给定两个图G1和G2 ,任务是找到两个给定图的并集和交集,即(G1 ∪ G2)和(G1 ∩ G2) 。
例子:
Input: G1 = { (“e1”, 1, 2), (“e2”, 1, 3), (“e3”, 3, 4), (“e4”, 2, 4) }, G2 = = { (“e4”, 2, 4), (“e5”, 2, 5), (“e6”, 4, 5) }
Output:
G1 union G2 is
e1 1 2
e2 1 3
e3 3 4
e4 2 4
e5 2 5
e6 4 5
G1 intersection G2 is
e4 2 4
Explanation:
Union of the graphs G1 and G2:
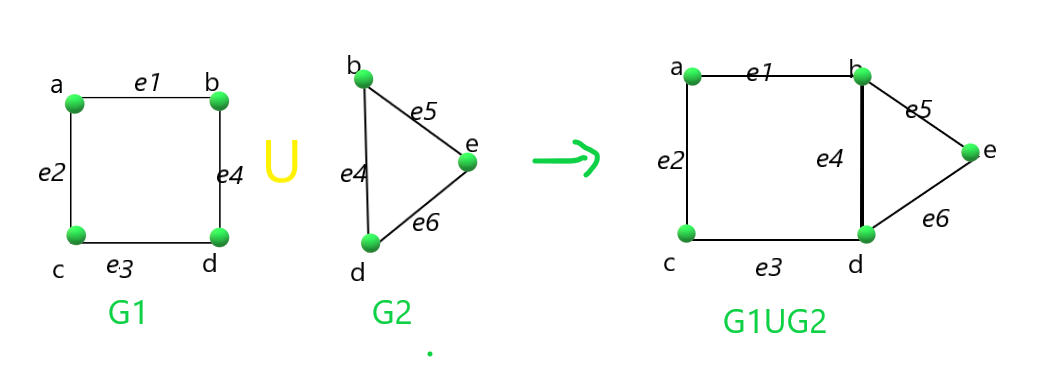
Intersection of the graphs G1 and G2:
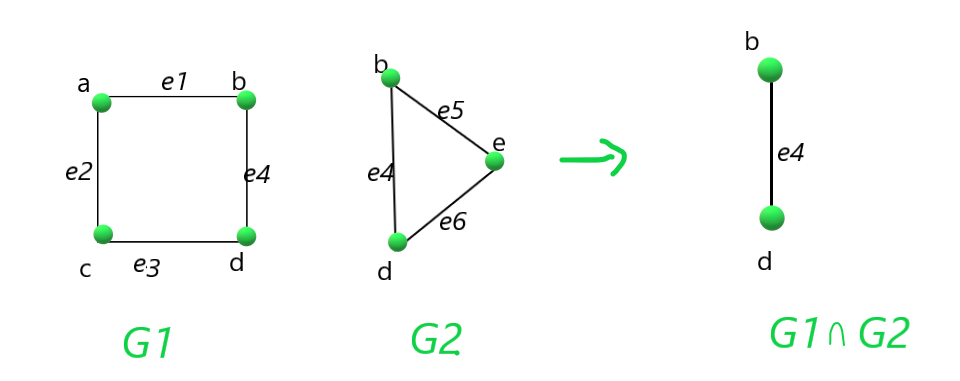
处理方法:按照以下步骤解决问题:
- 定义一个函数,比如Union(G1, G2) ,以找到G1和G2 的并集:
- 初始化一个地图,比如added ,它存储是否已经添加了一条边。
- 遍历图G1的边并推入图中的所有边,比如G ,并标记在added 中访问过的所有边。
- 现在,再次遍历图G2的边,如果还没有添加边,则将边推入G 中,然后在添加的地图中标记添加的边。
- 定义一个函数say Intersection(G1, G2)来找到G1和G2的交集:
- 初始化一个地图,比如added ,它存储是否已经添加了一条边。
- 遍历图G1的边并标记添加的地图中访问的所有边。
- 现在,再次遍历图G2的边并推动图G 中的边(如果已经添加了边)。然后,标记添加到地图中的边。
- 现在,打印Union(G1, G2)和Intersection(G1, G2)函数调用后得到的图形。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++14
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to find union of two graphs
void find_union(
vector > G1,
vector > G2)
{
// Stores an edge of the graph G1
map > added;
// Stores the unioun graph G1
vector > G;
// Iterate over the edges
// of the graph G1
for (auto p : G1) {
string a = get<0>(p);
// Get the edges
int b = get<1>(p);
int c = get<2>(p);
// Insert the current
// edges into graph G
G.push_back(
make_tuple(a, b, c));
added[a] = { b, c };
}
// Iterate over the edges
// of the graph G1
for (auto p : G2) {
string a = get<0>(p);
int b = get<1>(p);
int c = get<2>(p);
pair x = { b, c };
pair y = { c, b };
// If either edge x or
// y is already added
if (added[a] == x || added[a] == y)
continue;
// Otherwise
G.push_back(make_tuple(a, b, c));
}
// Print the unioun
cout << "G1 union G2 is\n";
for (auto p : G) {
string a = get<0>(p);
int b = get<1>(p);
int c = get<2>(p);
cout << a << " " << b << " "
<< c << endl;
}
}
// Function to find intersection of two graphs
void find_intersection(
vector > G1,
vector > G2)
{
// Stores an edge
map > added;
// Stores the graph of intersection
vector > G;
// Iterate over edges of graph G1
for (auto p : G1) {
string a = get<0>(p);
int b = get<1>(p);
int c = get<2>(p);
added[a] = { b, c };
}
// Iterate over edges of graph G2
for (auto p : G2) {
string a = get<0>(p);
int b = get<1>(p);
int c = get<2>(p);
pair x = { b, c };
pair y = { c, b };
// If either edge x or
// y is already added
if (added[a] == x || added[a] == y)
G.push_back(make_tuple(a, b, c));
}
// Print the graph G
cout << "G1 intersection G2 is\n";
for (auto p : G) {
string a = get<0>(p);
int b = get<1>(p);
int c = get<2>(p);
cout << a << " " << b
<< " " << c << endl;
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
vector > G1
= { make_tuple("e1", 1, 2),
make_tuple("e2", 1, 3),
make_tuple("e3", 3, 4),
make_tuple("e4", 2, 4) };
vector > G2
= { make_tuple("e4", 2, 4),
make_tuple("e5", 2, 5),
make_tuple("e6", 4, 5) };
// Function call for finding the
// Union of the given graph
find_union(G1, G2);
// Function call for finding the
// Intersection of the given graph
find_intersection(G1, G2);
return 0;
} 输出:
G1 union G2 is
e1 1 2
e2 1 3
e3 3 4
e4 2 4
e5 2 5
e6 4 5
G1 intersection G2 is
e4 2 4
时间复杂度: O(N * log(N))
辅助空间: O(N)
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。