将链表表示的两个数字相加 | 2套
给定由两个链表表示的两个数字,编写一个返回总和列表的函数。和表是两个输入数相加的链表表示。不允许修改列表。此外,不允许使用显式的额外空间(提示:使用递归)。
示例:
Input:
First List: 5->6->3
Second List: 8->4->2
Output
Resultant list: 1->4->0->5我们在这里讨论了一个用于链表的解决方案,其中最低有效数字是列表的第一个节点,最高有效数字是最后一个节点。在这个问题中,最重要的节点是第一个节点,最不重要的数字是最后一个节点,我们不允许修改列表。这里使用递归来计算从右到左的总和。
以下是步骤。
1)计算给定两个链表的大小。
2)如果大小相同,则使用递归计算总和。将所有节点保持在递归调用堆栈中直到最右边的节点,计算最右边的节点之和并向前进位到左侧。
3)如果大小不一样,请按照以下步骤操作:
…… a)计算两个链表的大小差异。让差是DIFF
…… b)在更大的链表中向前移动diff节点。现在使用步骤 2 计算较小列表和较大列表的右子列表(相同大小)的总和。此外,存储此总和的进位。
…… c)计算进位(在上一步中计算)与较大列表的剩余左子列表的总和。这个总和的节点被添加到上一步获得的总和列表的开头。
以下是上述方法的试运行:
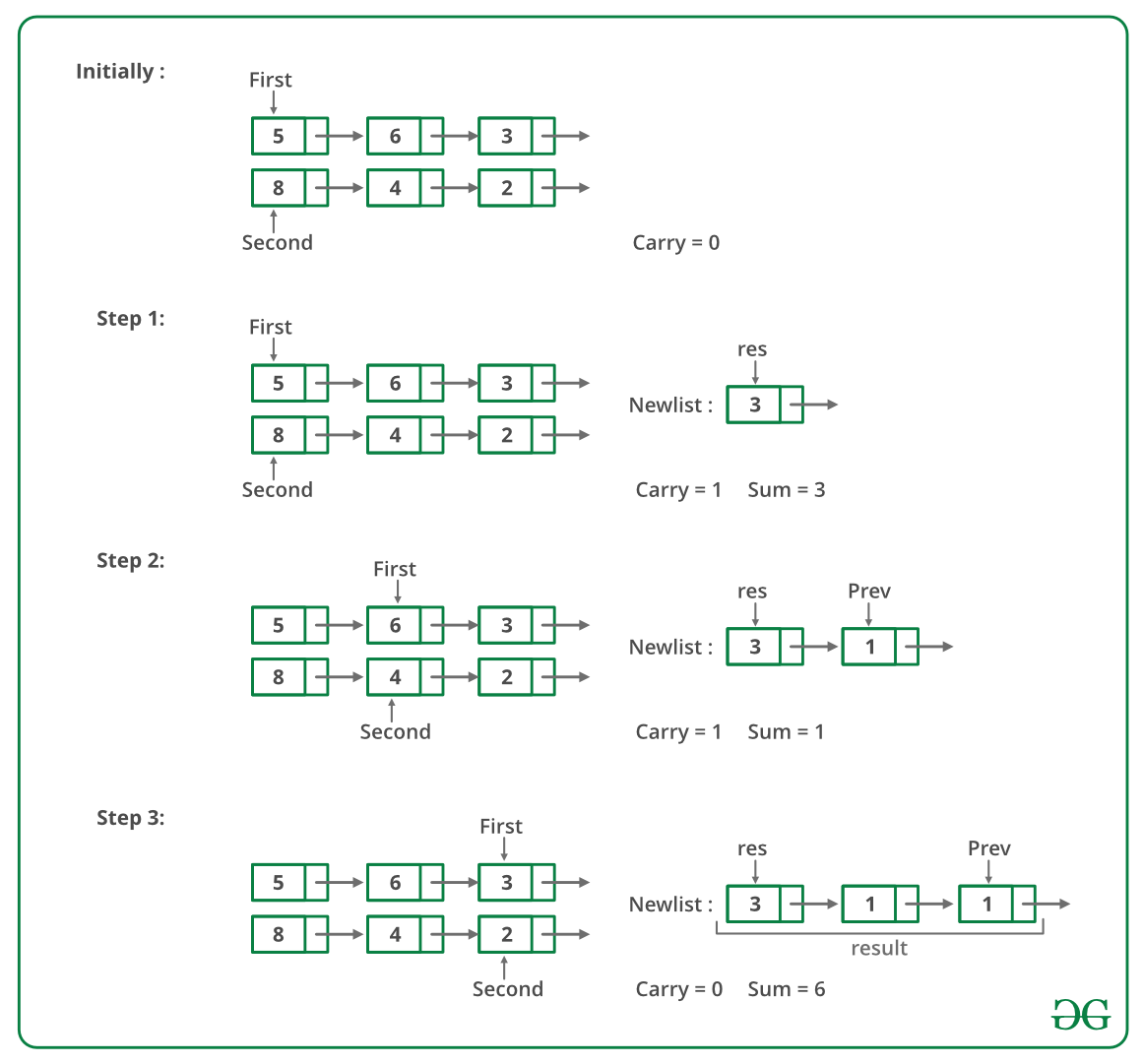
下图是上述方法的实现。
C++
// A C++ recursive program to add two linked lists
#include
using namespace std;
// A linked List Node
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
typedef Node node;
/* A utility function to insert
a node at the beginning of linked list */
void push(Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
/* allocate node */
Node* new_node = new Node[(sizeof(Node))];
/* put in the data */
new_node->data = new_data;
/* link the old list off the new node */
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
/* move the head to point to the new node */
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
/* A utility function to print linked list */
void printList(Node* node)
{
while (node != NULL) {
cout << node->data << " ";
node = node->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
// A utility function to swap two pointers
void swapPointer(Node** a, Node** b)
{
node* t = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = t;
}
/* A utility function to get size of linked list */
int getSize(Node* node)
{
int size = 0;
while (node != NULL) {
node = node->next;
size++;
}
return size;
}
// Adds two linked lists of same size
// represented by head1 and head2 and returns
// head of the resultant linked list. Carry
// is propagated while returning from the recursion
node* addSameSize(Node* head1, Node* head2, int* carry)
{
// Since the function assumes linked lists are of same
// size, check any of the two head pointers
if (head1 == NULL)
return NULL;
int sum;
// Allocate memory for sum node of current two nodes
Node* result = new Node[(sizeof(Node))];
// Recursively add remaining nodes and get the carry
result->next
= addSameSize(head1->next, head2->next, carry);
// add digits of current nodes and propagated carry
sum = head1->data + head2->data + *carry;
*carry = sum / 10;
sum = sum % 10;
// Assigne the sum to current node of resultant list
result->data = sum;
return result;
}
// This function is called after the
// smaller list is added to the bigger
// lists's sublist of same size. Once the
// right sublist is added, the carry
// must be added toe left side of larger
// list to get the final result.
