先决条件:用于处理视频的 Youtube Data API |组 1、组 2
在继续之前,首先看看如何获取有效视频类别的列表,以确定将视频放在哪个类别中。在示例中,我们为regionCode参数使用了“IN”值。您可以使用任何其他值。只有具有assignable参数为值“True”的 categoryId 才能用于视频插入或更新。
让我们讨论如何在授权用户的帐户 youtube 帐户中插入视频。
查找有效的视频类别:
# importing library
from apiclient.discovery import build
# Arguments that need to passed
# to the build function
DEVELOPER_KEY = "API_key"
YOUTUBE_API_SERVICE_NAME = "youtube"
YOUTUBE_API_VERSION = "v3"
# creating Youtube Resource Object
youtube_object = build(YOUTUBE_API_SERVICE_NAME,
YOUTUBE_API_VERSION,
developerKey = DEVELOPER_KEY)
def youtube_video_categories():
# calling the videoCategory.list method
# to retrieve youtube video categories result
video_category = youtube_object.videoCategories(
).list(part ='snippet', regionCode ='IN').execute()
# extracting the results
# from video_category response
results = video_category.get("items", [])
# empty list to store video category metadata
videos_categories = []
# extracting required info
# from each result object
for result in results:
# video_categories result object
videos_categories.append("% s, (% s % s)"
%(result["id"],
result["snippet"]["title"],
result["snippet"]["assignable"]))
print ("Video_Category_Id Catgeory_Name Assignable :\n",
"\n".join(videos_categories), "\n")
if __name__ == "__main__":
youtube_video_categories()
输出: 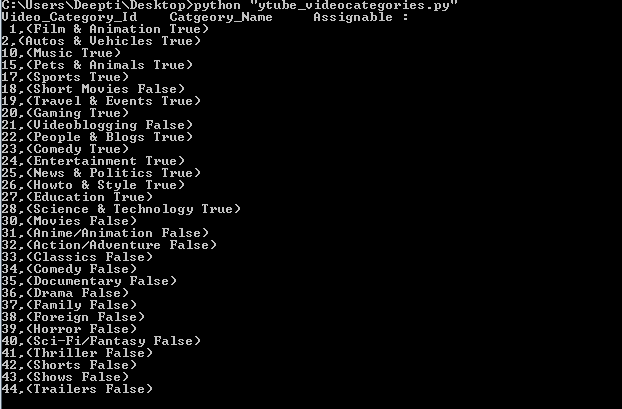
由于在授权用户的帐户中插入视频需要用户授权,因此我们将为此示例创建 OAuth 类型的凭据。按照以下步骤生成客户端 ID 和密钥。
- 转到 Google Google Developers Console,然后单击页面右上角的登录。使用有效 Google 帐户的凭据登录。如果您没有 google 帐户,请先设置一个帐户,然后使用详细信息在 Google Developers 主页上登录。
- 现在导航到开发人员仪表板并创建一个新项目。
- 单击启用 API 选项。
- 在搜索字段中,搜索 Youtube Data API 并选择下拉列表中的 Youtube Data API 选项。
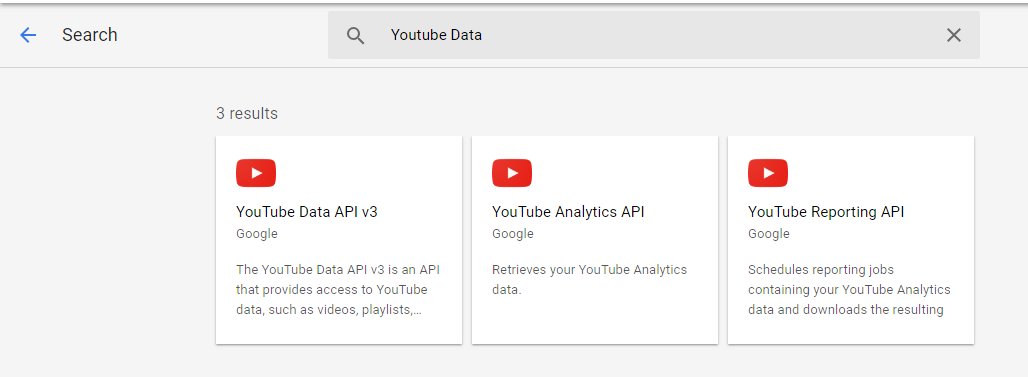
- 您将被重定向到一个屏幕,该屏幕显示有关 Youtube Data API 的信息,以及两个选项:ENABLE 和 TRY API。
- 单击启用选项以开始使用 API。
- 在 API 和服务下的侧边栏中,选择凭据。
- 在页面顶部,选择 OAuth 同意屏幕选项卡。选择一个电子邮件地址,如果尚未设置,请输入产品名称,然后单击保存按钮。
- 在凭据选项卡中,选择创建凭据下拉列表,然后选择 OAuth 客户端 ID。 OAuth 通常用于需要授权的情况,例如检索用户喜欢的视频。
- 选择其他应用程序类型,输入名称“YouTube Data API Myvideos”,然后单击“创建”按钮。
- 单击确定。
- 单击客户端 ID 右侧的下载按钮以下载 JSON 文件。
- 将文件保存并重命名为
client_secret.json并将其移动到工作目录。
pip命令安装其他库:
pip install --upgrade google-auth google-auth-oauthlib google-auth-httplib2我们下载了一个示例视频 – 学习 ABC 来展示上传的工作原理。 id、snippet.title 和snippet.categoryId 是必需的属性,所有其他都是可选的。
插入视频:此示例显示如何将视频上传到授权用户的帐户。视频上传受以下约束:
- 文件的最大大小为 128MB
- 可接受的媒体 MIME 类型仅为 video/*、application/octet-stream
# importing necessary libraries
import os
import urllib.request, urllib.parse, urllib.error
import http.client
import urllib.request
import urllib.error
import http.client
import httplib2
import random
import time
import google.oauth2.credentials
import google_auth_oauthlib.flow
from googleapiclient.discovery import build
from googleapiclient.errors import HttpError
from google_auth_oauthlib.flow import InstalledAppFlow
