给定文本和通配符模式,查找通配符模式是否与文本匹配。匹配应涵盖整个文本(而不是部分文本)。
通配符模式可以包含字符“?”和 ‘*’:
- ‘? – 匹配任何单个字符
- ‘*’ – 匹配任何字符序列(包括空序列)
先决条件:动态规划|通配符模式匹配
例子:
Text = "baaabab",
Pattern = “*****ba*****ab", output : true
Pattern = "baaa?ab", output : true
Pattern = "ba*a?", output : true
Pattern = "a*ab", output : false 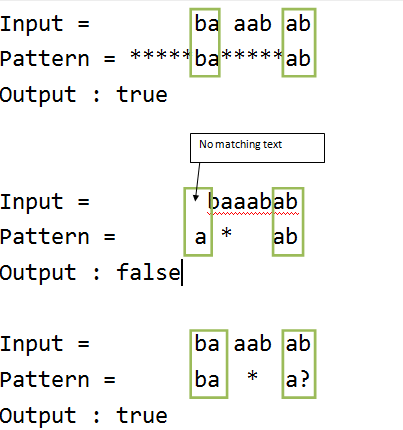
每次出现“?”通配符模式中的字符可以替换为任何其他字符,并且每次出现的 ‘*’ 都带有一个字符序列,这样通配符模式在替换后变得与输入字符串相同。
我们在这里讨论了一个具有 O(mxn) 时间和 O(mxn) 空间复杂度的解决方案。
为了应用优化,我们首先要注意BASE CASE ,它表示,如果模式的长度为零,那么仅当我们必须匹配模式的文本长度也为零时,答案才会为真。
算法:
- 让 i 成为指向文本当前字符的标记。
让 j 成为指向模式当前字符的标记。
让 index_txt 成为指向我们在模式中遇到 ‘*’ 的文本字符的标记。
让 index_pat 成为指向模式中“*”位置的标记。 - 在任何时候,如果我们观察到 txt[i] == pat[j],那么我们同时增加 i 和 j,因为在这种情况下不需要执行任何操作。
- 如果我们遇到 pat[j] == ‘?’,那么它类似于步骤 – (2) 中提到的情况为 ‘?’具有与任何单个字符匹配的属性。
- 如果我们遇到 pat[j] == ‘*’,那么我们更新 index_txt 和 index_pat 的值,因为 ‘*’ 具有匹配任何字符序列(包括空序列)的属性,我们会将 j 的值增加到将模式的下一个字符与文本的当前字符进行比较。 (由于 i 所代表的字符尚未得到答复)。
- 现在如果 txt[i] == pat[j],并且我们之前遇到过 ‘*’,那么这意味着 ‘*’ 包含空序列,否则如果 txt[i] != pat[j],一个字符需要由 ‘*’ 提供,以便进行当前字符匹配,然后 i 需要在现在回答时递增,但仍需要回答 j 表示的字符,因此,j = index_pat + 1, i = index_txt + 1(因为 ‘*’ 也可以捕获其他字符),index_txt++(因为匹配文本中的当前字符)。
- 如果步骤 – (5) 无效,则意味着 txt[i] != pat[j],我们也没有遇到 ‘*’,这意味着模式不可能匹配字符串。 (返回假)。
- 检查 j 是否达到其最终值,然后返回最终答案。
让我们看看上面的算法在运行,然后我们将进入编码部分:
文字 = “baaabab”
模式=“*****ba*****ab”
现在应用算法
步骤 – (1) : i = 0 (i –> ‘b’)
j = 0 (j –> ‘*’)
index_txt = -1
index_pat = -1
注意:循环会一直运行直到我到达它的最终
值或答案在中途变为错误。
第一次比较:-
正如我们在这里看到的 pat[j] == ‘*’,因此直接跳到步骤 – (4)。
步骤 – (4) : index_txt = i (index_txt –> ‘b’)
index_pat = j (index_pat –> ‘*’)
j++ (j –> ‘*’)
再进行四次比较后:i = 0 (i –> ‘b’)
j = 5 (j –> ‘b’)
index_txt = 0 (index_txt –> ‘b’)
index_pat = 4 (index_pat –> ‘*’)
第六次比较:-
正如我们在这里看到的 txt[i] == pat[j],但我们已经遇到了 ‘*’,因此使用步骤 – (5)。
步骤 – (5) : i = 1 (i –> ‘a’)
j = 6 (j –> ‘a’)
index_txt = 0 (index_txt –> ‘b’)
index_pat = 4 (index_pat –> ‘*’)
第七次比较:-
步骤 – (5) : i = 2 (i –> ‘a’)
j = 7 (j –> ‘*’)
index_txt = 0 (index_txt –> ‘b’)
index_pat = 4 (index_pat –> ‘*’)
第八次比较:-
步骤 – (4) : i = 2 (i –> ‘a’)
j = 8 (j –> ‘*’)
index_txt = 2 (index_txt –> ‘a’)
index_pat = 7 (index_pat –> ‘*’)
再进行四次比较后:i = 2 (i –> ‘a’)
j = 12 (j –> ‘a’)
index_txt = 2 (index_txt –> ‘a’)
index_pat = 11 (index_pat –> ‘*’)
第十三次比较:-
步骤 – (5) : i = 3 (i –> ‘a’)
j = 13 (j –> ‘b’)
index_txt = 2 (index_txt –> ‘a’)
index_pat = 11 (index_pat –> ‘*’)
第十四次比较:-
步骤 – (5) : i = 3 (i –> ‘a’)
j = 12 (j –> ‘a’)
index_txt = 3 (index_txt –> ‘a’)
index_pat = 11 (index_pat –> ‘*’)
第十五次比较:-
