将两个数组表示的两个数字相加
给定两个大小分别为n和m的数组A[0….n-1]和B[0….m-1] ,表示两个数字,使得数组的每个元素都代表一个数字。例如,A[] = { 1, 2, 3} 和 B[] = { 2, 1, 4 } 分别代表 123 和 214。任务是找到两个数字的总和。在上述情况下,答案是 337。
例子 :
Input : n = 3, m = 3
a[] = { 1, 2, 3 }
b[] = { 2, 1, 4 }
Output : 337
123 + 214 = 337
Input : n = 4, m = 3
a[] = { 9, 5, 4, 9 }
b[] = { 2, 1, 4 }
Output : 9763这个想法是从末尾开始同时遍历两个数组,直到我们到达任何一个数组的第 0 个索引。在遍历数组的每个元素时,将数组的元素相加并从前一个总和中进位。现在存储总和的个位并为下一个索引总和向前进位。如果进位向左,则添加第 0 个索引元素,然后将其附加到数字的开头。
下面是方法的说明:
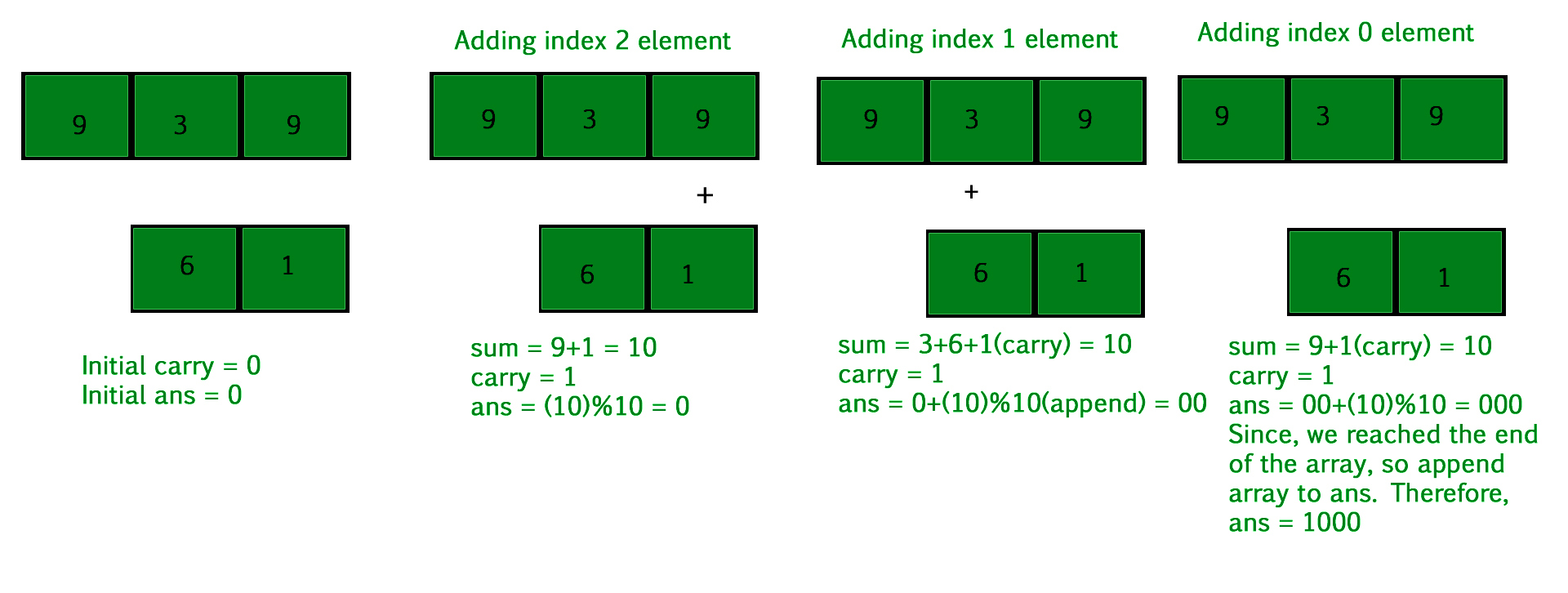
下面是这种方法的实现:
C++
// CPP program to sum two numbers represented two
// arrays.
