计算树大小的迭代程序
树的大小是树中存在的元素的数量。下面的树的大小是 5。
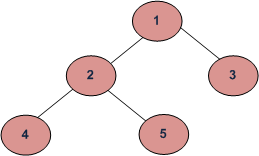
方法
这个想法是使用 Level Order Traversing
1) Create an empty queue q
2) temp_node = root /*start from root*/
3) Loop while temp_node is not NULL
a) Enqueue temp_node’s children (first left then right children) to q
b) Increase count with every enqueuing.
c) Dequeue a node from q and assign it’s value to temp_nodeC++
// C++ program to print size of tree in iterative
#include
#include
using namespace std;
struct Node
{
int data;
Node *left, *right;
};
// A utility function to
// create a new Binary Tree Node
Node *newNode(int data)
{
Node *temp = new Node;
temp->data = data;
temp->left = NULL;
temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
// return size of tree
int sizeoftree(Node *root)
{
// if tree is empty it will
// return 0
if(root == NULL)
return 0;
// Using level order Traversal.
queue q;
int count = 1;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty())
{
Node *temp = q.front();
if(temp->left)
{
// Enqueue left child
q.push(temp->left);
// Increment count
count++;
}
if(temp->right)
{
// Enqueue right child
q.push(temp->right);
// Increment count
count++;
}
q.pop();
}
return count;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
Node *root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
cout << "Size of the tree is " <<
sizeoftree(root) << endl;
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by SHAKEELMOHAMMADJava
// Java programn to calculate
// Size of a tree
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
class Node
{
int data;
Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
class BinaryTree
{
Node root;
public int size()
{
if (root == null)
return 0;
// Using level order Traversal.
Queue q = new LinkedList();
q.offer(root);
int count = 1;
while (!q.isEmpty())
{
Node tmp = q.poll();
// when the queue is empty:
// the poll() method returns null.
if (tmp != null)
{
if (tmp.left != null)
{
// Increment count
count++;
// Enqueue left child
q.offer(tmp.left);
}
if (tmp.right != null)
{
// Increment count
count++;
// Enqueue left child
q.offer(tmp.right);
}
}
}
return count;
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
/* creating a binary tree and entering
the nodes */
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
System.out.println("The size of binary tree" +
" is : " + tree.size());
}
}Python3
# Python Program to calculate size of the tree iteratively
# Node Structure
class newNode:
def __init__(self,data):
self.data = data
self.left = self.right = None
# Return size of tree
def sizeoftree(root):
if root == None:
return 0
q = []
q.append(root)
count = 1
while(len(q) != 0):
root = q.pop(0)
if(root.left):
q.append(root.left)
count += 1
if(root.right):
q.append(root.right)
count += 1
return count
# Driver Program
root = newNode(1)
root.left = newNode(2)
root.right = newNode(3)
root.left.left = newNode(4)
root.left.right = newNode(5)
print(sizeoftree(root))
# This is code is contributed by simranjenny84C#
// C# programn to calculate
// Size of a tree
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
public class BinaryTree
{
Node root;
public int size()
{
if (root == null)
return 0;
// Using level order Traversal.
Queue q = new Queue();
q.Enqueue(root);
int count = 1;
while (q.Count != 0)
{
Node tmp = q.Dequeue();
// when the queue is empty:
// the poll() method returns null.
if (tmp != null)
{
if (tmp.left != null)
{
// Increment count
count++;
// Enqueue left child
q.Enqueue(tmp.left);
}
if (tmp.right != null)
{
// Increment count
count++;
// Enqueue left child
q.Enqueue(tmp.right);
}
}
}
return count;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String []args)
{
/* creating a binary tree and entering
the nodes */
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
Console.WriteLine("The size of binary tree" +
" is : " + tree.size());
}
}
// This code has been contributed by 29AjayKumarJavascript
// JavaScript programn to calculate Size of a tree
class Node
{
constructor(item) {
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
this.data = item;
}
}
let root;
function size()
{
if (root == null)
return 0;
// Using level order Traversal.
let q = [];
q.push(root);
let count = 1;
while (q.length > 0)
{
let tmp = q[0];
q.shift();
// when the queue is empty:
// the poll() method returns null.
if (tmp != null)
{
if (tmp.left != null)
{
// Increment count
count++;
// Enqueue left child
q.push(tmp.left);
}
if (tmp.right != null)
{
// Increment count
count++;
// Enqueue left child
q.push(tmp.right);
}
}
}
return count;
}
/* creating a binary tree and entering
the nodes */
root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
document.write("Size of the tree is " + size());
Size of the tree is 5输出:
Size of the tree is 5时间复杂度: O(n)
辅助空间: O(level_max),其中 level max 是任何级别中的最大节点数。