无递归的 N 叉树的前序遍历
给定一个 n 叉树,打印它的前序遍历。
例子 :
Preorder traversal of below tree is A B K N M J F D G E C H I L
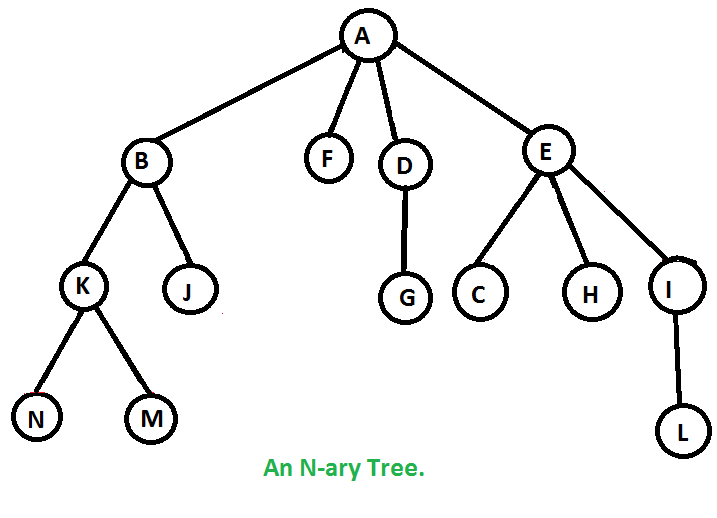
这个想法是使用堆栈,如二叉树的迭代前序遍历。
1)创建一个空栈来存储节点。
2) 将根节点压入堆栈。
3) 在堆栈不为空时运行一个循环
....a) 从堆栈中弹出顶部节点。
....b) 打印弹出的节点。
....c) 将弹出节点的所有子节点存储到堆栈中。我们必须从右到左存储子节点,以便首先弹出最左边的节点。
4)如果堆栈是空的,那么我们就完成了。
C++
// C++ program to traverse an N-ary tree
// without recursion
#include
using namespace std;
// Structure of a node of an n-ary tree
struct Node {
char key;
vector child;
};
// Utility function to create a new tree node
Node* newNode(int key)
{
Node* temp = new Node;
temp->key = key;
return temp;
}
// Function to traverse tree without recursion
void traverse_tree(struct Node* root)
{
// Stack to store the nodes
stack nodes;
// push the current node onto the stack
nodes.push(root);
// loop while the stack is not empty
while (!nodes.empty()) {
// store the current node and pop it from the stack
Node* curr = nodes.top();
nodes.pop();
// current node has been travarsed
if(curr != NULL)
{
cout << curr->key << " ";
// store all the childrent of current node from
// right to left.
vector::iterator it = curr->child.end();
while (it != curr->child.begin()) {
it--;
nodes.push(*it);
}
}
}
}
// Driver program
int main()
{
/* Let us create below tree
* A
* / / \ \
* B F D E
* / \ | /|\
* K J G C H I
* / \ | |
* N M O L
*/
Node* root = newNode('A');
(root->child).push_back(newNode('B'));
(root->child).push_back(newNode('F'));
(root->child).push_back(newNode('D'));
(root->child).push_back(newNode('E'));
(root->child[0]->child).push_back(newNode('K'));
(root->child[0]->child).push_back(newNode('J'));
(root->child[2]->child).push_back(newNode('G'));
(root->child[3]->child).push_back(newNode('C'));
(root->child[3]->child).push_back(newNode('H'));
(root->child[3]->child).push_back(newNode('I'));
(root->child[0]->child[0]->child).push_back(newNode('N'));
(root->child[0]->child[0]->child).push_back(newNode('M'));
(root->child[3]->child[0]->child).push_back(newNode('O'));
(root->child[3]->child[2]->child).push_back(newNode('L'));
traverse_tree(root);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to traverse an N-ary tree
// without recursion
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Stack;
class GFG{
// Structure of a node of
// an n-ary tree
static class Node
{
char key;
ArrayList child;
public Node(char key)
{
this.key = key;
child = new ArrayList<>();
}
};
// Function to traverse tree without recursion
static void traverse_tree(Node root)
{
// Stack to store the nodes
Stack nodes = new Stack<>();
// push the current node onto the stack
nodes.push(root);
// Loop while the stack is not empty
while (!nodes.isEmpty())
{
// Store the current node and pop
// it from the stack
Node curr = nodes.pop();
// Current node has been travarsed
if (curr != null)
{
System.out.print(curr.key + " ");
// Store all the childrent of
// current node from right to left.
