Java程序通过交替取元素来组合两个列表
列表是存储在一起以形成集合的有序元素序列。列表可以包含重复条目和空条目。列表允许我们执行基于索引的操作,即添加、删除、操作和位置访问。 Java提供了一个内置接口 << Java.util>> 来执行列表以及其他基于类的功能。
案例:根据列表的长度,可能会出现两种不同的情况
- 如果列表 2 在交替添加元素时耗尽,则列表 1 的剩余元素是第二个列表,即列表 1 的剩余元素以相同的出现顺序添加。
- 如果列表 1 耗尽等等,如上述案例中所述,反之亦然
So, the Aim is to completely remove the elements from second one and add to first one list and whatever is left will be the second list.
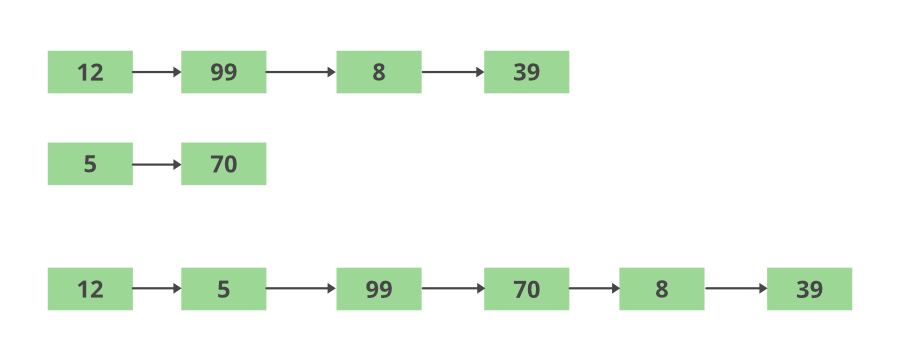
方法:采用以下方法将元素交替存储在合并列表中。
- 使用一组元素声明和初始化两个列表。
- 维护两个计数器 i 和 j 以在列表的长度上迭代。循环一直运行到两个列表的较短长度为止。
- 维护一个空列表以存储两个列表的合并内容,顺序是 list1 后跟 list2。
- 在循环结束时,列表中的一个,即较短的一个被用尽。然后使用循环遍历较长列表的剩余元素并将它们一一存储在末尾。
- 合并列表的数据类型应该类似于单个列表。
实现:下面讨论两个例子,同时考虑整数列表和字符串列表
示例 1:字符串列表
Java
// Java Program to Combine Two List
// by Alternatingly Taking Elements
// importing required packages
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.Iterator;
// Class to access alterate elements
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating(declaring) list1
List list1 = new ArrayList();
// Adding elements to list1
// Custom inputs
list1.add("Geeks");
list1.add("Geeks");
list1.add("portal");
// Creating(declaring) list2
List list2 = new ArrayList();
// Adding elements to list2
// Custom inputs
list2.add("for");
list2.add("is CSE");
list2.add("portal");
// Display message
System.out.print("List1 contents: ");
// Iterating over List1
Iterator iterator = list1.iterator();
// Condition check using hasNext() which holds true
// till there is single element remaining in the
// List
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
// Printing elements of List 1
System.out.print(iterator.next() + " ");
}
// Next Line
System.out.println();
// Display message
System.out.print("List2 contents: ");
// Iterating over List 2
iterator = list2.iterator();
// Condition check using hasNext() which holds true
// till there is single element remaining in the
// List
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
// Printing elements of List 2
System.out.print(iterator.next() + " ");
}
// Declaring counters
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
// Creating(declaring) merged List
List merged_list = new ArrayList();
// Iterating over both the lists until
// the elements of shorter List are exhausted
while (i < list1.size() && j < list2.size()) {
// Step 1: Adding List1 element
merged_list.add(list1.get(i));
// Step 2: Adding List2 element
merged_list.add(list2.get(j));
// Incrementing counters
i++;
j++;
}
// Iterating over the remaining part of List1
while (i < list1.size()) {
merged_list.add(list1.get(i));
// Incrementing List1 counter
i++;
}
// Iterating over the remaining part of List2
while (j < list2.size()) {
merged_list.add(list2.get(j));
// Incrementing List1 counter
j++;
}
// Next line
System.out.println();
// Display message
System.out.print("Merged List contents: ");
// Iterators
iterator = merged_list.iterator();
// Iterating over merged List using hasNext() method
// which holds true till there is single element
// remaining
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
// Printing merged list contents
System.out.print(iterator.next() + " ");
}
}
} Java
// Java Program to Combine Two List
// by Alternatingly Taking Elements
// importing required packages
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.Iterator;
// Class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating(declaring) List1
List list1 = new ArrayList();
// Adding elements to List1
// Custom inputs
list1.add(2);
list1.add(4);
list1.add(6);
// Creating(declaring) List2
List list2 = new ArrayList();
// Adding elements to List2
// Custom inputs
list2.add(1);
list2.add(3);
list2.add(5);
list2.add(7);
// Display message
System.out.print("List1 contents: ");
// Iterating over List1
Iterator iterator = list1.iterator();
// ConditionCheck using hasNext() method which hold
// true till single element in remaining List
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
// Printing List1 contents
System.out.print(iterator.next() + " ");
}
// New line
System.out.println();
// Display message
System.out.print("List2 contents: ");
iterator = list2.iterator();
// ConditionCheck using hasNext() method which hold
// true till single element in remaining List
