { 1, 1 }, { 1, 0 } };
// n - 1 times multiply the
// matrix to {{1,0},{0,1}}
for(i = 2; i <= n; i++)
multiply(F, M);
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int n = 9;
cout << " " << fib(n);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110 C
#include
/* Helper function that multiplies 2 matrices F and M of size 2*2, and
puts the multiplication result back to F[][] */
void multiply(int F[2][2], int M[2][2]);
/* Helper function that calculates F[][] raise to the power n and puts the
result in F[][]
Note that this function is designed only for fib() and won't work as general
power function */
void power(int F[2][2], int n);
int fib(int n)
{
int F[2][2] = {{1,1},{1,0}};
if (n == 0)
return 0;
power(F, n-1);
return F[0][0];
}
void multiply(int F[2][2], int M[2][2])
{
int x = F[0][0]*M[0][0] + F[0][1]*M[1][0];
int y = F[0][0]*M[0][1] + F[0][1]*M[1][1];
int z = F[1][0]*M[0][0] + F[1][1]*M[1][0];
int w = F[1][0]*M[0][1] + F[1][1]*M[1][1];
F[0][0] = x;
F[0][1] = y;
F[1][0] = z;
F[1][1] = w;
}
void power(int F[2][2], int n)
{
int i;
int M[2][2] = {{1,1},{1,0}};
// n - 1 times multiply the matrix to {{1,0},{0,1}}
for (i = 2; i <= n; i++)
multiply(F, M);
}
/* Driver program to test above function */
int main()
{
int n = 9;
printf("%d", fib(n));
getchar();
return 0;
} Java
class fibonacci
{
static int fib(int n)
{
int F[][] = new int[][]{{1,1},{1,0}};
if (n == 0)
return 0;
power(F, n-1);
return F[0][0];
}
/* Helper function that multiplies 2 matrices F and M of size 2*2, and
puts the multiplication result back to F[][] */
static void multiply(int F[][], int M[][])
{
int x = F[0][0]*M[0][0] + F[0][1]*M[1][0];
int y = F[0][0]*M[0][1] + F[0][1]*M[1][1];
int z = F[1][0]*M[0][0] + F[1][1]*M[1][0];
int w = F[1][0]*M[0][1] + F[1][1]*M[1][1];
F[0][0] = x;
F[0][1] = y;
F[1][0] = z;
F[1][1] = w;
}
/* Helper function that calculates F[][] raise to the power n and puts the
result in F[][]
Note that this function is designed only for fib() and won't work as general
power function */
static void power(int F[][], int n)
{
int i;
int M[][] = new int[][]{{1,1},{1,0}};
// n - 1 times multiply the matrix to {{1,0},{0,1}}
for (i = 2; i <= n; i++)
multiply(F, M);
}
/* Driver program to test above function */
public static void main (String args[])
{
int n = 9;
System.out.println(fib(n));
}
}
/* This code is contributed by Rajat Mishra */Python3
# Helper function that multiplies
# 2 matrices F and M of size 2*2,
# and puts the multiplication
# result back to F[][]
# Helper function that calculates
# F[][] raise to the power n and
# puts the result in F[][]
# Note that this function is
# designed only for fib() and
# won't work as general
# power function
def fib(n):
F = [[1, 1],
[1, 0]]
if (n == 0):
return 0
power(F, n - 1)
return F[0][0]
def multiply(F, M):
x = (F[0][0] * M[0][0] +
F[0][1] * M[1][0])
y = (F[0][0] * M[0][1] +
F[0][1] * M[1][1])
z = (F[1][0] * M[0][0] +
F[1][1] * M[1][0])
w = (F[1][0] * M[0][1] +
F[1][1] * M[1][1])
F[0][0] = x
F[0][1] = y
F[1][0] = z
F[1][1] = w
def power(F, n):
M = [[1, 1],
[1, 0]]
# n - 1 times multiply the
# matrix to {{1,0},{0,1}}
for i in range(2, n + 1):
multiply(F, M)
# Driver Code
if __name__ == "__main__":
n = 9
print(fib(n))
# This code is contributed
# by ChitraNayalC#
using System;
class GFG {
static int fib(int n)
{
int [,]F = new int[,] {{1, 1},
{1, 0} };
if (n == 0)
return 0;
power(F, n-1);
return F[0,0];
}
/* Helper function that multiplies 2
matrices F and M of size 2*2, and puts
the multiplication result back to F[][] */
static void multiply(int [,]F, int [,]M)
{
int x = F[0,0]*M[0,0] + F[0,1]*M[1,0];
int y = F[0,0]*M[0,1] + F[0,1]*M[1,1];
int z = F[1,0]*M[0,0] + F[1,1]*M[1,0];
int w = F[1,0]*M[0,1] + F[1,1]*M[1,1];
F[0,0] = x;
F[0,1] = y;
F[1,0] = z;
F[1,1] = w;
}
/* Helper function that calculates F[][]
raise to the power n and puts the result
in F[][] Note that this function is designed
only for fib() and won't work as general
power function */
static void power(int [,]F, int n)
{
int i;
int [,]M = new int[,]{{1, 1},
{1, 0} };
// n - 1 times multiply the matrix to
// {{1,0},{0,1}}
for (i = 2; i <= n; i++)
multiply(F, M);
}
/* Driver program to test above function */
public static void Main ()
{
int n = 9;
Console.WriteLine(fib(n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by anuj_67.PHP
Javascript
C++
// Fibonacci Series using Optimized Method
#include
using namespace std;
void multiply(int F[2][2], int M[2][2]);
void power(int F[2][2], int n);
// Function that returns nth Fibonacci number
int fib(int n)
{