void addCarryToRemaining(Node* head1, Node* cur, int* carry,
Node** result)
{
int sum;
// If diff. number of nodes are not traversed, add carry
if (head1 != cur) {
addCarryToRemaining(head1->next, cur, carry,
result);
sum = head1->data + *carry;
*carry = sum / 10;
sum %= 10;
// add this node to the front of the result
push(result, sum);
}
}
// The main function that adds two linked lists
// represented by head1 and head2. The sum of
// two lists is stored in a list referred by result
void addList(Node* head1, Node* head2, Node** result)
{
Node* cur;
// first list is empty
if (head1 == NULL) {
*result = head2;
return;
}
// second list is empty
else if (head2 == NULL) {
*result = head1;
return;
}
int size1 = getSize(head1);
int size2 = getSize(head2);
int carry = 0;
// Add same size lists
if (size1 == size2)
*result = addSameSize(head1, head2, &carry);
else {
int diff = abs(size1 - size2);
// First list should always be larger than second
// list. If not, swap pointers
if (size1 < size2)
swapPointer(&head1, &head2);
// move diff. number of nodes in first list
for (cur = head1; diff--; cur = cur->next)
;
// get addition of same size lists
*result = addSameSize(cur, head2, &carry);
// get addition of remaining first list and carry
addCarryToRemaining(head1, cur, &carry, result);
}
// if some carry is still there, add a new node to the
// fron of the result list. e.g. 999 and 87
if (carry)
push(result, carry);
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
Node *head1 = NULL, *head2 = NULL, *result = NULL;
int arr1[] = { 9, 9, 9 };
int arr2[] = { 1, 8 };
int size1 = sizeof(arr1) / sizeof(arr1[0]);
int size2 = sizeof(arr2) / sizeof(arr2[0]);
// Create first list as 9->9->9
int i;
for (i = size1 - 1; i >= 0; --i)
push(&head1, arr1[i]);
// Create second list as 1->8
for (i = size2 - 1; i >= 0; --i)
push(&head2, arr2[i]);
addList(head1, head2, &result);
printList(result);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by rathbhupendra C
// A C recursive program to add two linked lists
#include
#include
// A linked List Node
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
};
typedef struct Node node;
/* A utility function to insert a
node at the beginning of
* linked list */
void push(struct Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
/* allocate node */
struct Node* new_node
= (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
/* put in the data */
new_node->data = new_data;
/* link the old list off the new node */
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
/* move the head to point to the new node */
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
/* A utility function to print linked list */
void printList(struct Node* node)
{
while (node != NULL) {
printf("%d ", node->data);
node = node->next;
}
printf("n");
}
// A utility function to swap two pointers
void swapPointer(Node** a, Node** b)
{
node* t = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = t;
}
/* A utility function to get size
of linked list */
int getSize(struct Node* node)
{
int size = 0;
while (node != NULL) {
node = node->next;
size++;
}
return size;
}
// Adds two linked lists of same
// size represented by head1
// and head2 and returns head of
// the resultant linked list.
// Carry is propagated while
// returning from the recursion
node* addSameSize(Node* head1,
Node* head2, int* carry)
{
// Since the function assumes
// linked lists are of same
// size, check any of the two
// head pointers
if (head1 == NULL)
return NULL;
int sum;
// Allocate memory for sum
// node of current two nodes
Node* result = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
// Recursively add remaining nodes
// and get the carry
result->next
= addSameSize(head1->next,
head2->next, carry);
// add digits of current nodes
// and propagated carry
sum = head1->data + head2->data + *carry;
*carry = sum / 10;
sum = sum % 10;
// Assigne the sum to current
// node of resultant list
result->data = sum;
return result;
}
// This function is called after
// the smaller list is added
// to the bigger lists's sublist
// of same size. Once the
// right sublist is added, the
// carry must be added toe left
// side of larger list to get
// the final result.