from apiclient.http import MediaFileUpload
# The CLIENT_SECRETS_FILE variable
# specifies the name of a file that
# contains client_id and client_secret.
CLIENT_SECRETS_FILE = "client_secret.json"
# This scope allows for full read /
# write access to the authenticated
# user's account and requires requests
# to use an SSL connection.
SCOPES = ['https://www.googleapis.com/auth/youtube.force-ssl']
API_SERVICE_NAME = 'youtube'
API_VERSION = 'v3'
def get_authenticated_service():
flow = InstalledAppFlow.from_client_secrets_file(
CLIENT_SECRETS_FILE, SCOPES)
credentials = flow.run_console()
return build(API_SERVICE_NAME, API_VERSION,
credentials = credentials)
# Here we are telling HTTP Transport
# Library not to retry the video upload.
httplib2.RETRIES = 1
# MAX_RETRIES specifies the maximum number
# of retries that can done before giving up.
MAX_RETRIES = 10
# Always retry when these exceptions are raised.
RETRIABLE_EXCEPTIONS = (httplib2.HttpLib2Error, IOError,
http.client.NotConnected,
http.client.IncompleteRead,
http.client.ImproperConnectionState,
http.client.CannotSendRequest,
http.client.CannotSendHeader,
http.client.ResponseNotReady,
http.client.BadStatusLine)
# Always retry when an apiclient.errors.HttpError
# with one of these status codes is raised.
RETRIABLE_STATUS_CODES = [500, 502, 503, 504]
# This method implements an exponential
# backoff strategy to resume a failed upload.
def resumable_upload(request, resource, method):
response = None
error = None
retry = 0
while response is None:
try:
print("Uploading the file...")
status, response = request.next_chunk()
if response is not None:
if method == 'insert' and 'id' in response:
print(response)
elif method != 'insert' or 'id' not in response:
print(response)
else:
exit("The file upload failed with an\
unexpected response: % s" % response)
except HttpError as e:
if e.resp.status in RETRIABLE_STATUS_CODES:
error = "A retriable HTTP error % d occurred:\n % s"
% (e.resp.status, e.content)
else:
raise
except RETRIABLE_EXCEPTIONS as e:
error = "A retriable error occurred: % s" % e
if error is not None:
print(error)
retry += 1
if retry > MAX_RETRIES:
exit("No longer attempting to retry.")
max_sleep = 2 ** retry
sleep_seconds = random.random() * max_sleep
print(("Sleeping % f seconds and then retrying..."
% sleep_seconds))
time.sleep(sleep_seconds)
def print_response(response):
print(response)
# Build a resource based on a list of
# properties given as key-value pairs.
# Leave properties with empty values
# out of the inserted resource.
def build_resource(properties):
resource = {}
for p in properties:
# Given a key like "snippet.title", split into
# "snippet" and "title", where
# "snippet" will be an object and "title"
# will be a property in that object.
prop_array = p.split('.')