int F[2][2] = {{1, 1}, {1, 0}};
if (n == 0)
return 0;
power(F, n - 1);
return F[0][0];
}
// Optimized version of power() in method 4
void power(int F[2][2], int n)
{
if(n == 0 || n == 1)
return;
int M[2][2] = {{1, 1}, {1, 0}};
power(F, n / 2);
multiply(F, F);
if (n % 2 != 0)
multiply(F, M);
}
void multiply(int F[2][2], int M[2][2])
{
int x = F[0][0] * M[0][0] + F[0][1] * M[1][0];
int y = F[0][0] * M[0][1] + F[0][1] * M[1][1];
int z = F[1][0] * M[0][0] + F[1][1] * M[1][0];
int w = F[1][0] * M[0][1] + F[1][1] * M[1][1];
F[0][0] = x;
F[0][1] = y;
F[1][0] = z;
F[1][1] = w;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int n = 9;
cout << fib(9);
getchar();
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by Nidhi_biet C
#include
void multiply(int F[2][2], int M[2][2]);
void power(int F[2][2], int n);
/* function that returns nth Fibonacci number */
int fib(int n)
{
int F[2][2] = {{1,1},{1,0}};
if (n == 0)
return 0;
power(F, n-1);
return F[0][0];
}
/* Optimized version of power() in method 4 */
void power(int F[2][2], int n)
{
if( n == 0 || n == 1)
return;
int M[2][2] = {{1,1},{1,0}};
power(F, n/2);
multiply(F, F);
if (n%2 != 0)
multiply(F, M);
}
void multiply(int F[2][2], int M[2][2])
{
int x = F[0][0]*M[0][0] + F[0][1]*M[1][0];
int y = F[0][0]*M[0][1] + F[0][1]*M[1][1];
int z = F[1][0]*M[0][0] + F[1][1]*M[1][0];
int w = F[1][0]*M[0][1] + F[1][1]*M[1][1];
F[0][0] = x;
F[0][1] = y;
F[1][0] = z;
F[1][1] = w;
}
/* Driver program to test above function */
int main()
{
int n = 9;
printf("%d", fib(9));
getchar();
return 0;
} Java
//Fibonacci Series using Optimized Method
class fibonacci
{
/* function that returns nth Fibonacci number */
static int fib(int n)
{
int F[][] = new int[][]{{1,1},{1,0}};
if (n == 0)
return 0;
power(F, n-1);
return F[0][0];
}
static void multiply(int F[][], int M[][])
{
int x = F[0][0]*M[0][0] + F[0][1]*M[1][0];
int y = F[0][0]*M[0][1] + F[0][1]*M[1][1];
int z = F[1][0]*M[0][0] + F[1][1]*M[1][0];
int w = F[1][0]*M[0][1] + F[1][1]*M[1][1];
F[0][0] = x;
F[0][1] = y;
F[1][0] = z;
F[1][1] = w;
}
/* Optimized version of power() in method 4 */
static void power(int F[][], int n)
{
if( n == 0 || n == 1)
return;
int M[][] = new int[][]{{1,1},{1,0}};
power(F, n/2);
multiply(F, F);
if (n%2 != 0)
multiply(F, M);
}
/* Driver program to test above function */
public static void main (String args[])
{
int n = 9;
System.out.println(fib(n));
}
}
/* This code is contributed by Rajat Mishra */Python3
# Fibonacci Series using
# Optimized Method
# function that returns nth
# Fibonacci number
def fib(n):
F = [[1, 1],
[1, 0]]
if (n == 0):
return 0
power(F, n - 1)
return F[0][0]
def multiply(F, M):
x = (F[0][0] * M[0][0] +
F[0][1] * M[1][0])
y = (F[0][0] * M[0][1] +
F[0][1] * M[1][1])
z = (F[1][0] * M[0][0] +
F[1][1] * M[1][0])
w = (F[1][0] * M[0][1] +
F[1][1] * M[1][1])
F[0][0] = x
F[0][1] = y
F[1][0] = z
F[1][1] = w
# Optimized version of
# power() in method 4
def power(F, n):
if( n == 0 or n == 1):
return;
M = [[1, 1],
[1, 0]];
power(F, n // 2)
multiply(F, F)
if (n % 2 != 0):
multiply(F, M)
# Driver Code
if __name__ == "__main__":
n = 9
print(fib(n))
# This code is contributed
# by ChitraNayalC#
// Fibonacci Series using
// Optimized Method
using System;
class GFG
{
/* function that returns
nth Fibonacci number */
static int fib(int n)
{
int[,] F = new int[,]{{1, 1},
{1, 0}};
if (n == 0)
return 0;
power(F, n - 1);
return F[0, 0];
}
static void multiply(int[,] F,
int[,] M)
{
int x = F[0, 0] * M[0, 0] +
F[0, 1] * M[1, 0];
int y = F[0, 0] * M[0, 1] +
F[0, 1] * M[1, 1];
int z = F[1, 0] * M[0, 0] +
F[1, 1] * M[1, 0];
int w = F[1, 0] * M[0, 1] +
F[1, 1] * M[1, 1];
F[0, 0] = x;
F[0, 1] = y;
F[1, 0] = z;
F[1, 1] = w;
}
/* Optimized version of
power() in method 4 */
static void power(int[,] F, int n)
{
if( n == 0 || n == 1)
return;
int[,] M = new int[,]{{1, 1},
{1, 0}};
power(F, n / 2);
multiply(F, F);
if (n % 2 != 0)
multiply(F, M);
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main ()
{
int n = 9;
Console.Write(fib(n));
}
}
// This code is contributed
// by ChitraNayalJavascript
C++
// C++ Program to find n'th fibonacci Number in
// with O(Log n) arithmetic operations
#include
using namespace std;
const int MAX = 1000;
// Create an array for memoization
int f[MAX] = {0};
// Returns n'th fibonacci number using table f[]
int fib(int n)
{
// Base cases
if (n == 0)
return 0;
if (n == 1 || n == 2)
return (f[n] = 1);
// If fib(n) is already computed
if (f[n])
return f[n];
int k = (n & 1)? (n+1)/2 : n/2;
// Applying above formula [Note value n&1 is 1
// if n is odd, else 0.
