Lamport 的逻辑时钟是由 Leslie Lamport 创建的。它是确定事件发生顺序的过程。它为更高级的矢量时钟算法提供了基础。由于分布式操作系统中缺少全局时钟,因此需要 Lamport 逻辑时钟。
算法:
- 发生在关系(->)之前: a -> b,意味着“a”发生在“b”之前。
- 逻辑时钟:逻辑时钟的标准是:
- [C1]: C i (a) < C i (b), [ C i -> 逻辑时钟,如果’a’发生在’b’之前,那么’a’的时间将小于’b’在特定情况下过程。 ]
- [C2]:C i (a) < C j (b),[ C i (a) 的时钟值小于C j (b) ]
参考:
- 工艺: P i
- 事件: E ij ,其中 i 是进程编号, j:第i个进程中的第 j个事件。
- t m :消息 m 的向量时间跨度。
- C i向量时钟与进程P i相关联,第j个元素是Ci[j]并且包含进程 P j 中当前时间P i的最新值。
- d:漂移时间,一般d为1。
实施细则[IR]:
- [IR1]:如果 a -> b [‘a’ 发生在同一进程中的 ‘b’ 之前] 那么, C i (b) =C i (a) + d
- [IR2]: C j = max(C j , t m + d) [如果有更多的进程,那么 t m = C i (a) 的值,C j = C j和 t m + d 之间的最大值]
例如:
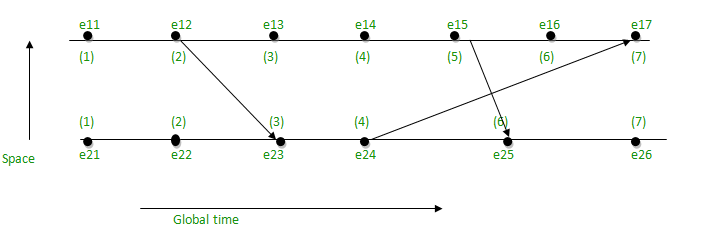
- 取起始值为1,因为它是第1个事件并且存在在起始点没有传入的值:
- e11 = 1
- e21 = 1
- 如果没有传入值,即跟随 [IR1],则下一个点的值将继续增加 d (d = 1)。
- e12 = e11 + d = 1 + 1 = 2
- e13 = e12 + d = 2 + 1 = 3
- e14 = e13 + d = 3 + 1 = 4
- e15 = e14 + d = 4 + 1 = 5
- e16 = e15 + d = 5 + 1 = 6
- e22 = e21 + d = 1 + 1 = 2
- e24 = e23 + d = 3 + 1 = 4
- e26 = e25 + d = 6 + 1 = 7
- 当有传入值时,则按照[IR2],即取C j和T m + d之间的最大值。
- e17 = max(7, 5) = 7, [e16 + d = 6 + 1 = 7, e24 + d = 4 + 1 = 5, 7 和 5 中最大为 7]
- e23 = max(3, 3) = 3, [e22 + d = 2 + 1 = 3, e12 + d = 2 + 1 = 3, 3和3中最大为3]
- e25 = max(5, 6) = 6, [e24 + 1 = 4 + 1 = 5, e15 + d = 5 + 1 = 6, 5和6中最大为6]
限制:
- 在 [IR1] 的情况下,如果 a -> b,则 C(a) < C(b) -> 为真。
- 在 [IR2] 的情况下,如果 a -> b,则 C(a) < C(b) -> 可能为真,也可能不为真。
下面是实现 Lamport 逻辑时钟的 C 程序:
C
// C program to illustrate the Lamport's
// Logical Clock
#include
// Function to find the maximum timestamp
// between 2 events
int max1(int a, int b)
{
// Return the greatest of th two
if (a > b)
return a;
else
return b;
}
// Function to display the logical timestamp
void display(int e1, int e2,
int p1[5], int p2[3])
{
int i;
printf("\nThe time stamps of "
"events in P1:\n");
for (i = 0; i < e1; i++) {
printf("%d ", p1[i]);
}
printf("\nThe time stamps of "
"events in P2:\n");
// Print the array p2[]
for (i = 0; i < e2; i++)
printf("%d ", p2[i]);
}
// Function to find the timestamp of events
void lamportLogicalClock(int e1, int e2,
int m[5][3])
{
int i, j, k, p1[e1], p2[e2];
// Initialize p1[] and p2[]
for (i = 0; i < e1; i++)
p1[i] = i + 1;
for (i = 0; i < e2; i++)
p2[i] = i + 1;
for (i = 0; i < e2; i++)
printf("\te2%d", i + 1);
for (i = 0; i < e1; i++) {
printf("\n e1%d \t", i + 1);
for (j = 0; j < e2; j++)
printf("%d\t", m[i][j]);
}
for (i = 0; i < e1; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < e2; j++) {
// Change the timestamp if the
// message is sent
if (m[i][j] == 1) {
p2[j] = max1(p2[j], p1[i] + 1);
for (k = j + 1; k < e2; k++)
p2[k] = p2[k - 1] + 1;
}
// Change the timestamp if the
// message is reeived
if (m[i][j] == -1) {
p1[i] = max1(p1[i], p2[j] + 1);
for (k = i + 1; k < e1; k++)
p1[k] = p1[k - 1] + 1;
}
}
}
// Function Call
