Python中运算符的优先级和关联性
在Python中处理运算符时,我们必须了解Python运算符优先级和关联性的概念,因为它们决定了运算符的优先级,否则,我们将看到意外的输出。
运算符优先级:这用于具有多个具有不同优先级的运算符的表达式中,以确定首先执行哪个操作。
示例:求解
10 + 20 * 30

10 + 20 * 30 is calculated as 10 + (20 * 30)
and not as (10 + 20) * 30
代码:
Python3
# Precedence of '+' & '*'
expr = 10 + 20 * 30
print(expr)Python3
# Precedence of 'or' & 'and'
name = "Alex"
age = 0
if name == "Alex" or name == "John" and age >= 2 :
print("Hello! Welcome.")
else :
print("Good Bye!!")Python3
# Precedence of 'or' & 'and'
name = "Alex"
age = 0
if ( name == "Alex" or name == "John" ) and age >= 2 :
print("Hello! Welcome.")
else :
print("Good Bye!!")Python3
# Left-right associativity
# 100 / 10 * 10 is calculated as
# (100 / 10) * 10 and not
# as 100 / (10 * 10)
print(100 / 10 * 10)
# Left-right associativity
# 5 - 2 + 3 is calculated as
# (5 - 2) + 3 and not
# as 5 - (2 + 3)
print(5 - 2 + 3)
# left-right associativity
print(5 - (2 + 3))
# right-left associativity
# 2 ** 3 ** 2 is calculated as
# 2 ** (3 ** 2) and not
# as (2 ** 3) ** 2
print(2 ** 3 ** 2)Python3
expression = 100 + 200 / 10 - 3 * 10
print(expression )输出:
610
示例:现在,让我们看一个关于逻辑'或' &逻辑'和'运算符的示例。 ' if ' 块即使年龄为 0 也会执行。因为逻辑 '和' 的优先级大于逻辑 '或'。