f[n] = (n & 1)? (fib(k)*fib(k) + fib(k-1)*fib(k-1))
: (2*fib(k-1) + fib(k))*fib(k);
return f[n];
}
/* Driver program to test above function */
int main()
{
int n = 9;
printf("%d ", fib(n));
return 0;
} Java
// Java Program to find n'th fibonacci
// Number with O(Log n) arithmetic operations
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
static int MAX = 1000;
static int f[];
// Returns n'th fibonacci number using
// table f[]
public static int fib(int n)
{
// Base cases
if (n == 0)
return 0;
if (n == 1 || n == 2)
return (f[n] = 1);
// If fib(n) is already computed
if (f[n] != 0)
return f[n];
int k = (n & 1) == 1? (n + 1) / 2
: n / 2;
// Applying above formula [Note value
// n&1 is 1 if n is odd, else 0.
f[n] = (n & 1) == 1? (fib(k) * fib(k) +
fib(k - 1) * fib(k - 1))
: (2 * fib(k - 1) + fib(k))
* fib(k);
return f[n];
}
/* Driver program to test above function */
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int n = 9;
f= new int[MAX];
System.out.println(fib(n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Arnav Kr. Mandal.Python
# Python3 Program to find n'th fibonacci Number in
# with O(Log n) arithmetic operations
MAX = 1000
# Create an array for memoization
f = [0] * MAX
# Returns n'th fibonacci number using table f[]
def fib(n) :
# Base cases
if (n == 0) :
return 0
if (n == 1 or n == 2) :
f[n] = 1
return (f[n])
# If fib(n) is already computed
if (f[n]) :
return f[n]
if( n & 1) :
k = (n + 1) // 2
else :
k = n // 2
# Applying above formula [Note value n&1 is 1
# if n is odd, else 0.
if((n & 1) ) :
f[n] = (fib(k) * fib(k) + fib(k-1) * fib(k-1))
else :
f[n] = (2*fib(k-1) + fib(k))*fib(k)
return f[n]
# Driver code
n = 9
print(fib(n))
# This code is contributed by Nikita Tiwari.C#
// C# Program to find n'th
// fibonacci Number with
// O(Log n) arithmetic operations
using System;
class GFG
{
static int MAX = 1000;
static int[] f;
// Returns n'th fibonacci
// number using table f[]
public static int fib(int n)
{
// Base cases
if (n == 0)
return 0;
if (n == 1 || n == 2)
return (f[n] = 1);
// If fib(n) is already
// computed
if (f[n] != 0)
return f[n];
int k = (n & 1) == 1 ? (n + 1) / 2
: n / 2;
// Applying above formula
// [Note value n&1 is 1 if
// n is odd, else 0.
f[n] = (n & 1) == 1 ? (fib(k) * fib(k) +
fib(k - 1) * fib(k - 1))
: (2 * fib(k - 1) + fib(k)) *
fib(k);
return f[n];
}
// Driver Code
static void Main()
{
int n = 9;
f = new int[MAX];
Console.WriteLine(fib(n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by mitsPHP
Javascript
C++
// C++ Program to find n'th fibonacci Number
#include
#include
int fib(int n) {
double phi = (1 + sqrt(5)) / 2;
return round(pow(phi, n) / sqrt(5));
}
// Driver Code
int main ()
{
int n = 9;
std::cout << fib(n) << std::endl;
return 0;
}
//This code is contributed by Lokesh Mohanty. C
// C Program to find n'th fibonacci Number
#include
#include
int fib(int n) {
double phi = (1 + sqrt(5)) / 2;
return round(pow(phi, n) / sqrt(5));
}
int main ()
{
int n = 9;
printf("%d", fib(n));
return 0;
} Java
// Java Program to find n'th fibonacci Number
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
static int fib(int n) {
double phi = (1 + Math.sqrt(5)) / 2;
return (int) Math.round(Math.pow(phi, n)
/ Math.sqrt(5));
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = 9;
System.out.println(fib(n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by PrinciRaj1992Python3
# Python3 program to find n'th
# fibonacci Number
import math
def fibo(n):
phi = (1 + math.sqrt(5)) / 2
return round(pow(phi, n) / math.sqrt(5))
# Driver code
if __name__ == '__main__':
n = 9
print(fibo(n))
# This code is contributed by prasun_parateC#
// C# Program to find n'th fibonacci Number
using System;
public class GFG
{
static int fib(int n)
{
double phi = (1 + Math.Sqrt(5)) / 2;
return (int) Math.Round(Math.Pow(phi, n)
/ Math.Sqrt(5));
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
int n = 9;
Console.WriteLine(fib(n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumarPHP
Javascript
C++
#include
using namespace std;
int dp[10];
int fib(int n)
{
if (n <= 1)
return n;
// temporary variables to store
// values of fib(n-1) & fib(n-2)
int first, second;
if (dp[n - 1] != -1)
first = dp[n - 1];
else
first = fib(n - 1);
if (dp[n - 2] != -1)
second = dp[n - 2];
else
second = fib(n - 2);
// memoization
return dp[n] = first + second;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int n = 9;
memset(dp, -1, sizeof(dp));
cout << fib(n);
getchar();
return 0;
// This code is contributed by Bhavneet Singh
} Java
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Initialize array of dp
static int[] dp = new int[10];
static int fib(int n)
{
if (n <= 1)
return n;
// Temporary variables to store
// values of fib(n-1) & fib(n-2)
int first, second;
if (dp[n - 1] != -1)
first = dp[n - 1];
else
first = fib(n - 1);
if (dp[n - 2] != -1)
second = dp[n - 2];
else
second = fib(n - 2);
// Memoization
return dp[n] = first + second;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int n = 9;
Arrays.fill(dp, -1);
System.out.print(fib(n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by sujitmeshramPython3
# Initialize array of dp
dp = [-1 for i in range(10)]
def fib(n):
if (n <= 1):
return n;
global dp;
# Temporary variables to store
# values of fib(n-1) & fib(n-2)
first = 0;
second = 0;
if (dp[n - 1] != -1):
first = dp[n - 1];
else:
first = fib(n - 1);
if (dp[n - 2] != -1):
second = dp[n - 2];
else:
second = fib(n - 2);
dp[n] = first + second;
# Memoization
return dp[n] ;
