给定一个大小为N的数组A[] ,找到最大异或子序列,使得A [ i ]和A [ N – i – 1 ] 都属于这个子序列,其中 i 的范围在[0, N – 1] 之间。
例子:
Input: N = 8, A [ ] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8}
Output: 13
Explanation:
Maximum Xor Subsequence is {1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8}
Input: N = 5, A [ ] = {3, 2, 6, 5, 4}
Output: 6
Explanation:
Maximum Xor Subsequence is {3, 2, 6, 5, 4}
方法:
因为 A[i] 和 A[Ni-1] 都应该出现在同一个子序列中,所以将它们配对,然后找到最大的异或和。对于每个有效索引i ,计算 (A[i] ^ A[Ni-1]) 并将其存储在新数组X 中。这个新数组的大小将为 N/2。
天真的解决方案:
对于这个问题,创建数组X[]后最简单的方法是递归生成X 的所有子序列,并找到最大的异或子序列。
以下是 maxXorSubseq(X, N, i) 的递归定义:
maxXorSubseq ( X, N, i ) = MAX ( X[ i ] ^ maxXorSubseq ( X, N, i + 1 ), maxXorSubseq (X, N, i + 1) )
可能的组合总数为2 N 。
时间复杂度: O(2 N )
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ implementation
// of the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Returns maximum xor
int maxXorSubseq(vector &x, int n,
int i)
{
if(i == n)
return 0;
return max(x[i] ^ maxXorSubseq(x, n,
i + 1),
maxXorSubseq(x, n,
i + 1));
}
vector compute(vector a, int n)
{
vector x;
// Calculate a[i]^a[n-i-1]
for(int i = 0; i < n / 2; i++)
x.push_back(a[i] ^ a[n - i - 1]);
// If n is odd
if(n & 1)
x.push_back(a[n / 2]);
return x;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int n = 8;
vector a = { 1, 2, 3, 4,
5, 6, 7, 8 };
// Getting new array x
vector x = compute(a, n);
int mxXor = maxXorSubseq(x, x.size(), 0);
cout << (mxXor);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29 Java
// Java implementation
// of the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Returns maximum xor
static int maxXorSubseq(List x, int n,
int i)
{
if(i == n)
return 0;
return Math.max(x.get(i) ^ maxXorSubseq(x, n,
i + 1),
maxXorSubseq(x, n,
i + 1));
}
static List compute(List a, int n)
{
List x = new ArrayList();
// Calculate a[i]^a[n-i-1]
for(int i = 0; i < n / 2; i++)
x.add(a.get(i) ^ a.get(n - i - 1));
// If n is odd
if((n & 1) == 1)
x.add(a.get(n / 2));
return x;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int n = 8;
List a = Arrays.asList( 1, 2, 3, 4,
5, 6, 7, 8 );
// Getting new array x
List x = compute(a, n);
int mxXor = maxXorSubseq(x, x.size(), 0);
System.out.println((mxXor));
}
}
// This code is contributed by offbeat Python3
# Python3 implementation
# of the above approach
# Returns maximum xor
def maxXorSubseq(x, n, i):
if(i == n):
return 0
return max(
x[i]^maxXorSubseq(
x, n, i + 1), maxXorSubseq(
x, n, i + 1))
def compute(a, n):
x = []
# Calculate a[i]^a[n-i-1]
for i in range(n//2):
x.append(a[i]^a[n-i-1])
# If n is odd
if(n&1):
x.append(a[n//2])
return x
# Driver code
if __name__ =="__main__":
n = 8
a = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]
# Getting new array x
x = compute(a, n)
mxXor = maxXorSubseq(x, len(x), 0)
print(mxXor)C#
// C# implementation
// of the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG {
// Returns maximum xor
static int maxXorSubseq(List x, int n, int i)
{
if(i == n)
return 0;