ref = resource
for pa in range(0, len(prop_array)):
is_array = False
key = prop_array[pa]
# For properties that have array values,
# convert a name like "snippet.tags[]" to
# snippet.tags, and set a flag to handle
# the value as an array.
if key[-2:] == '[]':
key = key[0:len(key)-2:]
is_array = True
if pa == (len(prop_array) - 1):
# Leave properties without values
# out of inserted resource.
if properties[p]:
if is_array:
ref[key] = properties[p].split(', ')
else:
ref[key] = properties[p]
elif key not in ref:
# For example, the property is "snippet.title",
# but the resource does not yet have a "snippet"
# object. Create the snippet object here.
# Setting "ref = ref[key]" means that in the
# next time through the "for pa in range ..." loop,
# we will be setting a property in the
# resource's "snippet" object.
ref[key] = {}
ref = ref[key]
else:
# For example, the property is "snippet.description",
# and the resource already has a "snippet" object.
ref = ref[key]
return resource
# Remove keyword arguments that are not set
def remove_empty_kwargs(**kwargs):
good_kwargs = {}
if kwargs is not None:
for key, value in list(kwargs.items()):
if value:
good_kwargs[key] = value
return good_kwargs
def videos_insert(client, properties, media_file, **kwargs):
resource = build_resource(properties)
kwargs = remove_empty_kwargs(**kwargs)
request = client.videos().insert(body = resource,
media_body = MediaFileUpload(media_file,
chunksize =-1, resumable = True), **kwargs)
return resumable_upload(request, 'video', 'insert')
if __name__ == '__main__':
# When running locally, disable OAuthlib's
# HTTPs verification. When running in production
# * do not * leave this option enabled.
os.environ['OAUTHLIB_INSECURE_TRANSPORT'] = '1'
client = get_authenticated_service()
media_file = 'videoplayback.3gp'
if not os.path.exists(media_file):
exit('Please specify the complete valid file location.')
videos_insert(client,
{'snippet.categoryId': '27',
'snippet.defaultLanguage': '',
'snippet.description': 'Sample Leran ABC Video',
'snippet.tags[]': '',
'snippet.title': 'Sample Test video upload',
'status.embeddable': '',
'status.license': '',
'status.privacyStatus': 'private',
'status.publicStatsViewable': ''},
media_file,
part ='snippet, status')
输出:
执行代码时,它会要求提供授权码。要获取代码,您需要按照以下行上方的命令提示符屏幕中提到的链接进行操作:输入授权代码。 
现在点击链接并复制粘贴您将通过授予权限获得的授权代码。 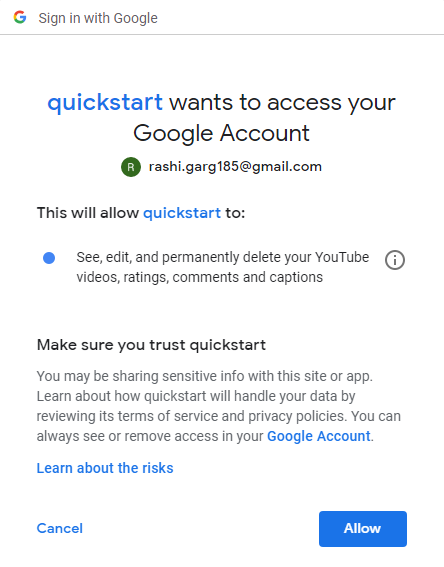

现在,您可以从使用的帐户中看到,它显示视频已上传。 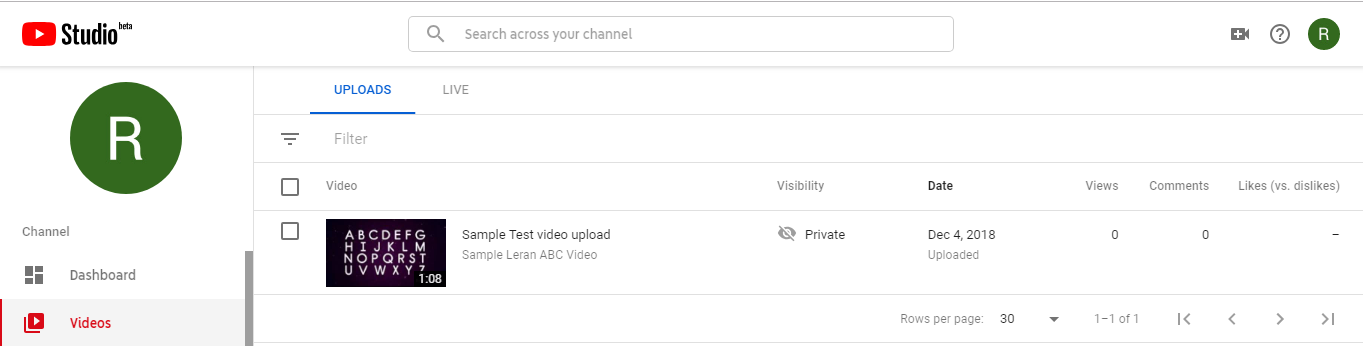
参考:
- https://developers.google.com/youtube/v3/docs/videos/insert
- https://developers.google.com/youtube/v3/docs/videoCategories/list