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
n = 9;
print(fib(n));
# This code contributed by Rajput-JiC#
using System;
class GFG {
// Initialize array of dp
static int[] dp = new int[10];
static int fib(int n)
{
if (n <= 1)
return n;
// Temporary variables to store
// values of fib(n-1) & fib(n-2)
int first, second;
if (dp[n - 1] != -1)
first = dp[n - 1];
else
first = fib(n - 1);
if (dp[n - 2] != -1)
second = dp[n - 2];
else
second = fib(n - 2);
// Memoization
return dp[n] = first + second;
}
// Driver code
static void Main()
{
int n = 9;
Array.Fill(dp, -1);
Console.Write(fib(n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by divyeshrabadiya07.Javascript
34时间复杂度: T(n) = T(n-1) + T(n-2) 这是指数。
我们可以观察到这个实现做了很多重复的工作(见下面的递归树)。所以这是第 n 个斐波那契数的糟糕实现。
fib(5)
/ \
fib(4) fib(3)
/ \ / \
fib(3) fib(2) fib(2) fib(1)
/ \ / \ / \
fib(2) fib(1) fib(1) fib(0) fib(1) fib(0)
/ \
fib(1) fib(0)额外空间:如果我们考虑函数调用堆栈大小,则为 O(n),否则为 O(1)。
方法二(使用动态规划)
我们可以通过存储到目前为止计算的斐波那契数来避免方法 1 中所做的重复工作。
C++
// C++ program for Fibonacci Series
// using Dynamic Programming
#include
using namespace std;
class GFG{
public:
int fib(int n)
{
// Declare an array to store
// Fibonacci numbers.
// 1 extra to handle
// case, n = 0
int f[n + 2];
int i;
// 0th and 1st number of the
// series are 0 and 1
f[0] = 0;
f[1] = 1;
for(i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
//Add the previous 2 numbers
// in the series and store it
f[i] = f[i - 1] + f[i - 2];
}
return f[n];
}
};
// Driver code
int main ()
{
GFG g;
int n = 9;
cout << g.fib(n);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by SoumikMondal
C
//Fibonacci Series using Dynamic Programming
#include
int fib(int n)
{
/* Declare an array to store Fibonacci numbers. */
int f[n+2]; // 1 extra to handle case, n = 0
int i;
/* 0th and 1st number of the series are 0 and 1*/
f[0] = 0;
f[1] = 1;
for (i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
/* Add the previous 2 numbers in the series
and store it */
f[i] = f[i-1] + f[i-2];
}
return f[n];
}
int main ()
{
int n = 9;
printf("%d", fib(n));
getchar();
return 0;
}
Java
// Fibonacci Series using Dynamic Programming
class fibonacci
{
static int fib(int n)
{
/* Declare an array to store Fibonacci numbers. */
int f[] = new int[n+2]; // 1 extra to handle case, n = 0
int i;
/* 0th and 1st number of the series are 0 and 1*/
f[0] = 0;
f[1] = 1;
for (i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
/* Add the previous 2 numbers in the series
and store it */
f[i] = f[i-1] + f[i-2];
}
return f[n];
}
public static void main (String args[])
{
int n = 9;
System.out.println(fib(n));
}
}
/* This code is contributed by Rajat Mishra */
Python
# Fibonacci Series using Dynamic Programming
def fibonacci(n):
# Taking 1st two fibonacci numbers as 0 and 1
f = [0, 1]
for i in range(2, n+1):
f.append(f[i-1] + f[i-2])
return f[n]
print(fibonacci(9))
C#
// C# program for Fibonacci Series
// using Dynamic Programming
using System;
class fibonacci {
static int fib(int n)
{
// Declare an array to
// store Fibonacci numbers.
// 1 extra to handle
// case, n = 0
int []f = new int[n + 2];
int i;
/* 0th and 1st number of the
series are 0 and 1 */
f[0] = 0;
f[1] = 1;
for (i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
/* Add the previous 2 numbers
in the series and store it */
f[i] = f[i - 1] + f[i - 2];
}
return f[n];
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main ()
{
int n = 9;
Console.WriteLine(fib(n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by anuj_67.
PHP
Javascript
34方法三(空间优化方法二)
我们可以通过存储前两个数字来优化方法 2 中使用的空间,因为这就是我们获得下一个斐波那契数列所需的全部内容。
C++
// Fibonacci Series using Space Optimized Method
#include
using namespace std;
int fib(int n)
{
int a = 0, b = 1, c, i;
if( n == 0)
return a;
for(i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
c = a + b;
a = b;
b = c;
}
return b;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int n = 9;
cout << fib(n);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by Code_Mech
C
// Fibonacci Series using Space Optimized Method
#include
int fib(int n)
{
int a = 0, b = 1, c, i;
if( n == 0)
return a;
for (i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
c = a + b;
a = b;
b = c;
}
return b;
}
int main ()
{
int n = 9;
printf("%d", fib(n));
getchar();
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program for Fibonacci Series using Space
// Optimized Method
class fibonacci
{
static int fib(int n)
{
int a = 0, b = 1, c;
if (n == 0)
return a;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
c = a + b;
a = b;
b = c;
}
return b;
}
public static void main (String args[])
{
int n = 9;
System.out.println(fib(n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Mihir Joshi
Python
# Function for nth fibonacci number - Space Optimisation
# Taking 1st two fibonacci numbers as 0 and 1
def fibonacci(n):
a = 0
b = 1
if n < 0:
print("Incorrect input")
elif n == 0:
return a
elif n == 1:
return b
else:
for i in range(2,n+1):
c = a + b
a = b
b = c
return b
# Driver Program
print(fibonacci(9))
#This code is contributed by Saket Modi
C#
// C# program for Fibonacci Series
// using Space Optimized Method
using System;
namespace Fib
{
public class GFG
{
static int Fib(int n)
{
int a = 0, b = 1, c = 0;
// To return the first Fibonacci number
if (n == 0) return a;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
c = a + b;
a = b;
b = c;
}
return b;
}
// Driver function
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
int n = 9;
Console.Write("{0} ", Fib(n));
}
}
}
// This code is contributed by Sam007.
