Python PostgreSQL – 选择数据
在本文中,我们将看到如何在 PostgreSQL 和 psycopg2 中使用Python使用选择数据。
安装
打开命令提示符并编写下面给出的命令。
pip install psycopg2SELECT语句用于检索 PostgreSQL 中现有表的所需详细信息。返回的数据存储在称为结果集的结果表中。使用 select 命令检索数据仅限于指定的列数。如果我们想检索所有列,那么我们使用 (*)。
Syntax:
Query to select all details of the table: SELECT * FROM table_name
Query to select some specific details of the table: SELECT column_name1, column_name2,….FROM table_name
SELECT 命令的表格演示:
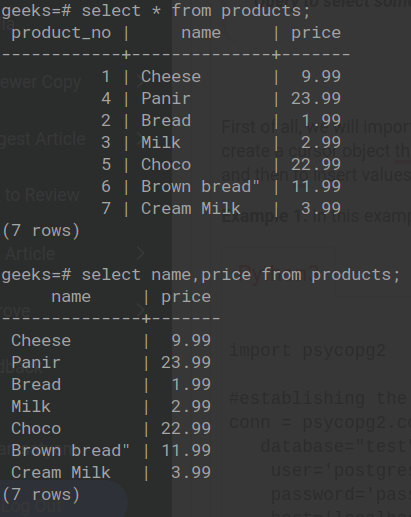
例1:显示表格中的所有数据。
Python3
import psycopg2
# establishing the connection
conn = psycopg2.connect(
database="test",
user='postgres',
password='password',
host='localhost',
port= '5432'
)
# Creating a cursor object using the cursor()
# method
cursor = conn.cursor()
sql = '''CREATE TABLE WORKER(
ID BIGSERIAL NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
NAME VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
COUNTRY VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
AGE INT,
SALARY FLOAT
)'''
cursor.execute(sql)
# Inserting values into the table
insert_stmt = "INSERT INTO WORKER (NAME, COUNTRY,\
AGE, SALARY) VALUES (%s, %s, %s, %s)"
data = [('Krishna', 'India', 19,2000),
('Harry', 'USA', 20,7000),
('Malang', 'Nepal', 25, 5000),
('Apple', 'London', 26, 2000),
('Vishnu', 'India', 29,2000),
('Frank', 'UAE', 21,7000),
('Master', 'USA', 25, 5000),
('Montu', 'India', 26, 2000),
]
cursor.executemany(insert_stmt, data)
# Display whole table
cursor.execute("SELECT * FROM WORKER")
print(cursor.fetchall())
# Commit your changes in the database
conn.commit()
#Closing the connection
conn.close()Python3
import psycopg2
# establishing the connection
conn = psycopg2.connect(
database="test",
user='postgres',
password='password',
host='localhost',
port= '5432'
)
# Creating a cursor object using the cursor()
# method
cursor = conn.cursor()
sql = '''CREATE TABLE WORKER(
ID BIGSERIAL NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
NAME VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
COUNTRY VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
AGE INT,
SALARY FLOAT
)'''
cursor.execute(sql)
# Inserting values into the table
insert_stmt = "INSERT INTO WORKER (NAME, COUNTRY,\
AGE, SALARY) VALUES (%s, %s, %s, %s)"
data = [('Krishna', 'India', 19,2000),
('Harry', 'USA', 20,7000),
('Malang', 'Nepal', 25, 5000),
('Apple', 'London', 26, 2000),
('Vishnu', 'India', 29,2000),
('Frank', 'UAE', 21,7000),
('Master', 'USA', 25, 5000),
('Montu', 'India', 26, 2000),
]
cursor.executemany(insert_stmt, data)
# Retrieving only NAME and SALARY FROM WORKER
cursor.execute("SELECT NAME, COUNTRY from WORKER")
print(cursor.fetchall())
# Commit your changes in the database
conn.commit()
# Closing the connection
conn.close()输出:
[(‘Krishna’, ‘India’, 19,2000),(‘Harry’, ‘USA’, 20,7000),(‘Malang’, ‘Nepal’, 25, 5000), (‘Apple’, ‘London’, 26, 2000),(‘Vishnu’, ‘India’, 29,2000),(‘Frank’, ‘UAE’, 21,7000), (‘Master’, ‘USA’, 25, 5000),(‘Montu’, ‘India’, 26, 2000)]
示例 2:返回表的一些具体细节。
蟒蛇3
import psycopg2
# establishing the connection
conn = psycopg2.connect(
database="test",
user='postgres',
password='password',
host='localhost',
port= '5432'
)
# Creating a cursor object using the cursor()
# method
cursor = conn.cursor()
sql = '''CREATE TABLE WORKER(
ID BIGSERIAL NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
NAME VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
COUNTRY VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
AGE INT,
SALARY FLOAT
)'''
cursor.execute(sql)
# Inserting values into the table
insert_stmt = "INSERT INTO WORKER (NAME, COUNTRY,\
AGE, SALARY) VALUES (%s, %s, %s, %s)"
data = [('Krishna', 'India', 19,2000),
('Harry', 'USA', 20,7000),
('Malang', 'Nepal', 25, 5000),
('Apple', 'London', 26, 2000),
('Vishnu', 'India', 29,2000),
('Frank', 'UAE', 21,7000),
('Master', 'USA', 25, 5000),
('Montu', 'India', 26, 2000),
]
cursor.executemany(insert_stmt, data)
# Retrieving only NAME and SALARY FROM WORKER
cursor.execute("SELECT NAME, COUNTRY from WORKER")
print(cursor.fetchall())
# Commit your changes in the database
conn.commit()
# Closing the connection
conn.close()
输出:
[(‘Krishna’, ‘India’), (‘Harry’, ‘USA’), (‘Malang’, ‘Nepal’), (‘Apple’, ‘London’), (‘Vishnu’, ‘India’), (‘Frank’, ‘UAE’), (‘Master’, ‘USA’), (‘Montu’, ‘India’)]