return Math.Max(x[i] ^ maxXorSubseq(x, n, i + 1), maxXorSubseq(x, n, i + 1));
}
static List compute(List a, int n)
{
List x = new List();
// Calculate a[i]^a[n-i-1]
for(int i = 0; i < n / 2; i++)
x.Add(a[i] ^ a[n - i - 1]);
// If n is odd
if((n & 1) == 1)
x.Add(a[n / 2]);
return x;
}
static void Main() {
int n = 8;
List a = new List{ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 };
// Getting new array x
List x = compute(a, n);
int mxXor = maxXorSubseq(x, x.Count, 0);
Console.WriteLine((mxXor));
}
}
// This code is contributed by divyeshrabadiya07 Javascript
C++
// C++ implementation of the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
vector dp;
// Returns maximum xor sum
int maxXorSubseq(vector x, int n, int idx)
{
if (idx == n)
{
return 0;
}
// If already precomputed
if (dp[idx] != -1)
{
return dp[idx];
}
int ans = 0;
ans = max(ans, x[idx] ^ maxXorSubseq(x, n, idx + 1));
ans = max(ans, maxXorSubseq(x, n, idx + 1));
// Store the maximum
dp[idx] = ans;
return ans;
}
vector compute(int a[],int n)
{
vector x;
// Calculate a[i]^a[n-i-1]
for(int i = 0; i < n / 2; i++)
{
x.push_back(a[i] ^ a[n - i - 1]);
}
// If n is odd
if ((n & 1) != 0)
{
x.push_back(a[n / 2]);
}
return x;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int n = 8;
int a[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 };
// Getting new array x
vector x = compute(a, n);
// Initialize dp array
for(int i = 0; i < x.size(); i++)
{
dp.push_back(-1);
}
int mxXor = maxXorSubseq(x, x.size(), 0);
cout << mxXor << endl;
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by divyesh072019. Java
// Java implementation of the above approach
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static Vector dp = new Vector();
// Returns maximum xor sum
static int maxXorSubseq(Vector x,
int n, int idx)
{
if (idx == n)
{
return 0;
}
// If already precomputed
if (dp.get(idx) != -1)
{
return dp.get(idx);
}
int ans = 0;
ans = Math.max(ans, x.get(idx) ^
maxXorSubseq(x, n, idx + 1));
ans = Math.max(ans,
maxXorSubseq(x, n, idx + 1));
// Store the maximum
dp.set(idx,ans);
return ans;
}
static Vector compute(int[] a,int n)
{
Vector x = new Vector();
// Calculate a[i]^a[n-i-1]
for(int i = 0; i < n / 2; i++)
{
x.add(a[i] ^ a[n - i - 1]);
}
// If n is odd
if ((n & 1) != 0)
{
x.add(a[n / 2]);
}
return x;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int n = 8;
int[] a = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 };
// Getting new array x
Vector x = compute(a, n);
// Initialize dp array
for(int i = 0; i < x.size(); i++)
{
dp.add(-1);
}
int mxXor = maxXorSubseq(x, x.size(), 0);
System.out.println(mxXor);
}
}
// This code is contributed by avanitrachhadiya2155 Python3
# Python3 implementation
# of the above approach
# Returns maximum xor sum
def maxXorSubseq(x, n, idx):
if(idx == n):
return 0
# If already precomputed
if(dp[idx]!=-1):
return dp[idx]
ans = 0
ans = max(
ans, x[idx] ^ maxXorSubseq(
x, n, idx + 1))
