📅 最后修改于: 2020-10-22 01:15:31 🧑 作者: Mango
C函数
在c中,我们可以将大型程序划分为称为函数的基本构建块。该函数包含用{}括起来的一组编程语句。可以多次调用一个函数,以为C程序提供可重用性和模块化。换句话说,我们可以说功能集合创建了一个程序。该函数在其他编程语言中也称为过程或子例程。
C函数的优势
C函数具有以下优点。
- 通过使用函数,我们可以避免在程序中一次又一次地重写相同的逻辑/代码。
- 我们可以在程序中以及在程序的任何位置多次调用C函数。
- 当大型C程序被划分为多个功能时,我们可以轻松地对其进行跟踪。
- 可重用性是C函数的主要成就。
- 但是,函数调用始终是C程序的开销。
功能方面
C函数包含三个方面。
- 函数声明必须在ac程序中全局声明函数,以告知编译器函数名称,函数参数和返回类型。
- 函数调用可以从程序中的任何位置调用函数。参数列表在函数调用和函数声明中不得不同。我们必须传递与函数声明中声明的函数数量相同的函数。
- 函数定义它包含要执行的实际语句。这是调用函数时控件所涉及的最重要方面。在这里,我们必须注意,该函数只能返回一个值。
| SN | C function aspects | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Function declaration | return_type function_name (argument list); |
| 2 | Function call | function_name (argument_list) |
| 3 | Function definition | return_type function_name (argument list) {function body;} |
使用C语言创建函数的语法如下:
return_type function_name(data_type parameter...){
//code to be executed
}
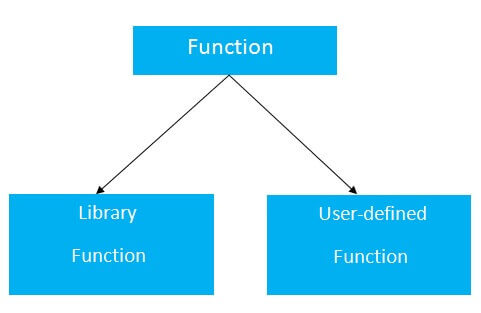
功能类型
C编程中有两种类型的函数:
- 库函数:是在C头文件中声明的函数,例如scanf(),printf(),gets(),puts(),ceil(),floor()等。
- 用户定义的函数:是C程序员创建的函数,因此他/她可以多次使用它。它降低了大型程序的复杂性并优化了代码。
返回值
AC函数可能会也可能不会从该函数返回值。如果您不必从函数返回任何值,则将void用作返回类型。
让我们看一个简单的C函数示例,该函数不从该函数返回任何值。
没有返回值的示例:
void hello(){
printf("hello c");
}
如果要从函数返回任何值,则需要使用任何数据类型,例如int,long,char等。返回类型取决于要从函数返回的值。
让我们看一个简单的C函数示例,该函数从函数中返回int值。
返回值示例:
int get(){
return 10;
}
在上面的示例中,我们必须返回10作为值,因此返回类型为int。如果要返回浮点值(例如10.2、3.1、54.5等),则需要使用float作为方法的返回类型。
float get(){
return 10.2;
}
现在,你需要调用的函数,来获取函数的值。
函数调用的不同方面
函数可以接受也可以不接受任何参数。它可能会也可能不会返回任何值。基于这些事实,函数调用有四个不同方面。
- 没有参数,并且没有返回值的函数
- 不带任何参数,并返回值的函数
- 与参数,并且没有返回值的函数
- 带参数与返回值的函数
不带参数和返回值的函数示例
例子1
#include
void printName();
void main ()
{
printf("Hello ");
printName();
}
void printName()
{
printf("Javatpoint");
}
输出量
Hello Javatpoint
例子2
#include
void sum();
void main()
{
printf("\nGoing to calculate the sum of two numbers:");
sum();
}
void sum()
{
int a,b;
printf("\nEnter two numbers");
scanf("%d %d",&a,&b);
printf("The sum is %d",a+b);
}
输出量
Going to calculate the sum of two numbers:
Enter two numbers 10
24
The sum is 34
不带参数返回值的函数示例
例子1
#include
int sum();
void main()
{
int result;
printf("\nGoing to calculate the sum of two numbers:");
result = sum();
printf("%d",result);
}
int sum()
{
int a,b;
printf("\nEnter two numbers");
scanf("%d %d",&a,&b);
return a+b;
}
输出量
Going to calculate the sum of two numbers:
Enter two numbers 10
24
The sum is 34
示例2:程序来计算正方形的面积
#include
int sum();
void main()
{
printf("Going to calculate the area of the square\n");
float area = square();
printf("The area of the square: %f\n",area);
}
int square()
{
float side;
printf("Enter the length of the side in meters: ");
scanf("%f",&side);
return side * side;
}
输出量
Going to calculate the area of the square
Enter the length of the side in meters: 10
The area of the square: 100.000000
带参数且不带返回值的函数示例
例子1
#include
void sum(int, int);
void main()
{
int a,b,result;
printf("\nGoing to calculate the sum of two numbers:");
printf("\nEnter two numbers:");