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
// Printing List2 contents
System.out.print(iterator.next() + " ");
}
// Setting counters to zeros
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
// Creating(declaring) merged list
List merged_list
= new ArrayList();
// Iterating over both the lists
// until the shorter list
while (i < list1.size() && j < list2.size()) {
// Step 1: Adding List2 element
merged_list.add(list2.get(j));
// Step 2: Adding List1 element
merged_list.add(list1.get(i));
// Incrementing counters
i++;
j++;
}
// Iterating over the remaining part of List1
// Case 1: Input: ShorterList following BiggerList
while (i < list1.size()) {
// Merge remaining List to List1, and
// making List2 final as NULL List
merged_list.add(list1.get(i));
i++;
}
// Case 2: Input: BiggerList following ShorterList
while (j < list2.size()) {
// Merge remaining List to List1,an d
// making List2 -> NULL List
merged_list.add(list2.get(j));
j++;
}
// New line
System.out.println();
// Display message
System.out.print("Merged List contents: ");
// Iterating over merged list
iterator = merged_list.iterator();
// Condition check using hasNext() method which
// holds true till there is single element remaining
// in the List
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
// Printing merged List contents i.e
// FinalList = List1 + List2(Null final List)
System.out.print(iterator.next() + " ");
}
}
} 输出
List1 contents: Geeks Geeks portal
List2 contents: for is CSE portal
Merged List contents: Geeks for Geeks is CSE portal portal 示例 2:整数列表
Java
// Java Program to Combine Two List
// by Alternatingly Taking Elements
// importing required packages
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.Iterator;
// Class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating(declaring) List1
List list1 = new ArrayList();
// Adding elements to List1
// Custom inputs
list1.add(2);
list1.add(4);
list1.add(6);
// Creating(declaring) List2
List list2 = new ArrayList();
// Adding elements to List2
// Custom inputs
list2.add(1);
list2.add(3);
list2.add(5);
list2.add(7);
// Display message
System.out.print("List1 contents: ");
// Iterating over List1
Iterator iterator = list1.iterator();
// ConditionCheck using hasNext() method which hold
// true till single element in remaining List
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
// Printing List1 contents
System.out.print(iterator.next() + " ");
}
// New line
System.out.println();
// Display message
System.out.print("List2 contents: ");
iterator = list2.iterator();
// ConditionCheck using hasNext() method which hold
// true till single element in remaining List
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
// Printing List2 contents
System.out.print(iterator.next() + " ");
}
// Setting counters to zeros
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
// Creating(declaring) merged list
List merged_list
= new ArrayList();
// Iterating over both the lists
// until the shorter list
while (i < list1.size() && j < list2.size()) {
// Step 1: Adding List2 element
merged_list.add(list2.get(j));
// Step 2: Adding List1 element
merged_list.add(list1.get(i));
// Incrementing counters
i++;
j++;
}
// Iterating over the remaining part of List1
// Case 1: Input: ShorterList following BiggerList
while (i < list1.size()) {
// Merge remaining List to List1, and
// making List2 final as NULL List
merged_list.add(list1.get(i));
i++;
}
// Case 2: Input: BiggerList following ShorterList
while (j < list2.size()) {
// Merge remaining List to List1,an d
// making List2 -> NULL List
merged_list.add(list2.get(j));
j++;
}
// New line
System.out.println();
// Display message
System.out.print("Merged List contents: ");
// Iterating over merged list
iterator = merged_list.iterator();
// Condition check using hasNext() method which
// holds true till there is single element remaining
// in the List
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
// Printing merged List contents i.e
// FinalList = List1 + List2(Null final List)
System.out.print(iterator.next() + " ");
}
}
}
输出
List1 contents: 2 4 6
List2 contents: 1 3 5 7
Merged List contents: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7