for(int i = curr.child.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
nodes.add(curr.child.get(i));
}
}
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
/* Let us create below tree
* A
* / / \ \
* B F D E
* / \ | /|\
* K J G C H I
* / \ | |
* N M O L
*/
Node root = new Node('A');
(root.child).add(new Node('B'));
(root.child).add(new Node('F'));
(root.child).add(new Node('D'));
(root.child).add(new Node('E'));
(root.child.get(0).child).add(new Node('K'));
(root.child.get(0).child).add(new Node('J'));
(root.child.get(2).child).add(new Node('G'));
(root.child.get(3).child).add(new Node('C'));
(root.child.get(3).child).add(new Node('H'));
(root.child.get(3).child).add(new Node('I'));
(root.child.get(0).child.get(0).child).add(new Node('N'));
(root.child.get(0).child.get(0).child).add(new Node('M'));
(root.child.get(3).child.get(0).child).add(new Node('O'));
(root.child.get(3).child.get(2).child).add(new Node('L'));
traverse_tree(root);
}
}
// This code is contributed by sanjeev2552 Python3
# Python3 program to find height of
# full binary tree
# using preorder
class newNode():
def __init__(self, key):
self.key = key
# all children are stored in a list
self.child =[]
# Function to traverse tree without recursion
def traverse_tree(root):
# Stack to store the nodes
nodes=[]
# push the current node onto the stack
nodes.append(root)
# loop while the stack is not empty
while (len(nodes)):
# store the current node and pop it from the stack
curr = nodes[0]
nodes.pop(0)
# current node has been travarsed
print(curr.key,end=" ")
# store all the childrent of current node from
# right to left.
for it in range(len(curr.child)-1,-1,-1):
nodes.insert(0,curr.child[it])
# Driver program to test above functions
if __name__ == '__main__':
""" Let us create below tree
* A
* / / \ \
* B F D E
* / \ | /|\
* K J G C H I
* / \ | |
* N M O L
"""
root = newNode('A')
(root.child).append(newNode('B'))
(root.child).append(newNode('F'))
(root.child).append(newNode('D'))
(root.child).append(newNode('E'))
(root.child[0].child).append(newNode('K'))
(root.child[0].child).append(newNode('J'))
(root.child[2].child).append(newNode('G'))
(root.child[3].child).append(newNode('C'))
(root.child[3].child).append(newNode('H'))
(root.child[3].child).append(newNode('I'))
(root.child[0].child[0].child).append(newNode('N'))
(root.child[0].child[0].child).append(newNode('M'))
(root.child[3].child[0].child).append(newNode('O'))
(root.child[3].child[2].child).append(newNode('L'))
traverse_tree(root)
# This code is contributed by SHUBHAMSINGH10C#
// C# program to traverse an N-ary tree
// without recursion
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class GFG{
// Structure of a node of
// an n-ary tree
public class Node
{
public char key;
public List child;
public Node(char key)
{
this.key = key;
child = new List();
}
};
// Function to traverse tree without recursion
static void traverse_tree(Node root)
{
// Stack to store the nodes
Stack nodes = new Stack();
// push the current node onto the stack
nodes.Push(root);
// Loop while the stack is not empty
while (nodes.Count!=0)
{
// Store the current node and pop
// it from the stack
Node curr = nodes.Pop();
// Current node has been travarsed
if (curr != null)
{
Console.Write(curr.key + " ");
// Store all the childrent of
// current node from right to left.
for(int i = curr.child.Count - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
nodes.Push(curr.child[i]);
}
}
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
/* Let us create below tree
* A
* / / \ \
* B F D E
* / \ | /|\
* K J G C H I
* / \ | |
* N M O L
*/
Node root = new Node('A');
(root.child).Add(new Node('B'));
(root.child).Add(new Node('F'));
(root.child).Add(new Node('D'));
(root.child).Add(new Node('E'));
(root.child[0].child).Add(new Node('K'));
(root.child[0].child).Add(new Node('J'));
(root.child[2].child).Add(new Node('G'));
(root.child[3].child).Add(new Node('C'));
(root.child[3].child).Add(new Node('H'));
(root.child[3].child).Add(new Node('I'));
(root.child[0].child[0].child).Add(new Node('N'));
(root.child[0].child[0].child).Add(new Node('M'));
(root.child[3].child[0].child).Add(new Node('O'));
(root.child[3].child[2].child).Add(new Node('L'));
traverse_tree(root);
}
}
// This code contributed by shikhasingrajput Javascript
输出:
A B K N M J F D G E C O H I L