PHP
Javascript
34时间复杂度: O(n)
额外空间: O(1)
方法 4(使用矩阵 {{1, 1}, {1, 0}} 的幂)
这是另一个 O(n),它依赖于这样一个事实:如果我们将矩阵 M = {{1,1},{1,0}} 乘以 n 次(换句话说,计算 power(M, n)),那么我们得到第 (n+1) 个斐波那契数作为结果矩阵中第 (0, 0) 行和第 (0, 0) 列的元素。
矩阵表示给出了以下斐波那契数列的封闭表达式:
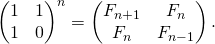
C++
#include
using namespace std;
// Helper function that multiplies 2
// matrices F and M of size 2*2, and
// puts the multiplication result
// back to F[][]
void multiply(int F[2][2], int M[2][2]);
// Helper function that calculates F[][]
// raise to the power n and puts the
// result in F[][]
// Note that this function is designed
// only for fib() and won't work as
// general power function
void power(int F[2][2], int n);
int fib(int n)
{
int F[2][2] = { { 1, 1 }, { 1, 0 } };
if (n == 0)
return 0;
power(F, n - 1);
return F[0][0];
}
void multiply(int F[2][2], int M[2][2])
{
int x = F[0][0] * M[0][0] +
F[0][1] * M[1][0];
int y = F[0][0] * M[0][1] +
F[0][1] * M[1][1];
int z = F[1][0] * M[0][0] +
F[1][1] * M[1][0];
int w = F[1][0] * M[0][1] +
F[1][1] * M[1][1];
F[0][0] = x;
F[0][1] = y;
F[1][0] = z;
F[1][1] = w;
}
void power(int F[2][2], int n)
{
int i;
int M[2][2] = { { 1, 1 }, { 1, 0 } };
// n - 1 times multiply the
// matrix to {{1,0},{0,1}}
for(i = 2; i <= n; i++)
multiply(F, M);
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int n = 9;
cout << " " << fib(n);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110
C
#include
/* Helper function that multiplies 2 matrices F and M of size 2*2, and
puts the multiplication result back to F[][] */
void multiply(int F[2][2], int M[2][2]);
/* Helper function that calculates F[][] raise to the power n and puts the
result in F[][]
Note that this function is designed only for fib() and won't work as general
power function */
void power(int F[2][2], int n);
int fib(int n)
{
int F[2][2] = {{1,1},{1,0}};
if (n == 0)
return 0;
power(F, n-1);
return F[0][0];
}
void multiply(int F[2][2], int M[2][2])
{
int x = F[0][0]*M[0][0] + F[0][1]*M[1][0];
int y = F[0][0]*M[0][1] + F[0][1]*M[1][1];
int z = F[1][0]*M[0][0] + F[1][1]*M[1][0];
int w = F[1][0]*M[0][1] + F[1][1]*M[1][1];
F[0][0] = x;
F[0][1] = y;
F[1][0] = z;
F[1][1] = w;
}
void power(int F[2][2], int n)
{
int i;
int M[2][2] = {{1,1},{1,0}};
// n - 1 times multiply the matrix to {{1,0},{0,1}}
for (i = 2; i <= n; i++)
multiply(F, M);
}
/* Driver program to test above function */
int main()
{
int n = 9;
printf("%d", fib(n));
getchar();
return 0;
}
Java
class fibonacci
{
static int fib(int n)
{
int F[][] = new int[][]{{1,1},{1,0}};
if (n == 0)
return 0;
power(F, n-1);
return F[0][0];
}
/* Helper function that multiplies 2 matrices F and M of size 2*2, and
puts the multiplication result back to F[][] */
static void multiply(int F[][], int M[][])
{
int x = F[0][0]*M[0][0] + F[0][1]*M[1][0];
int y = F[0][0]*M[0][1] + F[0][1]*M[1][1];
int z = F[1][0]*M[0][0] + F[1][1]*M[1][0];
int w = F[1][0]*M[0][1] + F[1][1]*M[1][1];
F[0][0] = x;
F[0][1] = y;
F[1][0] = z;
F[1][1] = w;
}
/* Helper function that calculates F[][] raise to the power n and puts the
result in F[][]
Note that this function is designed only for fib() and won't work as general
power function */
static void power(int F[][], int n)
{
int i;
int M[][] = new int[][]{{1,1},{1,0}};
// n - 1 times multiply the matrix to {{1,0},{0,1}}
for (i = 2; i <= n; i++)
multiply(F, M);
}
/* Driver program to test above function */
public static void main (String args[])
{
int n = 9;
System.out.println(fib(n));
}
}
/* This code is contributed by Rajat Mishra */
蟒蛇3
# Helper function that multiplies
# 2 matrices F and M of size 2*2,
# and puts the multiplication
# result back to F[][]
# Helper function that calculates
# F[][] raise to the power n and
# puts the result in F[][]
# Note that this function is
# designed only for fib() and
# won't work as general
# power function
def fib(n):
F = [[1, 1],
[1, 0]]
if (n == 0):
return 0
power(F, n - 1)
return F[0][0]
def multiply(F, M):
x = (F[0][0] * M[0][0] +
F[0][1] * M[1][0])
y = (F[0][0] * M[0][1] +
F[0][1] * M[1][1])
z = (F[1][0] * M[0][0] +
F[1][1] * M[1][0])
w = (F[1][0] * M[0][1] +
F[1][1] * M[1][1])
F[0][0] = x
F[0][1] = y
F[1][0] = z
F[1][1] = w
def power(F, n):
M = [[1, 1],
[1, 0]]
# n - 1 times multiply the
# matrix to {{1,0},{0,1}}
for i in range(2, n + 1):
multiply(F, M)
# Driver Code
if __name__ == "__main__":
n = 9
print(fib(n))
# This code is contributed
# by ChitraNayal
C#
using System;
class GFG {
static int fib(int n)
{
int [,]F = new int[,] {{1, 1},
{1, 0} };
if (n == 0)
return 0;
power(F, n-1);
return F[0,0];
}
/* Helper function that multiplies 2
matrices F and M of size 2*2, and puts
the multiplication result back to F[][] */
static void multiply(int [,]F, int [,]M)
{
int x = F[0,0]*M[0,0] + F[0,1]*M[1,0];
int y = F[0,0]*M[0,1] + F[0,1]*M[1,1];
int z = F[1,0]*M[0,0] + F[1,1]*M[1,0];
int w = F[1,0]*M[0,1] + F[1,1]*M[1,1];
F[0,0] = x;
F[0,1] = y;
F[1,0] = z;
F[1,1] = w;
}
/* Helper function that calculates F[][]
raise to the power n and puts the result
in F[][] Note that this function is designed
only for fib() and won't work as general
power function */
static void power(int [,]F, int n)
{
int i;
int [,]M = new int[,]{{1, 1},
{1, 0} };
// n - 1 times multiply the matrix to
// {{1,0},{0,1}}
for (i = 2; i <= n; i++)
multiply(F, M);
}
/* Driver program to test above function */
public static void Main ()
{
int n = 9;
Console.WriteLine(fib(n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by anuj_67.