Python3
# Precedence of 'or' & 'and'
name = "Alex"
age = 0
if name == "Alex" or name == "John" and age >= 2 :
print("Hello! Welcome.")
else :
print("Good Bye!!")
输出:
Hello! Welcome.
因此,要运行“ else ”块,我们可以使用括号() ,因为它们的优先级在所有运算符中最高。
Python3
# Precedence of 'or' & 'and'
name = "Alex"
age = 0
if ( name == "Alex" or name == "John" ) and age >= 2 :
print("Hello! Welcome.")
else :
print("Good Bye!!")
输出:
Good Bye!!
运算符关联性:如果一个表达式包含两个或多个具有相同优先级的运算符符,则使用运算符关联性来确定。它可以是从左到右或从右到左。
示例: '*' 和 '/' 具有相同的优先级,并且它们的关联性是从左到右,因此表达式“100 / 10 * 10”被视为“(100 / 10) * 10”。
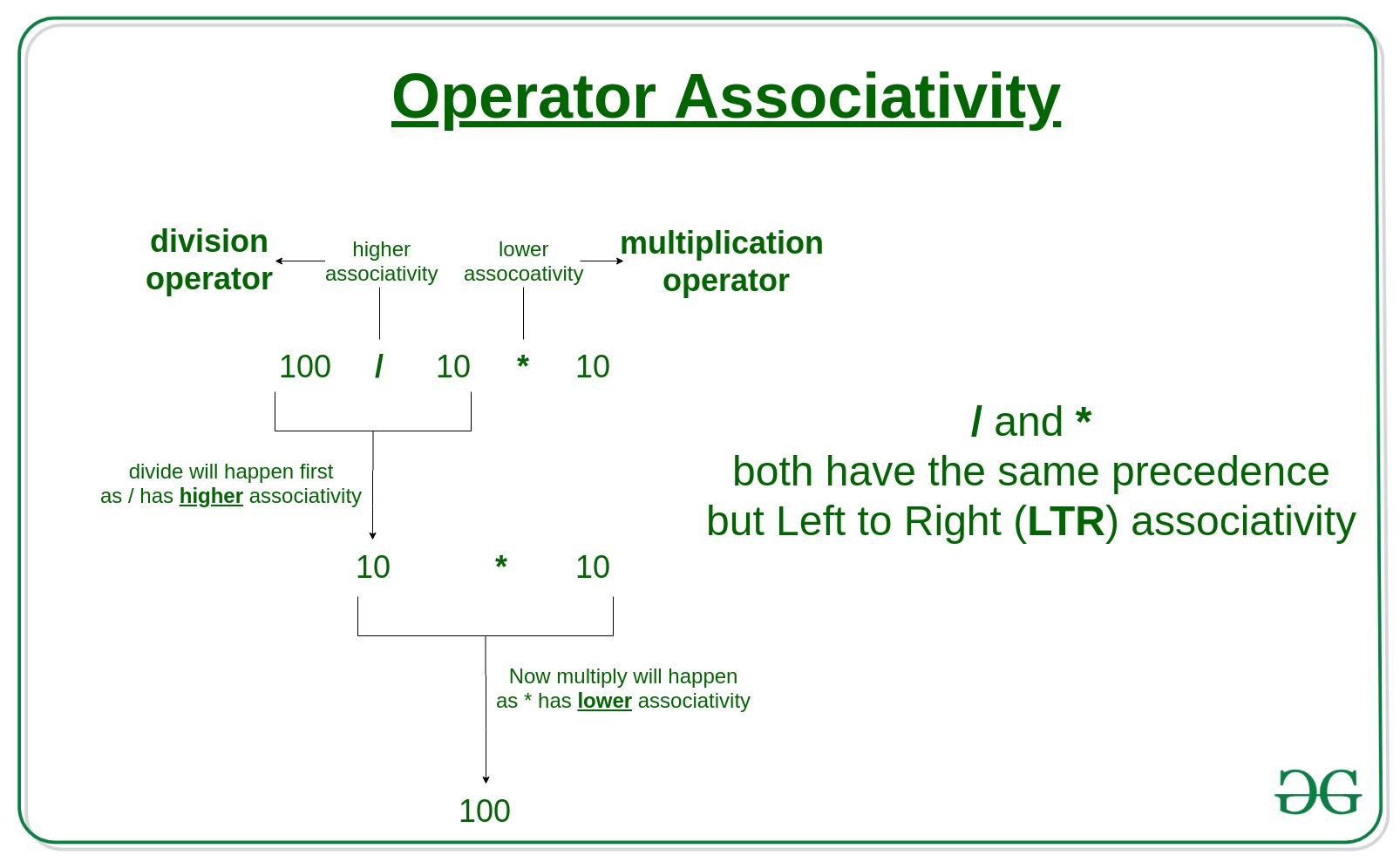
代码:
Python3
# Left-right associativity
# 100 / 10 * 10 is calculated as
# (100 / 10) * 10 and not
# as 100 / (10 * 10)
print(100 / 10 * 10)
# Left-right associativity
# 5 - 2 + 3 is calculated as
# (5 - 2) + 3 and not
# as 5 - (2 + 3)
print(5 - 2 + 3)
# left-right associativity
print(5 - (2 + 3))
# right-left associativity
# 2 ** 3 ** 2 is calculated as
# 2 ** (3 ** 2) and not
# as (2 ** 3) ** 2
print(2 ** 3 ** 2)
输出:
100
6
0
512
Operators Precedence and Associativity are two main characteristics of operators that determine the evaluation order of sub-expressions in absence of brackets.