void addCarryToRemaining(Node* head1,
Node* cur, int* carry,
Node** result)
{
int sum;
// If diff. number of nodes are
// not traversed, add carry
if (head1 != cur) {
addCarryToRemaining(head1->next,
cur, carry,
result);
sum = head1->data + *carry;
*carry = sum / 10;
sum %= 10;
// add this node to the front of the result
push(result, sum);
}
}
// The main function that adds two
// linked lists represented
// by head1 and head2. The sum of
// two lists is stored in a
// list referred by result
void addList(Node* head1,
Node* head2, Node** result)
{
Node* cur;
// first list is empty
if (head1 == NULL) {
*result = head2;
return;
}
// second list is empty
else if (head2 == NULL)
{
*result = head1;
return;
}
int size1 = getSize(head1);
int size2 = getSize(head2);
int carry = 0;
// Add same size lists
if (size1 == size2)
*result = addSameSize(head1, head2, &carry);
else {
int diff = abs(size1 - size2);
// First list should always be
// larger than second
// list. If not, swap pointers
if (size1 < size2)
swapPointer(&head1, &head2);
// move diff. number of nodes in first list
for (cur = head1; diff--; cur = cur->next)
;
// get addition of same size lists
*result = addSameSize(cur,
head2, &carry);
// get addition of remaining first list and carry
addCarryToRemaining(head1,
cur, &carry, result);
}
// if some carry is still there, add a new node to the
// fron of the result list. e.g. 999 and 87
if (carry)
push(result, carry);
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
Node *head1 = NULL, *head2 = NULL, *result = NULL;
int arr1[] = { 9, 9, 9 };
int arr2[] = { 1, 8 };
int size1 = sizeof(arr1) / sizeof(arr1[0]);
int size2 = sizeof(arr2) / sizeof(arr2[0]);
// Create first list as 9->9->9
int i;
for (i = size1 - 1; i >= 0; --i)
push(&head1, arr1[i]);
// Create second list as 1->8
for (i = size2 - 1; i >= 0; --i)
push(&head2, arr2[i]);
addList(head1, head2, &result);
printList(result);
return 0;
} Java
// A Java recursive program to add two linked lists
public class linkedlistATN
{
class node
{
int val;
node next;
public node(int val)
{
this.val = val;
}
}
// Function to print linked list
void printlist(node head)
{
while (head != null)
{
System.out.print(head.val + " ");
head = head.next;
}
}
node head1, head2, result;
int carry;
/* A utility function to push a value to linked list */
void push(int val, int list)
{
node newnode = new node(val);
if (list == 1)
{
newnode.next = head1;
head1 = newnode;
}
else if (list == 2)
{
newnode.next = head2;
head2 = newnode;
}
else
{
newnode.next = result;
result = newnode;
}
}
// Adds two linked lists of same size represented by
// head1 and head2 and returns head of the resultant
// linked list. Carry is propagated while returning
// from the recursion
void addsamesize(node n, node m)
{
// Since the function assumes linked lists are of
// same size, check any of the two head pointers
if (n == null)
return;
// Recursively add remaining nodes and get the carry
addsamesize(n.next, m.next);
// add digits of current nodes and propagated carry
int sum = n.val + m.val + carry;
carry = sum / 10;
sum = sum % 10;
// Push this to result list
push(sum, 3);
}
node cur;
// This function is called after the smaller list is
// added to the bigger lists's sublist of same size.
// Once the right sublist is added, the carry must be
// added to the left side of larger list to get the
// final result.
void propogatecarry(node head1)
{
// If diff. number of nodes are not traversed, add carry
if (head1 != cur)
{
propogatecarry(head1.next);
int sum = carry + head1.val;
carry = sum / 10;
sum %= 10;
// add this node to the front of the result
push(sum, 3);
}
}
int getsize(node head)
{
int count = 0;
while (head != null)
{
count++;
head = head.next;
}
return count;
}
// The main function that adds two linked lists
// represented by head1 and head2. The sum of two
// lists is stored in a list referred by result
void addlists()
{
// first list is empty
if (head1 == null)
{
result = head2;
return;
}
// first list is empty
if (head2 == null)
{
result = head1;
return;
}
int size1 = getsize(head1);
int size2 = getsize(head2);
// Add same size lists
if (size1 == size2)
{
addsamesize(head1, head2);
}
else
{
// First list should always be larger than second list.