步骤 – (5) : i = 4 (i –> ‘b’)
j = 13 (j –> ‘b’)
index_txt = 3 (index_txt –> ‘a’)
index_pat = 11 (index_pat –> ‘*’)
第十六次比较:-
步骤 – (5) : i = 5 (i –> ‘a’)
j = 14 (j –> 结束)
index_txt = 3 (index_txt –> ‘a’)
index_pat = 11 (index_pat –> ‘*’)
第十七次比较:-
步骤 – (5) : i = 4 (i –> ‘b’)
j = 12 (j –> ‘a’)
index_txt = 4 (index_txt –> ‘b’)
index_pat = 11 (index_pat –> ‘*’)
第十八次比较:-
步骤 – (5) : i = 5 (i –> ‘a’)
j = 12 (j –> ‘a’)
index_txt = 5 (index_txt –> ‘a’)
index_pat = 11 (index_pat –> ‘*’)
第十九次比较:-
步骤 – (5) : i = 6 (i –> ‘b’)
j = 13 (j –> ‘b’)
index_txt = 5 (index_txt –> ‘a’)
index_pat = 11 (index_pat –> ‘*’)
第二十次比较:-
步骤 – (5) : i = 7 (i –> end)
j = 14 (j –> 结束)
index_txt = 5 (index_txt –> ‘a’)
index_pat = 11 (index_pat –> ‘*’)
注意:现在我们将跳出循环运行步骤 – 7。
步骤 – (7) : j 已经出现在它的结束位置,因此答案为真。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program to implement wildcard
// pattern matching algorithm
#include
using namespace std;
// Function that matches input text
// with given wildcard pattern
bool strmatch(char txt[], char pat[],
int n, int m)
{
// empty pattern can only
// match with empty string.
// Base Case :
if (m == 0)
return (n == 0);
// step-1 :
// initialize markers :
int i = 0, j = 0, index_txt = -1,
index_pat = -1;
while (i < n)
{
// For step - (2, 5)
if (j < m && txt[i] == pat[j])
{
i++;
j++;
}
// For step - (3)
else if (j < m && pat[j] == '?')
{
i++;
j++;
}
// For step - (4)
else if (j < m && pat[j] == '*')
{
index_txt = i;
index_pat = j;
j++;
}
// For step - (5)
else if (index_pat != -1)
{
j = index_pat + 1;
i = index_txt + 1;
index_txt++;
}
// For step - (6)
else
{
return false;
}
}
// For step - (7)
while (j < m && pat[j] == '*')
{
j++;
}
// Final Check
if (j == m)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
char str[] = "baaabab";
char pattern[] = "*****ba*****ab";
// char pattern[] = "ba*****ab";
// char pattern[] = "ba*ab";
// char pattern[] = "a*ab";
if (strmatch(str, pattern,
strlen(str), strlen(pattern)))
cout << "Yes" << endl;
else
cout << "No" << endl;
char pattern2[] = "a*****ab";
if (strmatch(str, pattern2,
strlen(str), strlen(pattern2)))
cout << "Yes" << endl;
else
cout << "No" << endl;
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to implement wildcard
// pattern matching algorithm
class GFG {
// Function that matches input text
// with given wildcard pattern
static boolean strmatch(char txt[], char pat[],
int n, int m)
{
// empty pattern can only
// match with empty string.