ans = max(ans, maxXorSubseq(
x, n, idx + 1))
# Store the maximum
dp[idx] = ans
return ans
def compute(a, n):
x = []
# Calculate a[i]^a[n-i-1]
for i in range(n//2):
x.append(a[i]^a[n-i-1])
# If n is odd
if(n&1):
x.append(a[n//2])
return x
# Declared dp[] array globally
dp = []
# Driver code
if __name__ =="__main__":
n = 8
a =[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]
# Getting new array x
x = compute(a, n)
# Initialize dp array
dp = [-1 for i in range(len(x))]
mxXor = maxXorSubseq(x, len(x), 0)
print(mxXor)C#
// C# implementation of the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
static List dp = new List();
// Returns maximum xor sum
static int maxXorSubseq(List x, int n, int idx)
{
if (idx == n)
{
return 0;
}
// If already precomputed
if(dp[idx] != -1)
{
return dp[idx];
}
int ans = 0;
ans = Math.Max(ans, x[idx]^maxXorSubseq(x, n, idx + 1));
ans = Math.Max(ans, maxXorSubseq(x, n, idx + 1));
// Store the maximum
dp[idx] = ans;
return ans;
}
static List compute(int[] a,int n)
{
List x = new List();
// Calculate a[i]^a[n-i-1]
for(int i = 0; i < n / 2; i++)
{
x.Add(a[i] ^ a[n - i - 1]);
}
// If n is odd
if((n & 1) != 0)
{
x.Add(a[n / 2]);
}
return x;
}
// Driver code
static public void Main ()
{
int n = 8;
int[] a = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 };
// Getting new array x
List x = compute(a, n);
// Initialize dp array
for(int i = 0; i < x.Count; i++)
{
dp.Add(-1);
}
int mxXor = maxXorSubseq(x, x.Count, 0);
Console.WriteLine(mxXor);
}
}
// This code is contributed by rag2127 Javascript
13有效的方法:
考虑到上面的实现,下面是输入X = [9, 5, 1]的部分递归树
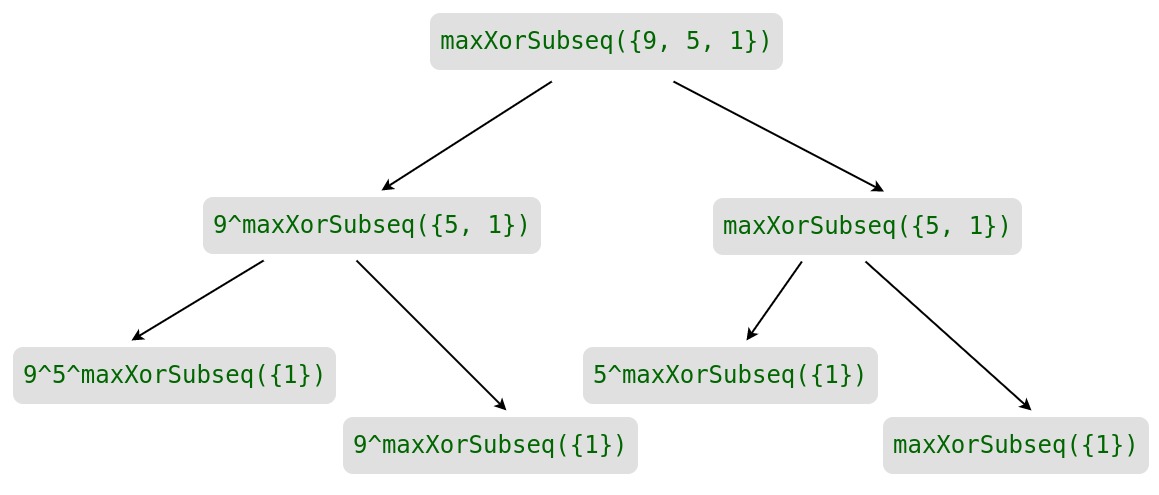
在上面的部分递归树中,maxXorSubseq({1}) 被求解了四次。在绘制完整的递归树时,可以观察到有许多子问题被一次又一次地解决。所以这个问题有重叠的子问题,使用Memoization可以避免相同子问题的重新计算。
为了记忆,创建一个数组dp [ ]数组并存储:
dp[i] = max(x[i] ^ maxXorSubseq(x, n, i + 1), maxXorSubseq(x, n, idx + 1)
这避免了对先前计算的索引的重新计算,从而优化了计算复杂度。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ implementation of the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
vector dp;
// Returns maximum xor sum
int maxXorSubseq(vector x, int n, int idx)
{
if (idx == n)
{
return 0;
}
// If already precomputed
if (dp[idx] != -1)
{
return dp[idx];
}
int ans = 0;
ans = max(ans, x[idx] ^ maxXorSubseq(x, n, idx + 1));
ans = max(ans, maxXorSubseq(x, n, idx + 1));
// Store the maximum
dp[idx] = ans;
return ans;
}
vector compute(int a[],int n)
{
vector x;
// Calculate a[i]^a[n-i-1]
for(int i = 0; i < n / 2; i++)
{
x.push_back(a[i] ^ a[n - i - 1]);
}
// If n is odd
if ((n & 1) != 0)
{
x.push_back(a[n / 2]);
}
return x;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int n = 8;
int a[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 };
// Getting new array x
vector x = compute(a, n);
// Initialize dp array
for(int i = 0; i < x.size(); i++)
{
dp.push_back(-1);
}
int mxXor = maxXorSubseq(x, x.size(), 0);
cout << mxXor << endl;
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by divyesh072019.