// If not, swap pointers
if (size1 < size2)
{
node temp = head1;
head1 = head2;
head2 = temp;
}
int diff = Math.abs(size1 - size2);
// move diff. number of nodes in first list
node temp = head1;
while (diff-- >= 0)
{
cur = temp;
temp = temp.next;
}
// get addition of same size lists
addsamesize(cur, head2);
// get addition of remaining first list and carry
propogatecarry(head1);
}
// if some carry is still there, add a new node to
// the front of the result list. e.g. 999 and 87
if (carry > 0)
push(carry, 3);
}
// Driver program to test above functions
public static void main(String args[])
{
linkedlistATN list = new linkedlistATN();
list.head1 = null;
list.head2 = null;
list.result = null;
list.carry = 0;
int arr1[] = { 9, 9, 9 };
int arr2[] = { 1, 8 };
// Create first list as 9->9->9
for (int i = arr1.length - 1; i >= 0; --i)
list.push(arr1[i], 1);
// Create second list as 1->8
for (int i = arr2.length - 1; i >= 0; --i)
list.push(arr2[i], 2);
list.addlists();
list.printlist(list.result);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rishabh MahrseeC#
// A C# recursive program to add two linked lists
using System;
public class linkedlistATN{
class node
{
public int val;
public node next;
public node(int val)
{
this.val = val;
}
}
// Function to print linked list
void printlist(node head)
{
while (head != null)
{
Console.Write(head.val + " ");
head = head.next;
}
}
node head1, head2, result;
int carry;
// A utility function to push a
// value to linked list
void push(int val, int list)
{
node newnode = new node(val);
if (list == 1)
{
newnode.next = head1;
head1 = newnode;
}
else if (list == 2)
{
newnode.next = head2;
head2 = newnode;
}
else
{
newnode.next = result;
result = newnode;
}
}
// Adds two linked lists of same size represented by
// head1 and head2 and returns head of the resultant
// linked list. Carry is propagated while returning
// from the recursion
void addsamesize(node n, node m)
{
// Since the function assumes linked
// lists are of same size, check any
// of the two head pointers
if (n == null)
return;
// Recursively add remaining nodes
// and get the carry
addsamesize(n.next, m.next);
// Add digits of current nodes
// and propagated carry
int sum = n.val + m.val + carry;
carry = sum / 10;
sum = sum % 10;
// Push this to result list
push(sum, 3);
}
node cur;
// This function is called after the smaller
// list is added to the bigger lists's sublist
// of same size. Once the right sublist is added,
// the carry must be added to the left side of
// larger list to get the final result.
void propogatecarry(node head1)
{
// If diff. number of nodes are
// not traversed, add carry
if (head1 != cur)
{
propogatecarry(head1.next);
int sum = carry + head1.val;
carry = sum / 10;
sum %= 10;
// Add this node to the front
// of the result
push(sum, 3);
}
}
int getsize(node head)
{
int count = 0;
while (head != null)
{
count++;
head = head.next;
}
return count;
}
// The main function that adds two linked
// lists represented by head1 and head2.
// The sum of two lists is stored in a
// list referred by result
void addlists()
{
// First list is empty
if (head1 == null)
{
result = head2;
return;
}
// Second list is empty
if (head2 == null)
{
result = head1;
return;
}
int size1 = getsize(head1);
int size2 = getsize(head2);
// Add same size lists
if (size1 == size2)
{
addsamesize(head1, head2);
}
else
{
// First list should always be
// larger than second list.
// If not, swap pointers
if (size1 < size2)
{
node temp = head1;
head1 = head2;
head2 = temp;
}
int diff = Math.Abs(size1 - size2);
// Move diff. number of nodes in
// first list
node tmp = head1;
while (diff-- >= 0)
{
cur = tmp;
tmp = tmp.next;
}
// Get addition of same size lists
addsamesize(cur, head2);
// Get addition of remaining
// first list and carry
propogatecarry(head1);
}
// If some carry is still there,
// add a new node to the front of
// the result list. e.g. 999 and 87
if (carry > 0)
push(carry, 3);