示例:求解
100 + 200 / 10 - 3 * 10
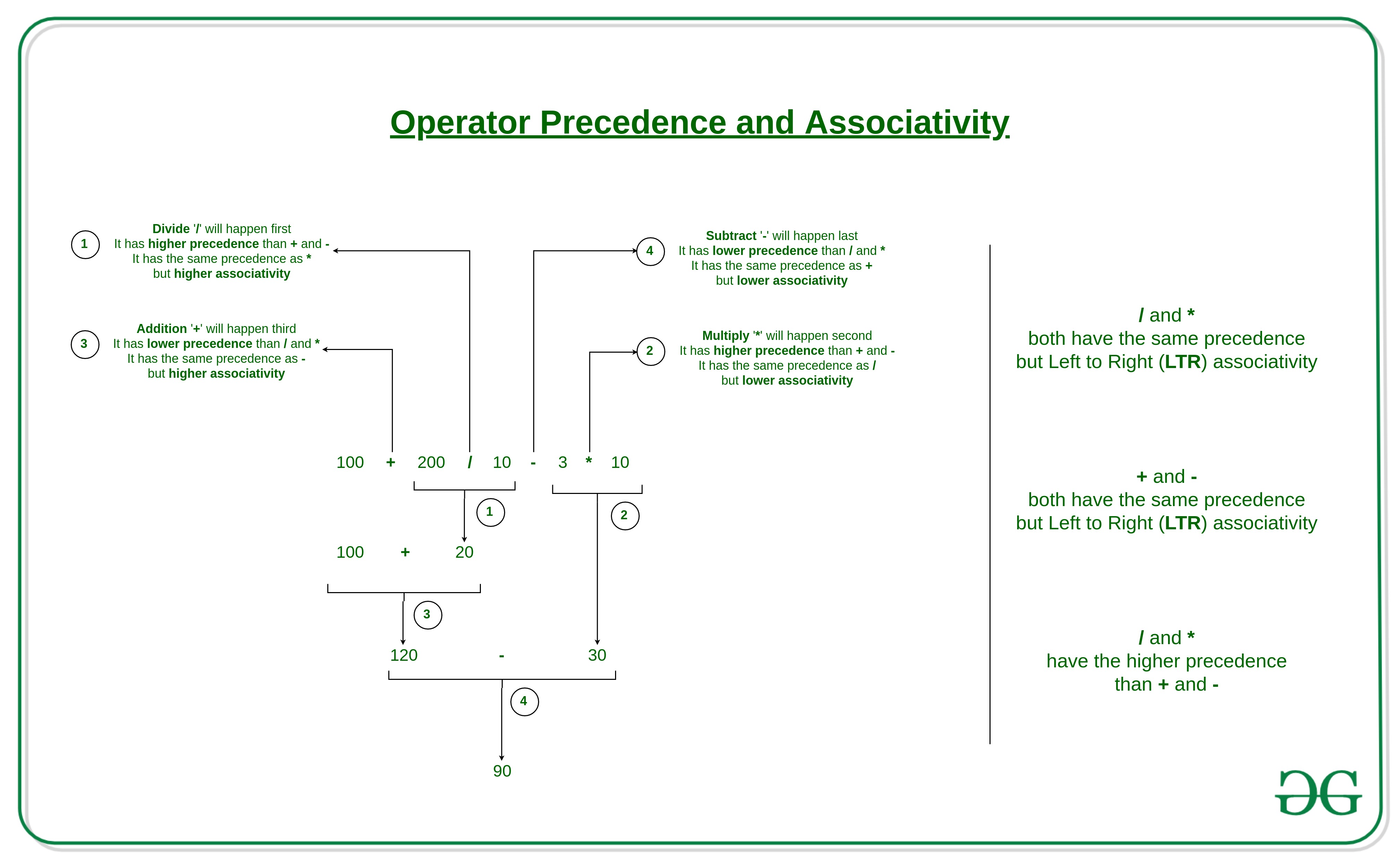
100 + 200 / 10 - 3 * 10 is calculated as 100 + (200 / 10) - (3 * 10)
and not as (100 + 200) / (10 - 3) * 10
代码:
Python3
expression = 100 + 200 / 10 - 3 * 10
print(expression )
输出:
90.0
请参阅以下优先级和关联性表以供参考。此表列出了从最高优先级到最低优先级的所有运算符。 is, is not in, not in Identity Membership operatorsOperator Description Associativity ( ) Parentheses left-to-right ** Exponent right-to-left * / % Multiplication/division/modulus left-to-right + – Addition/subtraction left-to-right << >> Bitwise shift left, Bitwise shift right left-to-right < <=
> >=Relational less than/less than or equal to
Relational greater than/greater than or equal toleft-to-right == != Relational is equal to/is not equal to left-to-right left-to-right & Bitwise AND left-to-right ^ Bitwise exclusive OR left-to-right | Bitwise inclusive OR left-to-right not Logical NOT right-to-left and Logical AND left-to-right or Logical OR left-to-right =
+= -=
*= /=
%= &=
^= |=
<<= >>=Assignment
Addition/subtraction assignment
Multiplication/division assignment
Modulus/bitwise AND assignment
Bitwise exclusive/inclusive OR assignment
Bitwise shift left/right assignmentright-to-left