📌 相关文章
- Python:MySQL 创建表
- Python:MySQL 创建表(1)
- Python MySQL创建表(1)
- Python MySQL-创建表(1)
- Python MySQL-创建表(1)
- Python MySQL-创建表
- MySQL创建表
- 在 MySQL 中创建表(1)
- 创建MySQL表(1)
- 创建表mysql(1)
- 创建MySQL表
- MySQL创建表(1)
- 创建表mysql代码示例
- 在 MySQL 代码示例中创建表
- PHP | MySQL(创建表)
- PHP | MySQL(创建表)(1)
- Python MySQL-创建数据库(1)
- Python MySQL-创建数据库(1)
- Python MySQL创建新数据库(1)
- Python MySQL – 创建数据库(1)
- Python MySQL-创建数据库
- Python MySQL – 创建数据库
- Python MySQL创建新数据库
- Python MySQL-创建数据库
- mysql 创建表 - SQL (1)
- mysql 创建池 - SQL (1)
- mysql 创建池 - SQL 代码示例
- mysql 创建表 - SQL 代码示例
- 创建索引mysql(1)
📜 Python MySQL创建表
📅 最后修改于: 2020-10-25 03:40:48 🧑 作者: Mango
创建表
在本教程的这一部分中,我们将创建新表Employee。建立连接对象时,我们必须提及数据库名称。
我们可以使用SQL的CREATE TABLE语句创建新表。在我们的数据库PythonDB中,表Employee最初将具有四列,即名称,id,薪水和department_id。
以下查询用于创建新表Employee。
> create table Employee (name varchar(20) not null, id int primary key, salary float not null, Dept_Id int not null)
例
import mysql.connector
#Create the connection object
myconn = mysql.connector.connect(host = "localhost", user = "root",passwd = "google",database = "PythonDB")
#creating the cursor object
cur = myconn.cursor()
try:
#Creating a table with name Employee having four columns i.e., name, id, salary, and department id
dbs = cur.execute("create table Employee(name varchar(20) not null, id int(20) not null primary key, salary float not null, Dept_id int not null)")
except:
myconn.rollback()
myconn.close()
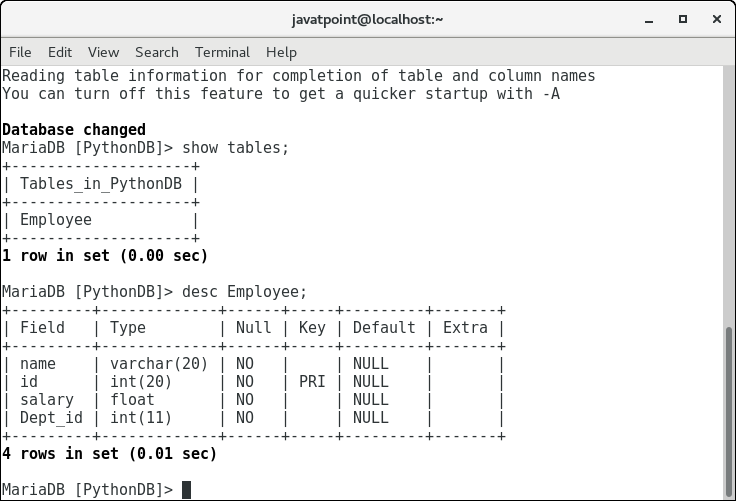
现在,我们可以检查表Employee是否存在于数据库中。
修改表
有时,我们可能忘记创建一些列,或者可能需要更新表架构。如果需要,可使用alter语句更改表架构。在这里,我们将把branch_name列添加到表Employee中。以下SQL查询用于此目的。
alter table Employee add branch_name varchar(20) not null
考虑以下示例。
例
import mysql.connector
#Create the connection object
myconn = mysql.connector.connect(host = "localhost", user = "root",passwd = "google",database = "PythonDB")
#creating the cursor object
cur = myconn.cursor()
try:
#adding a column branch name to the table Employee
cur.execute("alter table Employee add branch_name varchar(20) not null")
except:
myconn.rollback()
myconn.close()