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(string []args)
{
linkedlistATN list = new linkedlistATN();
list.head1 = null;
list.head2 = null;
list.result = null;
list.carry = 0;
int []arr1 = { 9, 9, 9 };
int []arr2 = { 1, 8 };
// Create first list as 9->9->9
for(int i = arr1.Length - 1; i >= 0; --i)
list.push(arr1[i], 1);
// Create second list as 1->8
for(int i = arr2.Length - 1; i >= 0; --i)
list.push(arr2[i], 2);
list.addlists();
list.printlist(list.result);
}
}
// This code is contributed by rutvik_56Javascript
C++
// C++ Iterative program to add two linked lists
#include
using namespace std;
// A linked List Node
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
// to push a new node to linked list
void push(Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
/* allocate node */
Node* new_node = new Node[(sizeof(Node))];
/* put in the data */
new_node->data = new_data;
/* link the old list off the new node */
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
/* move the head to point to the new node */
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
// to add two new numbers
Node* addTwoNumList(Node* l1, Node* l2) {
stack s1,s2;
while(l1!=NULL){
s1.push(l1->data);
l1=l1->next;
}
while(l2!=NULL){
s2.push(l2->data);
l2=l2->next;
}
int carry=0;
Node* result=NULL;
while(s1.empty()==false || s2.empty()==false){
int a=0,b=0;
if(s1.empty()==false){
a=s1.top();s1.pop();
}
if(s2.empty()==false){
b=s2.top();s2.pop();
}
int total=a+b+carry;
Node* temp=new Node();
temp->data=total%10;
carry=total/10;
if(result==NULL){
result=temp;
}else{
temp->next=result;
result=temp;
}
}
if(carry!=0){
Node* temp=new Node();
temp->data=carry;
temp->next=result;
result=temp;
}
return result;
}
// to print a linked list
void printList(Node *node)
{
while (node != NULL)
{
cout<data<<" ";
node = node->next;
}
cout<6->7
int i;
for (i = size1-1; i >= 0; --i)
push(&head1, arr1[i]);
// Create second list as 1->8
for (i = size2-1; i >= 0; --i)
push(&head2, arr2[i]);
Node* result=addTwoNumList(head1, head2);
printList(result);
return 0;
} Java
// Java Iterative program to add
// two linked lists
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static class Node
{
int data;
Node next;
public Node(int data)
{
this.data = data;
}
}
static Node l1, l2, result;
// To push a new node to linked list
public static void push(int new_data)
{
// Allocate node
Node new_node = new Node(0);
// Put in the data
new_node.data = new_data;
// Link the old list off the new node
new_node.next = l1;
// Move the head to point to the new node
l1 = new_node;
}
public static void push1(int new_data)
{
// Allocate node
Node new_node = new Node(0);
// Put in the data
new_node.data = new_data;
// Link the old list off the new node
new_node.next = l2;
// Move the head to point to
// the new node
l2 = new_node;
}
// To add two new numbers
public static Node addTwoNumbers()
{
Stack stack1 = new Stack<>();
Stack stack2 = new Stack<>();
while (l1 != null)
{
stack1.add(l1.data);
l1 = l1.next;
}
while (l2 != null)
{
stack2.add(l2.data);
l2 = l2.next;
}
int carry = 0;
Node result = null;
while (!stack1.isEmpty() ||
!stack2.isEmpty())
{
int a = 0, b = 0;
if (!stack1.isEmpty())
{
a = stack1.pop();
}
if (!stack2.isEmpty())
{
b = stack2.pop();
}
int total = a + b + carry;
Node temp = new Node(total % 10);
carry = total / 10;
if (result == null)
{
result = temp;
}
else
{
temp.next = result;
result = temp;
}
}
if (carry != 0)
{
Node temp = new Node(carry);
temp.next = result;
result = temp;
}
return result;
}
// To print a linked list
public static void printList()
{
while (result != null)
{
System.out.print(result.data + " ");
result = result.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr1[] = { 5, 6, 7 };
int arr2[] = { 1, 8 };
int size1 = 3;
int size2 = 2;
// Create first list as 5->6->7
int i;
for(i = size1 - 1; i >= 0; --i)
push(arr1[i]);
// Create second list as 1->8
for(i = size2 - 1; i >= 0; --i)
push1(arr2[i]);
result = addTwoNumbers();