scanf("%d %d",&a,&b);
sum(a,b);
}
void sum(int a, int b)
{
printf("\nThe sum is %d",a+b);
}
输出量
Going to calculate the sum of two numbers:
Enter two numbers 10
24
The sum is 34
示例2:程序计算五个数字的平均值。
#include
void average(int, int, int, int, int);
void main()
{
int a,b,c,d,e;
printf("\nGoing to calculate the average of five numbers:");
printf("\nEnter five numbers:");
scanf("%d %d %d %d %d",&a,&b,&c,&d,&e);
average(a,b,c,d,e);
}
void average(int a, int b, int c, int d, int e)
{
float avg;
avg = (a+b+c+d+e)/5;
printf("The average of given five numbers : %f",avg);
}
输出量
Going to calculate the average of five numbers:
Enter five numbers:10
20
30
40
50
The average of given five numbers : 30.000000
带参数和返回值的函数示例
例子1
#include
int sum(int, int);
void main()
{
int a,b,result;
printf("\nGoing to calculate the sum of two numbers:");
printf("\nEnter two numbers:");
scanf("%d %d",&a,&b);
result = sum(a,b);
printf("\nThe sum is : %d",result);
}
int sum(int a, int b)
{
return a+b;
}
输出量
Going to calculate the sum of two numbers:
Enter two numbers:10
20
The sum is : 30
示例2:检查数字是偶数还是奇数的程序
#include
int even_odd(int);
void main()
{
int n,flag=0;
printf("\nGoing to check whether a number is even or odd");
printf("\nEnter the number: ");
scanf("%d",&n);
flag = even_odd(n);
if(flag == 0)
{
printf("\nThe number is odd");
}
else
{
printf("\nThe number is even");
}
}
int even_odd(int n)
{
if(n%2 == 0)
{
return 1;
}
else
{
return 0;
}
}
输出量
Going to check whether a number is even or odd
Enter the number: 100
The number is even
C库函数
库函数是C中的内置函数,它们被分组并放置在称为库的公共位置。这些功能用于执行某些特定操作。例如,printf是用于在控制台上print的库函数。库函数由编译器的设计者创建。所有C标准库函数都在扩展名为.h的不同头文件中定义。我们需要在程序中包括这些头文件,以利用在这些头文件中定义的库函数。例如,要使用诸如printf / scanf之类的库函数,我们需要在程序中包含stdio.h,这是一个头文件,其中包含有关标准输入/输出的所有库函数。
下表列出了最常用的头文件。
| SN | Header file | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | stdio.h | This is a standard input/output header file. It contains all the library functions regarding standard input/output. |
| 2 | conio.h | This is a console input/output header file. |
| 3 | string.h | It contains all string related library functions like gets(), puts(),etc. |
| 4 | stdlib.h | This header file contains all the general library functions like malloc(), calloc(), exit(), etc. |
| 5 | math.h | This header file contains all the math operations related functions like sqrt(), pow(), etc. |
| 6 | time.h | This header file contains all the time-related functions. |
| 7 | ctype.h | This header file contains all character handling functions. |
| 8 | stdarg.h | Variable argument functions are defined in this header file. |
| 9 | signal.h | All the signal handling functions are defined in this header file. |
| 10 | setjmp.h | This file contains all the jump functions. |
| 11 | locale.h | This file contains locale functions. |
| 12 | errno.h | This file contains error handling functions. |
| 13 | assert.h | This file contains diagnostics functions. |