我们已经讨论了检测两个给定线段是否相交的问题。在这篇文章中,我们扩展了问题。在这里,我们给了n个线段,我们需要找出两个线段是否相交。
朴素算法解决此问题的朴素解决方案是检查每对线,并检查线对是否相交。我们可以检查O(1)时间中的两个线段。因此,该方法需要O(n 2 )。
扫描线算法:我们可以使用扫描线算法在O(nLogn)时间内解决此问题。该算法首先沿x轴从左到右对端点进行排序,然后使一条垂直线从左到右穿过所有点,并检查相交点。以下是详细步骤。
1)让n条给定的行。必须有2n个端点才能代表n条线。根据x坐标对所有点进行排序。排序时,维护一个标志以指示该点是其线的左点还是右点。
2)从最左边的点开始。遵循每一点
….. a)如果当前点是其线段的左点,请检查其线段与其正上方和正下方的线段的交点。并将其线添加到活动线段(可以看到其左端点但尚未看到右端点的线段)。请注意,我们仅考虑那些仍处于活动状态的邻居。
…。 b)如果当前点是正确的点,则从活动列表中删除其线段,并检查其两个活动邻居(正好位于上方和下方的点)是否相交。
步骤2就像是从最左边的点到最右边的点从所有点传递一条垂直线一样。这就是为什么将该算法称为“扫描线算法”的原因。扫描线技术在许多其他几何算法中很有用,例如计算2D Voronoi图
应该使用哪些数据结构来有效实施?
在第2步中,我们需要存储所有活动线段。我们需要有效地执行以下操作:
a)插入新的线段
b)删除线段
c)根据y坐标值找到前任和后任
上述操作的明显选择是自平衡二进制搜索树,例如AVL树,红黑树。使用自平衡BST,我们可以在O(Logn)时间内完成上述所有操作。
另外,在步骤1中,我们可以使用最小堆数据结构来代替排序。构建一个最小堆需要O(n)时间,每个提取min操作都需要O(Logn)时间(请参阅此内容)。
伪代码:
以下伪代码不使用堆。它只是对数组进行排序。
sweepLineIntersection(Points[0..2n-1]):
1. Sort Points[] from left to right (according to x coordinate)
2. Create an empty Self-Balancing BST T. It will contain
all active line Segments ordered by y coordinate.
// Process all 2n points
3. for i = 0 to 2n-1
// If this point is left end of its line
if (Points[i].isLeft)
T.insert(Points[i].line()) // Insert into the tree
// Check if this points intersects with its predecessor and successor
if ( doIntersect(Points[i].line(), T.pred(Points[i].line()) )
return true
if ( doIntersect(Points[i].line(), T.succ(Points[i].line()) )
return true
else // If it's a right end of its line
// Check if its predecessor and successor intersect with each other
if ( doIntersect(T.pred(Points[i].line(), T.succ(Points[i].line()))
return true
T.delete(Points[i].line()) // Delete from tree
4. return False例子:
让我们考虑下面的示例。有5个线段1,2,3,4和5。绿点线表示扫掠线。
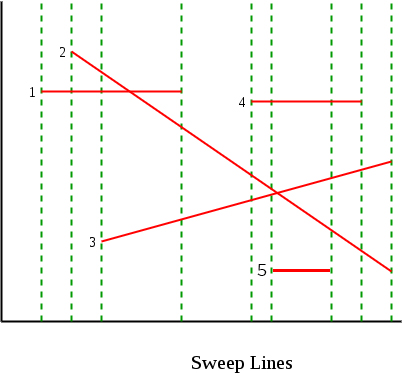
以下是算法所遵循的步骤。从左到右的所有点都一一处理。我们维护一个自平衡的二进制搜索树。
处理线段1的左端点:将1插入到Tree中。该树包含1 。没有路口。
处理线段2的左端点:检查1和2的交点。 2被插入到Tree中。没有路口。该树包含1,2。
处理线段3的左端点:检查3与1的交点。没有路口。 3被插入到树中。该树包含2,1,3。
处理线段1的右端点:从树中删除1。检查2和3的交点。报告了2和3的交点。该树包含2,3。请注意,上面的伪代码将在此时返回。我们可以从这里继续报告所有交叉点。
处理线段4的左端点:检查线4与线2和3的交点。没有路口。 4被插入到树中。该树包含2,4,3。
处理线段5的左端点:检查5与3的交点。没有路口。 5被插入到树中。该树包含2、4、3、5 。
处理线段5的右端点:从树中删除5。该树包含2,4,3。
处理线段4的右端点:从树中删除4。该树包含2,4,3。检查2与3的交集。报告了2与3的交集。该树包含2,3。请注意,将再次报告2和3的交集。我们可以添加一些逻辑来检查重复项。
处理线段2和3的右端点:两者都从树中删除,并且树变为空。
C++14
// Implementation of Sweep Line Algorithm
#include
using namespace std;
// A point in 2D plane
struct Point
{
int x, y;
};
// A line segment with left as Point
// with smaller x value and right with
// larger x value.