printList();
}
}
// This code is contributed by RohitOberoi C#
// C# Iterative program to add
// two linked lists
using System;
using System.Collections;
class GFG{
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node next;
public Node(int data)
{
this.data = data;
}
}
static Node l1, l2, result;
// To push a new node to linked list
public static void push(int new_data)
{
// Allocate node
Node new_node = new Node(0);
// Put in the data
new_node.data = new_data;
// Link the old list off the new node
new_node.next = l1;
// Move the head to point to the new node
l1 = new_node;
}
public static void push1(int new_data)
{
// Allocate node
Node new_node = new Node(0);
// Put in the data
new_node.data = new_data;
// Link the old list off the new node
new_node.next = l2;
// Move the head to point to
// the new node
l2 = new_node;
}
// To add two new numbers
public static Node addTwoNumbers()
{
Stack stack1 = new Stack();
Stack stack2 = new Stack();
while (l1 != null)
{
stack1.Push(l1.data);
l1 = l1.next;
}
while (l2 != null)
{
stack2.Push(l2.data);
l2 = l2.next;
}
int carry = 0;
Node result = null;
while (stack1.Count != 0 ||
stack2.Count != 0)
{
int a = 0, b = 0;
if (stack1.Count != 0)
{
a = (int)stack1.Pop();
}
if (stack2.Count != 0)
{
b = (int)stack2.Pop();
}
int total = a + b + carry;
Node temp = new Node(total % 10);
carry = total / 10;
if (result == null)
{
result = temp;
}
else
{
temp.next = result;
result = temp;
}
}
if (carry != 0)
{
Node temp = new Node(carry);
temp.next = result;
result = temp;
}
return result;
}
// To print a linked list
public static void printList()
{
while (result != null)
{
Console.Write(result.data + " ");
result = result.next;
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
int []arr1 = { 5, 6, 7 };
int []arr2 = { 1, 8 };
int size1 = 3;
int size2 = 2;
// Create first list as 5->6->7
int i;
for(i = size1 - 1; i >= 0; --i)
push(arr1[i]);
// Create second list as 1->8
for(i = size2 - 1; i >= 0; --i)
push1(arr2[i]);
result = addTwoNumbers();
printList();
}
}
// This code is contributed by pratham76Javascript
输出
1 0 1 7时间复杂度:O(m+n) 其中 m 和 n 是给定两个链表的大小。
迭代方法:
这个实现没有任何递归调用开销,这意味着它是一个迭代解决方案。
因为我们需要从两个链表中的最后一个开始添加数字。所以,这里我们将使用堆栈数据结构来实现这一点。
- 我们将首先从给定的两个链表中创建两个堆栈。
- 然后,我们将运行一个循环,直到堆栈都变空。
- 在每次迭代中,我们都会跟踪进位。
- 最后,如果进位>0,这意味着我们需要在结果列表的开头额外的节点来容纳这个进位。
C++
// C++ Iterative program to add two linked lists
#include
using namespace std;
// A linked List Node
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
// to push a new node to linked list
void push(Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
/* allocate node */
Node* new_node = new Node[(sizeof(Node))];
/* put in the data */
new_node->data = new_data;
/* link the old list off the new node */
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
/* move the head to point to the new node */
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
// to add two new numbers
Node* addTwoNumList(Node* l1, Node* l2) {
stack s1,s2;
while(l1!=NULL){
s1.push(l1->data);
l1=l1->next;
}
while(l2!=NULL){
s2.push(l2->data);
l2=l2->next;
}
int carry=0;
Node* result=NULL;
while(s1.empty()==false || s2.empty()==false){
int a=0,b=0;
if(s1.empty()==false){
a=s1.top();s1.pop();
}
if(s2.empty()==false){
b=s2.top();s2.pop();
}
int total=a+b+carry;
Node* temp=new Node();
temp->data=total%10;
carry=total/10;
if(result==NULL){
result=temp;
}else{
temp->next=result;
result=temp;
}
}
if(carry!=0){
Node* temp=new Node();
temp->data=carry;
temp->next=result;
result=temp;
}
return result;
}
// to print a linked list
void printList(Node *node)
{
while (node != NULL)
{
cout<data<<" ";
node = node->next;
}
cout<6->7
int i;
for (i = size1-1; i >= 0; --i)
push(&head1, arr1[i]);
// Create second list as 1->8
for (i = size2-1; i >= 0; --i)
push(&head2, arr2[i]);
Node* result=addTwoNumList(head1, head2);
printList(result);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java Iterative program to add
// two linked lists