PHP
Javascript
34时间复杂度: O(n)
额外空间: O(1)
方法五(优化方法四)
方法 4 可以优化为 O(Logn) 时间复杂度。我们可以在之前的方法中进行递归乘法来获得 power(M, n) (类似于本文中所做的优化)
C++
// Fibonacci Series using Optimized Method
#include
using namespace std;
void multiply(int F[2][2], int M[2][2]);
void power(int F[2][2], int n);
// Function that returns nth Fibonacci number
int fib(int n)
{
int F[2][2] = {{1, 1}, {1, 0}};
if (n == 0)
return 0;
power(F, n - 1);
return F[0][0];
}
// Optimized version of power() in method 4
void power(int F[2][2], int n)
{
if(n == 0 || n == 1)
return;
int M[2][2] = {{1, 1}, {1, 0}};
power(F, n / 2);
multiply(F, F);
if (n % 2 != 0)
multiply(F, M);
}
void multiply(int F[2][2], int M[2][2])
{
int x = F[0][0] * M[0][0] + F[0][1] * M[1][0];
int y = F[0][0] * M[0][1] + F[0][1] * M[1][1];
int z = F[1][0] * M[0][0] + F[1][1] * M[1][0];
int w = F[1][0] * M[0][1] + F[1][1] * M[1][1];
F[0][0] = x;
F[0][1] = y;
F[1][0] = z;
F[1][1] = w;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int n = 9;
cout << fib(9);
getchar();
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by Nidhi_biet
C
#include
void multiply(int F[2][2], int M[2][2]);
void power(int F[2][2], int n);
/* function that returns nth Fibonacci number */
int fib(int n)
{
int F[2][2] = {{1,1},{1,0}};
if (n == 0)
return 0;
power(F, n-1);
return F[0][0];
}
/* Optimized version of power() in method 4 */
void power(int F[2][2], int n)
{
if( n == 0 || n == 1)
return;
int M[2][2] = {{1,1},{1,0}};
power(F, n/2);
multiply(F, F);
if (n%2 != 0)
multiply(F, M);
}
void multiply(int F[2][2], int M[2][2])
{
int x = F[0][0]*M[0][0] + F[0][1]*M[1][0];
int y = F[0][0]*M[0][1] + F[0][1]*M[1][1];
int z = F[1][0]*M[0][0] + F[1][1]*M[1][0];
int w = F[1][0]*M[0][1] + F[1][1]*M[1][1];
F[0][0] = x;
F[0][1] = y;
F[1][0] = z;
F[1][1] = w;
}
/* Driver program to test above function */
int main()
{
int n = 9;
printf("%d", fib(9));
getchar();
return 0;
}
Java
//Fibonacci Series using Optimized Method
class fibonacci
{
/* function that returns nth Fibonacci number */
static int fib(int n)
{
int F[][] = new int[][]{{1,1},{1,0}};
if (n == 0)
return 0;
power(F, n-1);
return F[0][0];
}
static void multiply(int F[][], int M[][])
{
int x = F[0][0]*M[0][0] + F[0][1]*M[1][0];
int y = F[0][0]*M[0][1] + F[0][1]*M[1][1];
int z = F[1][0]*M[0][0] + F[1][1]*M[1][0];
int w = F[1][0]*M[0][1] + F[1][1]*M[1][1];
F[0][0] = x;
F[0][1] = y;
F[1][0] = z;
F[1][1] = w;
}
/* Optimized version of power() in method 4 */
static void power(int F[][], int n)
{
if( n == 0 || n == 1)
return;
int M[][] = new int[][]{{1,1},{1,0}};
power(F, n/2);
multiply(F, F);
if (n%2 != 0)
multiply(F, M);
}
/* Driver program to test above function */
public static void main (String args[])
{
int n = 9;
System.out.println(fib(n));
}
}
/* This code is contributed by Rajat Mishra */
蟒蛇3
# Fibonacci Series using
# Optimized Method
# function that returns nth
# Fibonacci number
def fib(n):
F = [[1, 1],
[1, 0]]
if (n == 0):
return 0
power(F, n - 1)
return F[0][0]
def multiply(F, M):
x = (F[0][0] * M[0][0] +
F[0][1] * M[1][0])
y = (F[0][0] * M[0][1] +
F[0][1] * M[1][1])
z = (F[1][0] * M[0][0] +
F[1][1] * M[1][0])
w = (F[1][0] * M[0][1] +
F[1][1] * M[1][1])
F[0][0] = x
F[0][1] = y
F[1][0] = z
F[1][1] = w
# Optimized version of
# power() in method 4
def power(F, n):
if( n == 0 or n == 1):
return;
M = [[1, 1],
[1, 0]];
power(F, n // 2)
multiply(F, F)
if (n % 2 != 0):
multiply(F, M)
# Driver Code
if __name__ == "__main__":
n = 9
print(fib(n))
# This code is contributed
# by ChitraNayal
C#
