Java中的主线程
Java为多线程编程提供了内置支持。多线程程序包含两个或多个可以同时运行的部分。这种程序的每个部分都称为一个线程,每个线程定义一个单独的执行路径。
当Java程序启动时,一个线程立即开始运行。这通常被称为我们程序的主线程,因为它是在我们的程序开始时执行的。
与主线程相关的某些属性如下:
- 它是其他“子”线程将产生的线程。
- 通常,它必须是完成执行的最后一个线程,因为它执行各种关闭操作
流程图如下:
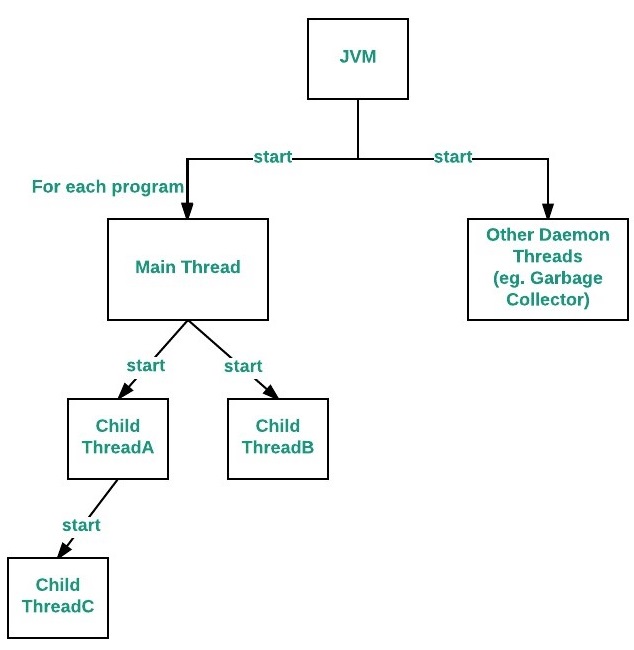
如何控制主线程
主线程是在我们的程序启动时自动创建的。为了控制它,我们必须获得对它的引用。这可以通过调用存在于 Thread 类中的方法currentThread()来完成。此方法返回对调用它的线程的引用。主线程的默认优先级为 5,所有剩余用户线程的优先级将从父线程继承到子线程。
例子
Java
// Java program to control the Main Thread
// Importing required classes
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
// Class 1
// Main class extending thread class
public class Test extends Thread {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Getting reference to Main thread
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
// Getting name of Main thread
System.out.println("Current thread: "
+ t.getName());
// Changing the name of Main thread
t.setName("Geeks");
System.out.println("After name change: "
+ t.getName());
// Getting priority of Main thread
System.out.println("Main thread priority: "
+ t.getPriority());
// Setting priority of Main thread to MAX(10)
t.setPriority(MAX_PRIORITY);
// Print and display the main thread priority
System.out.println("Main thread new priority: "
+ t.getPriority());
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println("Main thread");
}
// Main thread creating a child thread
Thread ct = new Thread() {
// run() method of a thread
public void run()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println("Child thread");
}
}
};
// Getting priority of child thread
// which will be inherited from Main thread
// as it is created by Main thread
System.out.println("Child thread priority: "
+ ct.getPriority());
// Setting priority of Main thread to MIN(1)
ct.setPriority(MIN_PRIORITY);
System.out.println("Child thread new priority: "
+ ct.getPriority());
// Starting child thread
ct.start();
}
}
// Class 2
// Helper class extending Thread class
// Child Thread class
class ChildThread extends Thread {
@Override public void run()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
// Print statement whenever child thread is
// called
System.out.println("Child thread");
}
}
}Java
// Java program to demonstrate deadlock
// using Main thread
// Main class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Try block to check for exceptions
try {
// Print statement
System.out.println("Entering into Deadlock");
// Joining the current thread
Thread.currentThread().join();
// This statement will never execute
System.out.println("This statement will never execute");
}
// Catch block to handle the exceptions
catch (InterruptedException e) {
// Display the exception along with line number
// using printStackTrace() method
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}输出
Current thread: main
After name change: Geeks
Main thread priority: 5
Main thread new priority: 10
Main thread
Main thread
Main thread
Main thread
Main thread
Child thread priority: 10
Child thread new priority: 1
Child thread
Child thread
Child thread
Child thread
Child thread现在让我们讨论一下 main() 方法和Java中的主线程之间的关系。 对于每个程序,由 JVM(Java虚拟机)创建一个主线程。 “Main”线程首先验证 main() 方法的存在,然后初始化类。请注意,从 JDK 6 开始,main() 方法在独立的Java应用程序中是必需的。
使用主线程死锁(仅单线程)
我们可以通过只使用主线程来创建死锁,即只使用单个线程。
例子
Java
// Java program to demonstrate deadlock
// using Main thread
// Main class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Try block to check for exceptions
try {
// Print statement
System.out.println("Entering into Deadlock");
// Joining the current thread
Thread.currentThread().join();
// This statement will never execute
System.out.println("This statement will never execute");
}
// Catch block to handle the exceptions
catch (InterruptedException e) {
// Display the exception along with line number
// using printStackTrace() method
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
输出:
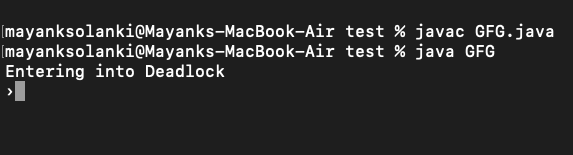
输出说明:
语句“Thread.currentThread().join()”,将告诉主线程等待这个线程(即等待自己)死亡。因此主线程等待自己死亡,这不过是死锁。