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static class Node
{
int data;
Node next;
public Node(int data)
{
this.data = data;
}
}
static Node l1, l2, result;
// To push a new node to linked list
public static void push(int new_data)
{
// Allocate node
Node new_node = new Node(0);
// Put in the data
new_node.data = new_data;
// Link the old list off the new node
new_node.next = l1;
// Move the head to point to the new node
l1 = new_node;
}
public static void push1(int new_data)
{
// Allocate node
Node new_node = new Node(0);
// Put in the data
new_node.data = new_data;
// Link the old list off the new node
new_node.next = l2;
// Move the head to point to
// the new node
l2 = new_node;
}
// To add two new numbers
public static Node addTwoNumbers()
{
Stack stack1 = new Stack<>();
Stack stack2 = new Stack<>();
while (l1 != null)
{
stack1.add(l1.data);
l1 = l1.next;
}
while (l2 != null)
{
stack2.add(l2.data);
l2 = l2.next;
}
int carry = 0;
Node result = null;
while (!stack1.isEmpty() ||
!stack2.isEmpty())
{
int a = 0, b = 0;
if (!stack1.isEmpty())
{
a = stack1.pop();
}
if (!stack2.isEmpty())
{
b = stack2.pop();
}
int total = a + b + carry;
Node temp = new Node(total % 10);
carry = total / 10;
if (result == null)
{
result = temp;
}
else
{
temp.next = result;
result = temp;
}
}
if (carry != 0)
{
Node temp = new Node(carry);
temp.next = result;
result = temp;
}
return result;
}
// To print a linked list
public static void printList()
{
while (result != null)
{
System.out.print(result.data + " ");
result = result.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr1[] = { 5, 6, 7 };
int arr2[] = { 1, 8 };
int size1 = 3;
int size2 = 2;
// Create first list as 5->6->7
int i;
for(i = size1 - 1; i >= 0; --i)
push(arr1[i]);
// Create second list as 1->8
for(i = size2 - 1; i >= 0; --i)
push1(arr2[i]);
result = addTwoNumbers();
printList();
}
}
// This code is contributed by RohitOberoi
C#
// C# Iterative program to add
// two linked lists
using System;
using System.Collections;
class GFG{
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node next;
public Node(int data)
{
this.data = data;
}
}
static Node l1, l2, result;
// To push a new node to linked list
public static void push(int new_data)
{
// Allocate node
Node new_node = new Node(0);
// Put in the data
new_node.data = new_data;
// Link the old list off the new node
new_node.next = l1;
// Move the head to point to the new node
l1 = new_node;
}
public static void push1(int new_data)
{
// Allocate node
Node new_node = new Node(0);
// Put in the data
new_node.data = new_data;
// Link the old list off the new node
new_node.next = l2;
// Move the head to point to
// the new node
l2 = new_node;
}
// To add two new numbers
public static Node addTwoNumbers()
{
Stack stack1 = new Stack();
Stack stack2 = new Stack();
while (l1 != null)
{
stack1.Push(l1.data);
l1 = l1.next;
}
while (l2 != null)
{
stack2.Push(l2.data);
l2 = l2.next;
}
int carry = 0;
Node result = null;
while (stack1.Count != 0 ||
stack2.Count != 0)
{
int a = 0, b = 0;
if (stack1.Count != 0)
{
a = (int)stack1.Pop();
}
if (stack2.Count != 0)
{
b = (int)stack2.Pop();
}
int total = a + b + carry;
Node temp = new Node(total % 10);
carry = total / 10;
if (result == null)
{
result = temp;
}
else
{
temp.next = result;
result = temp;
}
}
if (carry != 0)
{
Node temp = new Node(carry);
temp.next = result;
result = temp;
}
return result;
}
// To print a linked list
public static void printList()
{
while (result != null)
{
Console.Write(result.data + " ");
result = result.next;
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
int []arr1 = { 5, 6, 7 };
int []arr2 = { 1, 8 };
int size1 = 3;
int size2 = 2;
// Create first list as 5->6->7
int i;
for(i = size1 - 1; i >= 0; --i)
push(arr1[i]);
// Create second list as 1->8
for(i = size2 - 1; i >= 0; --i)
push1(arr2[i]);
result = addTwoNumbers();
printList();
}
}
// This code is contributed by pratham76
Javascript
输出
5 8 5如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。