线段给定点 P 的方向只是意味着给定点 P 和线段(比如 AB)的坐标,我们必须从线段确定点 P 的方向。即点位于线段的右侧还是线段的左侧。
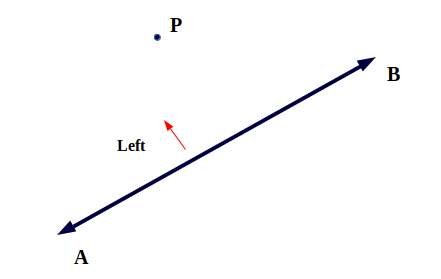
该点可能位于线段后面,在这种情况下,我们通过延长线段并确定点的方向来假设假想线。
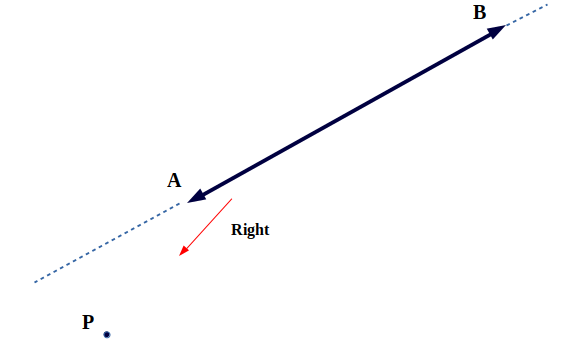
* 只有三种情况,要么点在左侧,要么在右侧,要么在线段本身。
这是一个非常基本的问题,在线地图中的方向经常遇到,
示例:假设用户 A 必须去下图中的 C 点,该用户首先到达 B 点,但之后用户 A 如何知道他必须右转还是左转。

从线段知道点的方向也可以作为解决更复杂问题的基石,例如:
- 线段交点:判断两条线段是否相交
- 一组点的凸包。
我们将使用的坐标系是笛卡尔平面,因为大多数二维问题使用笛卡尔平面,因为这是一个二维问题。
这个问题可以用向量代数的叉积来解决
两点 A 和 B 的叉积为: A x * B y – A y * B x
其中A x和A y分别是A 的x 和y 坐标。类似地,B x和 B y分别是 B 的 x 和 y 坐标。
Cross-Product有一个有趣的属性,它将用于从线段确定点的方向。也就是说,当且仅当这些点在原点 (0, 0) 处的角度为逆时针方向时,两点的叉积为正。相反,当且仅当这些点在原点的角度为顺时针方向时,叉积为负。
一个例子肯定会澄清它,
在下图中,角度 BOP 为逆时针方向,BXP = 29*28 – 15*(-15) = 1037 的叉积为正。
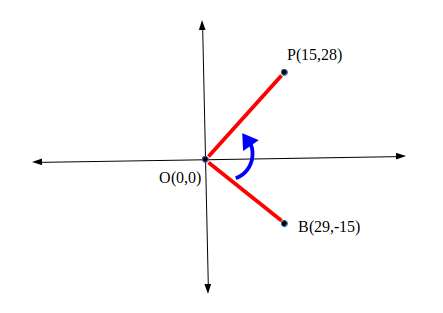
这有助于我们得出结论,右侧的点必须具有正的叉积,而左侧的点必须具有负的叉积。还要注意,我们假设线段的一个点是原点,因此我们需要转换任何三点系统,使得线段的一个点是原点。
下面的例子解释了这个概念:
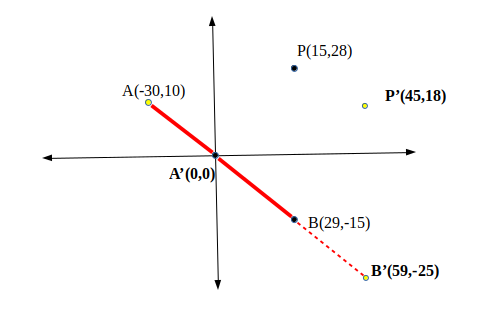
将A、B、P三点换算成A’、B’ 、 P’ ,以A为原点(可以简单地用P、B点减去A的坐标即可),然后计算交叉积:59*18 – (-25)*18 = 2187
由于这是正数,因此点 P 位于线段 AB 的右侧。
C++
// C++ Program to Determine Direction of Point
// from line segment
#include
using namespace std;
// structure for point in cartesian plane.