#include
using namespace std;
// Return sum of two number represented by the arrays.
// Size of a[] is greater than b[]. It is made sure
// be the wrapper function
int calSumUtil(int a[], int b[], int n, int m)
{
// array to store sum.
int sum[n];
int i = n - 1, j = m - 1, k = n - 1;
int carry = 0, s = 0;
// Until we reach beginning of array.
// we are comparing only for second array
// because we have already compare the size
// of array in wrapper function.
while (j >= 0) {
// find sum of corresponding element
// of both arrays.
s = a[i] + b[j] + carry;
sum[k] = (s % 10);
// Finding carry for next sum.
carry = s / 10;
k--;
i--;
j--;
}
// If second array size is less the first
// array size.
while (i >= 0) {
// Add carry to first array elements.
s = a[i] + carry;
sum[k] = (s % 10);
carry = s / 10;
i--;
k--;
}
int ans = 0;
// If there is carry on adding 0 index elements.
// append 1 to total sum.
if (carry)
ans = 10;
// Converting array into number.
for (int i = 0; i <= n - 1; i++) {
ans += sum[i];
ans *= 10;
}
return ans / 10;
}
// Wrapper Function
int calSum(int a[], int b[], int n, int m)
{
// Making first array which have
// greater number of element
if (n >= m)
return calSumUtil(a, b, n, m);
else
return calSumUtil(b, a, m, n);
}
// Driven Program
int main()
{
int a[] = { 9, 3, 9 };
int b[] = { 6, 1 };
int n = sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]);
int m = sizeof(b) / sizeof(b[0]);
cout << calSum(a, b, n, m) << endl;
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to sum two numbers
// represented two arrays.
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
// Return sum of two number represented by
// the arrays. Size of a[] is greater than
// b[]. It is made sure be the wrapper
// function
static int calSumUtil(int a[], int b[],
int n, int m)
{
// array to store sum.
int[] sum= new int[n];
int i = n - 1, j = m - 1, k = n - 1;
int carry = 0, s = 0;
// Until we reach beginning of array.
// we are comparing only for second
// array because we have already compare
// the size of array in wrapper function.
while (j >= 0)
{
// find sum of corresponding element
// of both array.
s = a[i] + b[j] + carry;
sum[k] = (s % 10);
// Finding carry for next sum.
carry = s / 10;
k--;
i--;
j--;
}
// If second array size is less
// the first array size.
while (i >= 0)
{
// Add carry to first array elements.
s = a[i] + carry;
sum[k] = (s % 10);
carry = s / 10;
i--;
k--;
}
int ans = 0;
// If there is carry on adding 0 index
// elements append 1 to total sum.
if (carry == 1)
ans = 10;
// Converting array into number.
for ( i = 0; i <= n - 1; i++) {
ans += sum[i];
ans *= 10;
}
return ans / 10;
}
// Wrapper Function
static int calSum(int a[], int b[], int n,
int m)
{
// Making first array which have
// greater number of element
if (n >= m)
return calSumUtil(a, b, n, m);
else
return calSumUtil(b, a, m, n);
}
/* Driver program to test above function */
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int a[] = { 9, 3, 9 };
int b[] = { 6, 1 };
int n = a.length;
int m = b.length;
System.out.println(calSum(a, b, n, m));
}
}
// This article is contributed by Gitanjali.Python3
# Python3 code to sum two numbers
# representer two arrays.
# Return sum of two number represented
# by the arrays. Size of a[] is greater
# than b[]. It is made sure be the
# wrapper function
def calSumUtil( a , b , n , m ):