struct Segment
{
Point left, right;
};
// An event for sweep line algorithm
// An event has a point, the position
// of point (whether left or right) and
// index of point in the original input
// array of segments.
struct Event {
int x, y;
bool isLeft;
int index;
Event(int x, int y, bool l, int i) : x(x), y(y), isLeft(l), index(i) {}
// This is for maintaining the order in set.
bool operator<(const Event& e) const {
return y < e.y;
}
};
// Given three colinear points p, q, r, the function checks if
// point q lies on line segment 'pr'
bool onSegment(Point p, Point q, Point r)
{
if (q.x <= max(p.x, r.x) && q.x >= min(p.x, r.x) &&
q.y <= max(p.y, r.y) && q.y >= min(p.y, r.y))
return true;
return false;
}
// To find orientation of ordered triplet (p, q, r).
// The function returns following values
// 0 --> p, q and r are colinear
// 1 --> Clockwise
// 2 --> Counterclockwise
int orientation(Point p, Point q, Point r)
{
// See https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/orientation-3-ordered-points/
// for details of below formula.
int val = (q.y - p.y) * (r.x - q.x) -
(q.x - p.x) * (r.y - q.y);
if (val == 0) return 0; // colinear
return (val > 0)? 1: 2; // clock or counterclock wise
}
// The main function that returns true if line segment 'p1q1'
// and 'p2q2' intersect.
bool doIntersect(Segment s1, Segment s2)
{
Point p1 = s1.left, q1 = s1.right, p2 = s2.left, q2 = s2.right;
// Find the four orientations needed for general and
// special cases
int o1 = orientation(p1, q1, p2);
int o2 = orientation(p1, q1, q2);
int o3 = orientation(p2, q2, p1);
int o4 = orientation(p2, q2, q1);
// General case
if (o1 != o2 && o3 != o4)
return true;
// Special Cases
// p1, q1 and p2 are colinear and p2 lies on segment p1q1
if (o1 == 0 && onSegment(p1, p2, q1)) return true;
// p1, q1 and q2 are colinear and q2 lies on segment p1q1
if (o2 == 0 && onSegment(p1, q2, q1)) return true;
// p2, q2 and p1 are colinear and p1 lies on segment p2q2
if (o3 == 0 && onSegment(p2, p1, q2)) return true;
// p2, q2 and q1 are colinear and q1 lies on segment p2q2
if (o4 == 0 && onSegment(p2, q1, q2)) return true;
return false; // Doesn't fall in any of the above cases
}
// Find predecessor of iterator in s.
auto pred(set &s, set::iterator it) {
return it == s.begin() ? s.end() : --it;
}
// Find successor of iterator in s.
auto succ(set &s, set::iterator it) {
return ++it;
}
// Returns true if any two lines intersect.
bool isIntersect(Segment arr[], int n)
{
// Pushing all points to a vector of events
vector e;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
e.push_back(Event(arr[i].left.x, arr[i].left.y, true, i));
e.push_back(Event(arr[i].right.x, arr[i].right.y, false, i));
}
// Sorting all events according to x coordinate.
sort(e.begin(), e.end(), [](Event &e1, Event &e2) {return e1.x < e2.x;});
// For storing active segments.
set s;
// Traversing through sorted points
for (int i=0; i<2*n; i++)
{
Event curr = e[i];
int index = curr.index;
// If current point is left of its segment
if (curr.isLeft)
{
// Get above and below points
auto next = s.lower_bound(curr);
auto prev = pred(s, next);
// Check if current point intersects with
// any of its adjacent
if (next != s.end() && doIntersect(arr[next->index], arr[index]))
return true;
if (prev != s.end() && doIntersect(arr[prev->index], arr[index]))
return true;
// Insert current point (or event)
s.insert(curr);
}
// If current point is right of its segment
else
{
// Find the iterator
auto it = s.find(curr);
// Find above and below points
auto next = succ(s, it);
auto prev = pred(s, it);
// If above and below point intersect
if (next != s.end() && prev != s.end())
if (doIntersect(arr[prev->index], arr[next->index]))
return true;
// Return current point
s.erase(curr);
}
}
return false;
}
// Driver code
int main() {
Segment arr[] = { {{0, 0}, {0, 4}}, {{1, 0}, {5, 0}}};
int n = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
cout << isIntersect(arr, n);
return 0;
} 输出:
0
时间复杂度:第一步是排序,这需要O(nLogn)时间。第二步处理2n点,处理每个点需要O(Logn)时间。因此,整体时间复杂度为O(nLogn)
参考:
http://www.cs.uiuc.edu/~jeffe/teaching/373/notes/x06-sweepline.pdf
http://courses.csail.mit.edu/6.006/spring11/lectures/lec24.pdf
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dePDHVovJlE
http://www.eecs.wsu.edu/~cook/aa/lectures/l25/node10.html