先决条件:MongoDB:简介
MongoDB 是一个跨平台、面向文档的数据库,它基于集合和文档的概念。 MongoDB 提供高速、高可用性和高可扩展性。
人们脑海中出现的下一个问题是“为什么是MongoDB”?
选择 MongoDB 的原因:
- 支持分层数据结构(详情请参考文档)
- 它支持像Python的Dictionaries 这样的关联数组。
- 内置Python驱动程序将 python 应用程序与数据库连接。示例 – PyMongo
- 它专为大数据而设计。
- MongoDB 的部署非常简单。
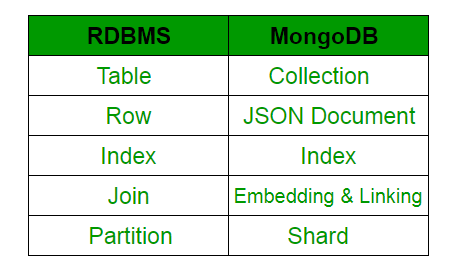
MongoDB 与 RDBMS
MongoDB 和 PyMongo 安装指南
- 首先使用以下命令从命令提示符启动 MongoDB:
方法一:mongod要么
方法二:net start MongoDB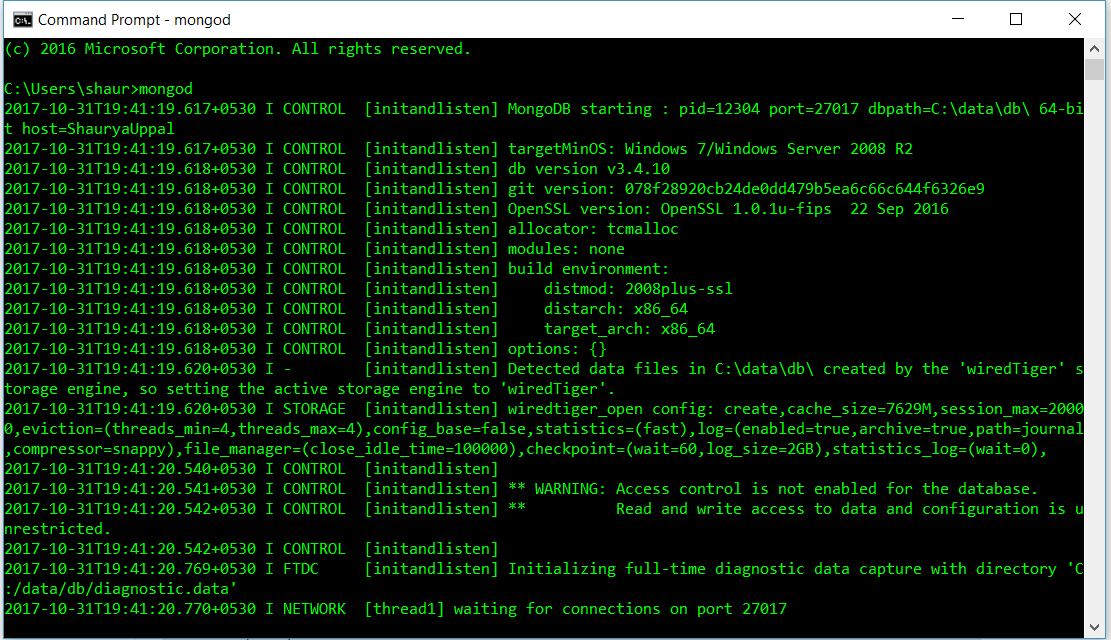
查看端口号默认设置为 27017(上图中的最后一行)。
Python有一个用于 MongoDB 的本机库。可用库的名称是“PyMongo”。要导入它,请执行以下命令:from pymongo import MongoClient - 创建连接:导入模块后的第一件事是创建一个 MongoClient。
from pymongo import MongoClient client = MongoClient()之后,连接到默认主机和端口。与主机和端口的连接是明确完成的。以下命令用于连接运行在端口号 27017 上的本地主机上的 MongoClient。
client = MongoClient(‘host’, port_number) example:- client = MongoClient(‘localhost’, 27017)也可以使用以下命令来完成:
client = MongoClient(“mongodb://localhost:27017/”) - 访问数据库对象:要创建数据库或切换到现有数据库,我们使用:
方法一:字典式mydatabase = client[‘name_of_the_database’]方法二:
mydatabase = client.name_of_the_database如果之前没有创建同名的数据库,MongoDB 会为用户隐式创建一个。
注意:数据库填充的名称不允许在其中使用任何破折号 (-)。像 my-Table 这样的名称会引发错误。因此,允许在名称中使用下划线。 - 访问集合:集合相当于 RDBMS 中的表。我们以与访问 RDBMS 中的表相同的方式访问 PyMongo 中的集合。要访问该表,请说数据库的表名“myTable”,说“mydatabase”。
方法一:mycollection = mydatabase[‘myTable’]方法二:
mycollection = mydatabase.myTable>MongoDB以字典的形式存储数据库,如图:>
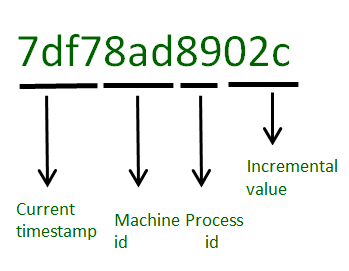
record = { title: 'MongoDB and Python', description: 'MongoDB is no SQL database', tags: ['mongodb', 'database', 'NoSQL'], viewers: 104 }‘_id’ 是特殊键,如果程序员忘记显式添加,它会自动添加。 _id 是 12 字节的十六进制数,它确保每个插入文档的唯一性。
- 在集合中插入数据:
使用的方法:insert_one() or insert_many()我们通常在我们的集合中使用 insert_one() 方法文档。假设我们希望将名为 record 的数据输入到“mydatabase”的“myTable”中。
rec = myTable.insert_one(record)当需要实现时,整个代码看起来像这样。
# importing module from pymongo import MongoClient # creation of MongoClient client=MongoClient() # Connect with the portnumber and host client = MongoClient(“mongodb://localhost:27017/”) # Access database mydatabase = client[‘name_of_the_database’] # Access collection of the database mycollection=mydatabase[‘myTable’] # dictionary to be added in the database rec={ title: 'MongoDB and Python', description: 'MongoDB is no SQL database', tags: ['mongodb', 'database', 'NoSQL'], viewers: 104 } # inserting the data in the database rec = mydatabase.myTable.insert(record) - 在 MongoDB 中查询:有一些查询函数用于过滤数据库中的数据。最常用的两个函数是:
- 寻找()
find() 用于作为查询结果获取多个单个文档。for i in mydatabase.myTable.find({title: 'MongoDB and Python'}) print(i)这将输出 mydatabase 的 myTable 中标题为“MongoDB and Python”的所有文档。
- 数数()
count() 用于获取具有传入参数的名称的文档数。print(mydatabase.myTable.count({title: 'MongoDB and Python'}))这将输出 mydatabase 的 myTable 中标题为“MongoDB and Python”的文档数量。
可以将这两个查询函数相加以给出过滤最多的结果,如下所示。
print(mydatabase.myTable.find({title: 'MongoDB and Python'}).count()) - 要打印数据库“mydatabase”的“myTable”中的所有文档/条目:使用以下代码:
from pymongo import MongoClient try: conn = MongoClient() print("Connected successfully!!!") except: print("Could not connect to MongoDB") # database name: mydatabase db = conn.mydatabase # Created or Switched to collection names: myTable collection = db.myTable # To find() all the entries inside collection name 'myTable' cursor = collection.find() for record in cursor: print(record)
- 寻找()