// Fibonacci Series using
// Optimized Method
using System;
class GFG
{
/* function that returns
nth Fibonacci number */
static int fib(int n)
{
int[,] F = new int[,]{{1, 1},
{1, 0}};
if (n == 0)
return 0;
power(F, n - 1);
return F[0, 0];
}
static void multiply(int[,] F,
int[,] M)
{
int x = F[0, 0] * M[0, 0] +
F[0, 1] * M[1, 0];
int y = F[0, 0] * M[0, 1] +
F[0, 1] * M[1, 1];
int z = F[1, 0] * M[0, 0] +
F[1, 1] * M[1, 0];
int w = F[1, 0] * M[0, 1] +
F[1, 1] * M[1, 1];
F[0, 0] = x;
F[0, 1] = y;
F[1, 0] = z;
F[1, 1] = w;
}
/* Optimized version of
power() in method 4 */
static void power(int[,] F, int n)
{
if( n == 0 || n == 1)
return;
int[,] M = new int[,]{{1, 1},
{1, 0}};
power(F, n / 2);
multiply(F, F);
if (n % 2 != 0)
multiply(F, M);
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main ()
{
int n = 9;
Console.Write(fib(n));
}
}
// This code is contributed
// by ChitraNayal
Javascript
34时间复杂度: O(Logn)
额外空间:如果我们考虑函数调用堆栈大小,则为 O(Logn),否则为 O(1)。
方法 6(O(Log n) 时间)
下面是一个更有趣的递归公式,可用于在 O(Log n) 时间内找到第 n 个斐波那契数。
If n is even then k = n/2:
F(n) = [2*F(k-1) + F(k)]*F(k)
If n is odd then k = (n + 1)/2
F(n) = F(k)*F(k) + F(k-1)*F(k-1)这个公式是如何工作的?
该公式可以从上述矩阵方程推导出来。
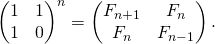
Taking determinant on both sides, we get
(-1)n = Fn+1Fn-1 - Fn2
Moreover, since AnAm = An+m for any square matrix A,
the following identities can be derived (they are obtained
form two different coefficients of the matrix product)
FmFn + Fm-1Fn-1 = Fm+n-1 ---------------------------(1)
By putting n = n+1 in equation(1),
FmFn+1 + Fm-1Fn = Fm+n --------------------------(2)
Putting m = n in equation(1).
F2n-1 = Fn2 + Fn-12
Putting m = n in equation(2)
F2n = (Fn-1 + Fn+1)Fn = (2Fn-1 + Fn)Fn (Source: Wiki) --------
( By putting Fn+1 = Fn + Fn-1 )
To get the formula to be proved, we simply need to do the following
If n is even, we can put k = n/2
If n is odd, we can put k = (n+1)/2下面是上述想法的实现。
C++
// C++ Program to find n'th fibonacci Number in
// with O(Log n) arithmetic operations
#include
using namespace std;
const int MAX = 1000;
// Create an array for memoization
int f[MAX] = {0};
// Returns n'th fibonacci number using table f[]
int fib(int n)
{
// Base cases
if (n == 0)
return 0;
if (n == 1 || n == 2)
return (f[n] = 1);
// If fib(n) is already computed
if (f[n])
return f[n];
int k = (n & 1)? (n+1)/2 : n/2;
// Applying above formula [Note value n&1 is 1
// if n is odd, else 0.
f[n] = (n & 1)? (fib(k)*fib(k) + fib(k-1)*fib(k-1))
: (2*fib(k-1) + fib(k))*fib(k);
return f[n];
}
/* Driver program to test above function */
int main()
{
int n = 9;
printf("%d ", fib(n));
return 0;
}
Java
// Java Program to find n'th fibonacci
// Number with O(Log n) arithmetic operations
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
static int MAX = 1000;
static int f[];
// Returns n'th fibonacci number using
// table f[]
public static int fib(int n)
{
// Base cases
if (n == 0)
return 0;
if (n == 1 || n == 2)
return (f[n] = 1);
// If fib(n) is already computed
if (f[n] != 0)
return f[n];
int k = (n & 1) == 1? (n + 1) / 2
: n / 2;
// Applying above formula [Note value
// n&1 is 1 if n is odd, else 0.
f[n] = (n & 1) == 1? (fib(k) * fib(k) +
fib(k - 1) * fib(k - 1))
: (2 * fib(k - 1) + fib(k))
* fib(k);
return f[n];
}
/* Driver program to test above function */
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int n = 9;
f= new int[MAX];
System.out.println(fib(n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Arnav Kr. Mandal.