display(e1, e2, p1, p2);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int e1 = 5, e2 = 3, m[5][3];
// message is sent and received
// between two process
/*dep[i][j] = 1, if message is sent
from ei to ej
dep[i][j] = -1, if message is received
by ei from ej
dep[i][j] = 0, otherwise*/
m[0][0] = 0;
m[0][1] = 0;
m[0][2] = 0;
m[1][0] = 0;
m[1][1] = 0;
m[1][2] = 1;
m[2][0] = 0;
m[2][1] = 0;
m[2][2] = 0;
m[3][0] = 0;
m[3][1] = 0;
m[3][2] = 0;
m[4][0] = 0;
m[4][1] = -1;
m[4][2] = 0;
// Function Call
lamportLogicalClock(e1, e2, m);
return 0;
} C++
// C++ program to illustrate the Lamport's
// Logical Clock
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to find the maximum timestamp
// between 2 events
int max1(int a, int b)
{
// Return the greatest of th two
if (a > b)
return a;
else
return b;
}
// Function to display the logical timestamp
void display(int e1, int e2,
int p1[5], int p2[3])
{
int i;
cout << "\nThe time stamps of "
"events in P1:\n";
for (i = 0; i < e1; i++) {
cout << p1[i] << " ";
}
cout << "\nThe time stamps of "
"events in P2:\n";
// Print the array p2[]
for (i = 0; i < e2; i++)
cout << p2[i] << " ";
}
// Function to find the timestamp of events
void lamportLogicalClock(int e1, int e2,
int m[5][3])
{
int i, j, k, p1[e1], p2[e2];
// Initialize p1[] and p2[]
for (i = 0; i < e1; i++)
p1[i] = i + 1;
for (i = 0; i < e2; i++)
p2[i] = i + 1;
for (i = 0; i < e2; i++)
cout << "\te2" << i + 1;
for (i = 0; i < e1; i++) {
cout << "\n e1\t" << i + 1;
for (j = 0; j < e2; j++)
cout << m[i][j] << "\t";
}
for (i = 0; i < e1; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < e2; j++) {
// Change the timestamp if the
// message is sent
if (m[i][j] == 1) {
p2[j] = max1(p2[j], p1[i] + 1);
for (k = j + 1; k < e2; k++)
p2[k] = p2[k - 1] + 1;
}
// Change the timestamp if the
// message is reeived
if (m[i][j] == -1) {
p1[i] = max1(p1[i], p2[j] + 1);
for (k = i + 1; k < e1; k++)
p1[k] = p1[k - 1] + 1;
}
}
}
// Function Call
display(e1, e2, p1, p2);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int e1 = 5, e2 = 3, m[5][3];
// message is sent and received
// between two process
/*dep[i][j] = 1, if message is sent
from ei to ej
dep[i][j] = -1, if message is received
by ei from ej
dep[i][j] = 0, otherwise*/
m[0][0] = 0;
m[0][1] = 0;
m[0][2] = 0;
m[1][0] = 0;
m[1][1] = 0;
m[1][2] = 1;
m[2][0] = 0;
m[2][1] = 0;
m[2][2] = 0;
m[3][0] = 0;
m[3][1] = 0;
m[3][2] = 0;
m[4][0] = 0;
m[4][1] = -1;
m[4][2] = 0;
// Function Call
lamportLogicalClock(e1, e2, m);
return 0;
} 输出:
e21 e22 e23
e11 0 0 0
e12 0 0 1
e13 0 0 0
e14 0 0 0
e15 0 -1 0
The time stamps of events in P1:
1 2 3 4 5
The time stamps of events in P2:
1 2 3时间复杂度: O(e1 * e2 * (e1 + e2))
辅助空间: O(e1 + e2)
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。