// Base Case :
if (m == 0)
return (n == 0);
// step-1 :
// initialize markers :
int i = 0, j = 0, index_txt = -1,
index_pat = -1;
while (i < n)
{
// For step - (2, 5)
if (j < m && txt[i] == pat[j])
{
i++;
j++;
}
// For step - (3)
else if (j < m && pat[j] == '?')
{
i++;
j++;
}
// For step - (4)
else if (j < m && pat[j] == '*')
{
index_txt = i;
index_pat = j;
j++;
}
// For step - (5)
else if (index_pat != -1)
{
j = index_pat + 1;
i = index_txt + 1;
index_txt++;
}
// For step - (6)
else
{
return false;
}
}
// For step - (7)
while (j < m && pat[j] == '*')
{
j++;
}
// Final Check
if (j == m)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
char str[] = "baaabab".toCharArray();
char pattern[] = "*****ba*****ab".toCharArray();
// char pattern[] = "ba*****ab";
// char pattern[] = "ba*ab";
// char pattern[] = "a*ab";
if (strmatch(str, pattern, str.length,
pattern.length))
System.out.println("Yes");
else
System.out.println("No");
char pattern2[] = "a*****ab".toCharArray();
if (strmatch(str, pattern2, str.length,
pattern2.length))
System.out.println("Yes");
else
System.out.println("No");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-JiPython3
# Python3 program to implement
# wildcard pattern matching
# algorithm
# Function that matches input
# txt with given wildcard pattern
def stringmatch(txt, pat, n, m):
# empty pattern can only
# match with empty sting
# Base case
if (m == 0):
return (n == 0)
# step 1
# initialize markers :
i = 0
j = 0
index_txt = -1
index_pat = -1
while(i < n - 2):
# For step - (2, 5)
if (j < m and txt[i] == pat[j]):
i += 1
j += 1
# For step - (3)
elif(j < m and pat[j] == '?'):
i += 1
j += 1
# For step - (4)
elif(j < m and pat[j] == '*'):
index_txt = i
index_pat = j
j += 1
# For step - (5)
elif(index_pat != -1):
j = index_pat + 1
i = index_txt + 1
index_txt += 1
# For step - (6)
else:
return False
# For step - (7)
while (j < m and pat[j] == '*'):
j += 1
# Final Check
if(j == m):
return True
return False
# Driver code
strr = "baaabab"
pattern = "*****ba*****ab"
# char pattern[] = "ba*****ab"
# char pattern[] = "ba * ab"
# char pattern[] = "a * ab"
if (stringmatch(strr, pattern, len(strr),
len(pattern))):
print("Yes")
else:
print( "No")
pattern2 = "a*****ab";
if (stringmatch(strr, pattern2, len(strr),
len(pattern2))):
print("Yes")
else:
print( "No")
# This code is contributed
# by sahilhelangiaC#
// C# program to implement wildcard
// pattern matching algorithm
using System;
class GFG {
// Function that matches input text
// with given wildcard pattern
static Boolean strmatch(char[] txt, char[] pat,
int n, int m)
{
// empty pattern can only
// match with empty string.
// Base Case :
if (m == 0)
return (n == 0);
// step-1 :
// initialize markers :
int i = 0, j = 0, index_txt = -1,
index_pat = -1;
while (i < n) {
// For step - (2, 5)
if (j < m && txt[i] == pat[j]) {
i++;
j++;
}
// For step - (3)
else if (j < m && pat[j] == '?') {
i++;
j++;
}
// For step - (4)
else if (j < m && pat[j] == '*') {
index_txt = i;
index_pat = j;
j++;
}
// For step - (5)
else if (index_pat != -1) {
j = index_pat + 1;
i = index_txt + 1;
index_txt++;
}
// For step - (6)
else {
return false;
}
}
// For step - (7)
while (j < m && pat[j] == '*') {
j++;
}
// Final Check
if (j == m) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
char[] str = "baaabab".ToCharArray();
char[] pattern = "*****ba*****ab".ToCharArray();
// char pattern[] = "ba*****ab";
// char pattern[] = "ba*ab";
// char pattern[] = "a*ab";
if (strmatch(str, pattern, str.Length,
pattern.Length))
Console.WriteLine("Yes");
else
Console.WriteLine("No");
char[] pattern2 = "a*****ab".ToCharArray();
if (strmatch(str, pattern2, str.Length,
pattern2.Length))
Console.WriteLine("Yes");
else
Console.WriteLine("No");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-JiJavascript
Yes
No复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度: O(m + n),其中“m”和“n”分别是文本和模式的长度。
- 辅助空间: O(1)。
不使用任何数据结构来存储值