Python
# Python3 Program to find n'th fibonacci Number in
# with O(Log n) arithmetic operations
MAX = 1000
# Create an array for memoization
f = [0] * MAX
# Returns n'th fibonacci number using table f[]
def fib(n) :
# Base cases
if (n == 0) :
return 0
if (n == 1 or n == 2) :
f[n] = 1
return (f[n])
# If fib(n) is already computed
if (f[n]) :
return f[n]
if( n & 1) :
k = (n + 1) // 2
else :
k = n // 2
# Applying above formula [Note value n&1 is 1
# if n is odd, else 0.
if((n & 1) ) :
f[n] = (fib(k) * fib(k) + fib(k-1) * fib(k-1))
else :
f[n] = (2*fib(k-1) + fib(k))*fib(k)
return f[n]
# Driver code
n = 9
print(fib(n))
# This code is contributed by Nikita Tiwari.
C#
// C# Program to find n'th
// fibonacci Number with
// O(Log n) arithmetic operations
using System;
class GFG
{
static int MAX = 1000;
static int[] f;
// Returns n'th fibonacci
// number using table f[]
public static int fib(int n)
{
// Base cases
if (n == 0)
return 0;
if (n == 1 || n == 2)
return (f[n] = 1);
// If fib(n) is already
// computed
if (f[n] != 0)
return f[n];
int k = (n & 1) == 1 ? (n + 1) / 2
: n / 2;
// Applying above formula
// [Note value n&1 is 1 if
// n is odd, else 0.
f[n] = (n & 1) == 1 ? (fib(k) * fib(k) +
fib(k - 1) * fib(k - 1))
: (2 * fib(k - 1) + fib(k)) *
fib(k);
return f[n];
}
// Driver Code
static void Main()
{
int n = 9;
f = new int[MAX];
Console.WriteLine(fib(n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by mits
PHP
Javascript
34该解决方案的时间复杂度为 O(Log n),因为我们在每次递归调用中将问题一分为二。
方法七
另一种方法(使用公式):
在这种方法中,我们直接实现了斐波那契数列中第 n 项的公式。
F n = {[(√5 + 1)/2] ^ n} / √5
参考:http://www.maths.surrey.ac.uk/hosted-sites/R.Knott/Fibonacci/fibFormula.html
C++
// C++ Program to find n'th fibonacci Number
#include
#include
int fib(int n) {
double phi = (1 + sqrt(5)) / 2;
return round(pow(phi, n) / sqrt(5));
}
// Driver Code
int main ()
{
int n = 9;
std::cout << fib(n) << std::endl;
return 0;
}
//This code is contributed by Lokesh Mohanty.
C
// C Program to find n'th fibonacci Number
#include
#include
int fib(int n) {
double phi = (1 + sqrt(5)) / 2;
return round(pow(phi, n) / sqrt(5));
}
int main ()
{
int n = 9;
printf("%d", fib(n));
return 0;
}
Java
// Java Program to find n'th fibonacci Number
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
static int fib(int n) {
double phi = (1 + Math.sqrt(5)) / 2;
return (int) Math.round(Math.pow(phi, n)
/ Math.sqrt(5));
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = 9;
System.out.println(fib(n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by PrinciRaj1992
蟒蛇3
# Python3 program to find n'th
# fibonacci Number
import math
def fibo(n):
phi = (1 + math.sqrt(5)) / 2
return round(pow(phi, n) / math.sqrt(5))
# Driver code
if __name__ == '__main__':
n = 9
print(fibo(n))
# This code is contributed by prasun_parate
C#
// C# Program to find n'th fibonacci Number
using System;
public class GFG
{
static int fib(int n)
{
double phi = (1 + Math.Sqrt(5)) / 2;
return (int) Math.Round(Math.Pow(phi, n)
/ Math.Sqrt(5));
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
int n = 9;
Console.WriteLine(fib(n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar
PHP
Javascript
34时间复杂度: O(logn),这是因为计算phi^n需要logn时间
空间复杂度: O(1)
方法八
DP 使用记忆化(自上而下的方法)
我们可以通过存储到目前为止计算的斐波那契数来避免方法 1 中所做的重复工作。我们只需要将所有值存储在一个数组中。
C++
#include
using namespace std;
int dp[10];
int fib(int n)
{
if (n <= 1)
return n;
// temporary variables to store
// values of fib(n-1) & fib(n-2)
int first, second;
if (dp[n - 1] != -1)
first = dp[n - 1];
else
first = fib(n - 1);
if (dp[n - 2] != -1)
second = dp[n - 2];
else
second = fib(n - 2);
// memoization
return dp[n] = first + second;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int n = 9;
memset(dp, -1, sizeof(dp));
cout << fib(n);
getchar();
return 0;
// This code is contributed by Bhavneet Singh
}
Java
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Initialize array of dp
static int[] dp = new int[10];
static int fib(int n)
{
if (n <= 1)
return n;
// Temporary variables to store
// values of fib(n-1) & fib(n-2)
int first, second;
if (dp[n - 1] != -1)
first = dp[n - 1];
else
first = fib(n - 1);
if (dp[n - 2] != -1)
second = dp[n - 2];
else
second = fib(n - 2);
// Memoization
return dp[n] = first + second;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int n = 9;
Arrays.fill(dp, -1);
System.out.print(fib(n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by sujitmeshram
蟒蛇3
# Initialize array of dp
dp = [-1 for i in range(10)]
def fib(n):
if (n <= 1):
return n;
global dp;
# Temporary variables to store
# values of fib(n-1) & fib(n-2)
first = 0;
second = 0;
if (dp[n - 1] != -1):
first = dp[n - 1];
else:
first = fib(n - 1);
if (dp[n - 2] != -1):
second = dp[n - 2];
else:
second = fib(n - 2);
dp[n] = first + second;
# Memoization
return dp[n] ;
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
n = 9;
print(fib(n));
# This code contributed by Rajput-Ji
C#
using System;
class GFG {
// Initialize array of dp
static int[] dp = new int[10];
static int fib(int n)
{
if (n <= 1)
return n;
// Temporary variables to store
// values of fib(n-1) & fib(n-2)
int first, second;
if (dp[n - 1] != -1)
first = dp[n - 1];
else
first = fib(n - 1);
if (dp[n - 2] != -1)
second = dp[n - 2];
else
second = fib(n - 2);
// Memoization
return dp[n] = first + second;
}
// Driver code
static void Main()
{
int n = 9;
Array.Fill(dp, -1);
Console.Write(fib(n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by divyeshrabadiya07.
Javascript
34 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LwZRsM7qhrI
该方法由 Chirag Agarwal 贡献。
参考:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fibonacci_number
http://www.ics.uci.edu/~eppstein/161/960109.html
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。