Java
// Java implementation of the above approach
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static Vector dp = new Vector();
// Returns maximum xor sum
static int maxXorSubseq(Vector x,
int n, int idx)
{
if (idx == n)
{
return 0;
}
// If already precomputed
if (dp.get(idx) != -1)
{
return dp.get(idx);
}
int ans = 0;
ans = Math.max(ans, x.get(idx) ^
maxXorSubseq(x, n, idx + 1));
ans = Math.max(ans,
maxXorSubseq(x, n, idx + 1));
// Store the maximum
dp.set(idx,ans);
return ans;
}
static Vector compute(int[] a,int n)
{
Vector x = new Vector();
// Calculate a[i]^a[n-i-1]
for(int i = 0; i < n / 2; i++)
{
x.add(a[i] ^ a[n - i - 1]);
}
// If n is odd
if ((n & 1) != 0)
{
x.add(a[n / 2]);
}
return x;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int n = 8;
int[] a = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 };
// Getting new array x
Vector x = compute(a, n);
// Initialize dp array
for(int i = 0; i < x.size(); i++)
{
dp.add(-1);
}
int mxXor = maxXorSubseq(x, x.size(), 0);
System.out.println(mxXor);
}
}
// This code is contributed by avanitrachhadiya2155
蟒蛇3
# Python3 implementation
# of the above approach
# Returns maximum xor sum
def maxXorSubseq(x, n, idx):
if(idx == n):
return 0
# If already precomputed
if(dp[idx]!=-1):
return dp[idx]
ans = 0
ans = max(
ans, x[idx] ^ maxXorSubseq(
x, n, idx + 1))
ans = max(ans, maxXorSubseq(
x, n, idx + 1))
# Store the maximum
dp[idx] = ans
return ans
def compute(a, n):
x = []
# Calculate a[i]^a[n-i-1]
for i in range(n//2):
x.append(a[i]^a[n-i-1])
# If n is odd
if(n&1):
x.append(a[n//2])
return x
# Declared dp[] array globally
dp = []
# Driver code
if __name__ =="__main__":
n = 8
a =[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]
# Getting new array x
x = compute(a, n)
# Initialize dp array
dp = [-1 for i in range(len(x))]
mxXor = maxXorSubseq(x, len(x), 0)
print(mxXor)
C#
// C# implementation of the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
static List dp = new List();
// Returns maximum xor sum
static int maxXorSubseq(List x, int n, int idx)
{
if (idx == n)
{
return 0;
}
// If already precomputed
if(dp[idx] != -1)
{
return dp[idx];
}
int ans = 0;
ans = Math.Max(ans, x[idx]^maxXorSubseq(x, n, idx + 1));
ans = Math.Max(ans, maxXorSubseq(x, n, idx + 1));
// Store the maximum
dp[idx] = ans;
return ans;
}
static List compute(int[] a,int n)
{
List x = new List();
// Calculate a[i]^a[n-i-1]
for(int i = 0; i < n / 2; i++)
{
x.Add(a[i] ^ a[n - i - 1]);
}
// If n is odd
if((n & 1) != 0)
{
x.Add(a[n / 2]);
}
return x;
}
// Driver code
static public void Main ()
{
int n = 8;
int[] a = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 };
// Getting new array x
List x = compute(a, n);
// Initialize dp array
for(int i = 0; i < x.Count; i++)
{
dp.Add(-1);
}
int mxXor = maxXorSubseq(x, x.Count, 0);
Console.WriteLine(mxXor);
}
}
// This code is contributed by rag2127
Javascript
13时间复杂度: O(N)
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。