struct point {
int x, y;
};
// constant integers for directions
const int RIGHT = 1, LEFT = -1, ZERO = 0;
int directionOfPoint(point A, point B, point P)
{
// subtracting co-ordinates of point A from
// B and P, to make A as origin
B.x -= A.x;
B.y -= A.y;
P.x -= A.x;
P.y -= A.y;
// Determining cross Product
int cross_product = B.x * P.y - B.y * P.x;
// return RIGHT if cross product is positive
if (cross_product > 0)
return RIGHT;
// return LEFT if cross product is negative
if (cross_product < 0)
return LEFT;
// return ZERO if cross product is zero.
return ZERO;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
point A, B, P;
A.x = -30;
A.y = 10; // A(-30, 10)
B.x = 29;
B.y = -15; // B(29, -15)
P.x = 15;
P.y = 28; // P(15, 28)
int direction = directionOfPoint(A, B, P);
if (direction == 1)
cout << "Right Direction" << endl;
else if (direction == -1)
cout << "Left Direction" << endl;
else
cout << "Point is on the Line" << endl;
return 0;
} Java
// Java Program to Determine Direction of Point
// from line segment
class GFG
{
// structure for point in cartesian plane.
static class point
{
int x, y;
};
// constant integers for directions
static int RIGHT = 1, LEFT = -1, ZERO = 0;
static int directionOfPoint(point A,
point B, point P)
{
// subtracting co-ordinates of point A
// from B and P, to make A as origin
B.x -= A.x;
B.y -= A.y;
P.x -= A.x;
P.y -= A.y;
// Determining cross Product
int cross_product = B.x * P.y - B.y * P.x;
// return RIGHT if cross product is positive
if (cross_product > 0)
return RIGHT;
// return LEFT if cross product is negative
if (cross_product < 0)
return LEFT;
// return ZERO if cross product is zero.
return ZERO;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
point A = new point(),
B = new point(), P = new point();
A.x = -30;
A.y = 10; // A(-30, 10)
B.x = 29;
B.y = -15; // B(29, -15)
P.x = 15;
P.y = 28; // P(15, 28)
int direction = directionOfPoint(A, B, P);
if (direction == 1)
System.out.println("Right Direction");
else if (direction == -1)
System.out.println("Left Direction");
else
System.out.println("Point is on the Line");
}
}
// This code is contributed
// by Princi SinghPython3
# Python3 program to determine direction
# of point from line segment
# Structure for point in cartesian plane.
class point:
def __init__(self):
self.x = 0
self.y = 0
# Constant integers for directions
RIGHT = 1
LEFT = -1
ZERO = 0
def directionOfPoint(A, B, P):
global RIGHT, LEFT, ZERO
# Subtracting co-ordinates of
# point A from B and P, to
# make A as origin
B.x -= A.x
B.y -= A.y
P.x -= A.x
P.y -= A.y
# Determining cross Product
cross_product = B.x * P.y - B.y * P.x
# Return RIGHT if cross product is positive
if (cross_product > 0):
return RIGHT
# Return LEFT if cross product is negative
if (cross_product < 0):
return LEFT
# Return ZERO if cross product is zero
return ZERO
# Driver code
if __name__=="__main__":
A = point()
B = point()
P = point()
A.x = -30
A.y = 10 # A(-30, 10)
B.x = 29
B.y = -15 # B(29, -15)
P.x = 15
P.y = 28 # P(15, 28)
direction = directionOfPoint(A, B, P)
if (direction == 1):
print("Right Direction")
elif (direction == -1):
print("Left Direction")
else:
print("Point is on the Line")
# This code is contributed by rutvik_56C#
// C# Program to Determine Direction of Point
// from line segment
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
// structure for point in cartesian plane.
public class point
{
public int x, y;
};
// constant integers for directions
static int RIGHT = 1, LEFT = -1, ZERO = 0;
static int directionOfPoint(point A,
point B, point P)
{
// subtracting co-ordinates of point A
// from B and P, to make A as origin
B.x -= A.x;
B.y -= A.y;
P.x -= A.x;
P.y -= A.y;
// Determining cross Product
int cross_product = B.x * P.y - B.y * P.x;
// return RIGHT if cross product is positive
if (cross_product > 0)
return RIGHT;
// return LEFT if cross product is negative
if (cross_product < 0)
return LEFT;
// return ZERO if cross product is zero.
return ZERO;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
point A = new point(),
B = new point(),
P = new point();
A.x = -30;
A.y = 10; // A(-30, 10)
B.x = 29;
B.y = -15; // B(29, -15)
P.x = 15;
P.y = 28; // P(15, 28)
int direction = directionOfPoint(A, B, P);
if (direction == 1)
Console.WriteLine("Right Direction");
else if (direction == -1)
Console.WriteLine("Left Direction");
else
Console.WriteLine("Point is on the Line");
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumarJavascript
输出:
Right Direction如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。