# array to store sum.
sum = [0] * n
i = n - 1
j = m - 1
k = n - 1
carry = 0
s = 0
# Until we reach beginning of array.
# we are comparing only for second array
# because we have already compare the size
# of array in wrapper function.
while j >= 0:
# find sum of corresponding element
# of both array.
s = a[i] + b[j] + carry
sum[k] = (s % 10)
# Finding carry for next sum.
carry = s // 10
k-=1
i-=1
j-=1
# If second array size is less the first
# array size.
while i >= 0:
# Add carry to first array elements.
s = a[i] + carry
sum[k] = (s % 10)
carry = s // 10
i-=1
k-=1
ans = 0
# If there is carry on adding 0 index elements.
# append 1 to total sum.
if carry:
ans = 10
# Converting array into number.
for i in range(n):
ans += sum[i]
ans *= 10
return ans // 10
# Wrapper Function
def calSum(a, b, n, m ):
# Making first array which have
# greater number of element
if n >= m:
return calSumUtil(a, b, n, m)
else:
return calSumUtil(b, a, m, n)
# Driven Code
a = [ 9, 3, 9 ]
b = [ 6, 1 ]
n = len(a)
m = len(b)
print(calSum(a, b, n, m))
# This code is contributed by "Sharad_Bhardwaj".C#
// C# program to sum two numbers
// represented two arrays.
using System;
class GFG {
// Return sum of two number represented by
// the arrays. Size of a[] is greater than
// b[]. It is made sure be the wrapper
// function
static int calSumUtil(int []a, int []b,
int n, int m)
{
// array to store sum.
int[] sum= new int[n];
int i = n - 1, j = m - 1, k = n - 1;
int carry = 0, s = 0;
// Until we reach beginning of array.
// we are comparing only for second
// array because we have already compare
// the size of array in wrapper function.
while (j >= 0)
{
// find sum of corresponding element
// of both array.
s = a[i] + b[j] + carry;
sum[k] = (s % 10);
// Finding carry for next sum.
carry = s / 10;
k--;
i--;
j--;
}
// If second array size is less
// the first array size.
while (i >= 0)
{
// Add carry to first array elements.
s = a[i] + carry;
sum[k] = (s % 10);
carry = s / 10;
i--;
k--;
}
int ans = 0;
// If there is carry on adding 0 index
// elements append 1 to total sum.
if (carry == 1)
ans = 10;
// Converting array into number.
for ( i = 0; i <= n - 1; i++) {
ans += sum[i];
ans *= 10;
}
return ans / 10;
}
// Wrapper Function
static int calSum(int []a, int []b, int n,
int m)
{
// Making first array which have
// greater number of element
if (n >= m)
return calSumUtil(a, b, n, m);
else
return calSumUtil(b, a, m, n);
}
// Driver program
public static void Main()
{
int []a = { 9, 3, 9 };
int []b = { 6, 1 };
int n = a.Length;
int m = b.Length;
Console.WriteLine(calSum(a, b, n, m));
}
}
// This article is contributed by vt_m.PHP
= 0)
{
// find sum of corresponding
// element of both array.
$s = $a[$i] + $b[$j] + $carry;
$sum[$k] = ($s % 10);
// Finding carry for next sum.
$carry = $s / 10;
$k--;
$i--;
$j--;
}
// If second array size is less
// than the first array size.
while ($i >= 0)
{
// Add carry to first array elements.
$s = $a[$i] + $carry;
$sum[$k] = ($s % 10);
$carry = $s / 10;
$i--;
$k--;
}
$ans = 0;
// If there is carry on
// adding 0 index elements.
// append 1 to total sum.
if ($carry)
$ans = 10;
// Converting array into number.
for ( $i = 0; $i <= $n - 1; $i++)
{
$ans += $sum[$i];
$ans *= 10;
}
return $ans / 10;
}
// Wrapper Function
function calSum( $a, $b, $n, $m)
{
// Making first array which have
// greater number of element
if ($n >= $m)
return calSumUtil($a, $b, $n, $m);
else
return calSumUtil($b, $a, $m, $n);
}
// Driven Code
$a = array( 9, 3, 9 );
$b = array( 6, 1 );
$n = count($a);
$m = count($b);
echo calSum($a, $b, $n, $m);
// This article is contributed by anuj_67.
?>Javascript
输出 :
1000时间复杂度: O(n + m)
辅助空间: O(max(n, m))