二叉树到带括号的字符串
使用前序遍历方式从二叉树构造一个由括号和整数组成的字符串。
空节点需要用空括号对“()”表示。省略所有不影响字符串与原二叉树一一映射关系的空括号对。
例子:
Input : Preorder: [1, 2, 3, 4]
1
/ \
2 3
/
4
Output: "1(2(4))(3)"
Explanation: Originally it needs to be "1(2(4)
())(3()())", but we need to omit all the
unnecessary empty parenthesis pairs.
And it will be "1(2(4))(3)".
Input : Preorder: [1, 2, 3, null, 4]
1
/ \
2 3
\
4
Output: "1(2()(4))(3)"这与用括号表示从字符串构造二叉树相反
这个想法是对给定的二叉树进行前序遍历,同时我们需要在适当的位置使用大括号。但是,我们还需要确保省略不必要的大括号。我们打印当前节点并按该顺序(如果它们存在)为节点的左右子节点调用相同的给定函数。对于遇到的每个节点,以下情况都是可能的。
情况1:当前节点的左孩子和右孩子都存在。在这种情况下,我们需要将大括号 () 放在左孩子的前序遍历输出和右孩子的前序遍历输出周围。
情况 2:当前节点不存在左子节点或右子节点。在这种情况下,如下图所示,为空的左右孩子考虑空括号是多余的。因此,我们不需要为它们中的任何一个放置大括号。
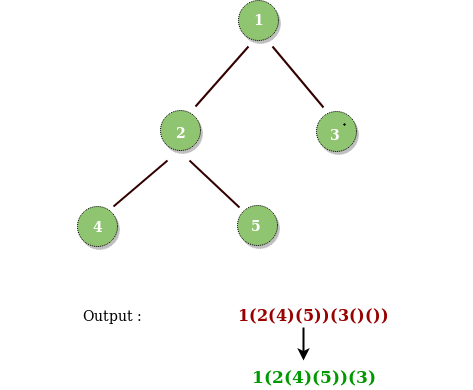
情况3:当前节点只存在左孩子。如下图所示,在考虑前序遍历时,在这种情况下为右孩子放置空括号是不必要的。这是因为在前序遍历中,右孩子总是在左孩子之后。因此,省略右孩子的空括号也会导致字符串和二叉树之间的映射相同。
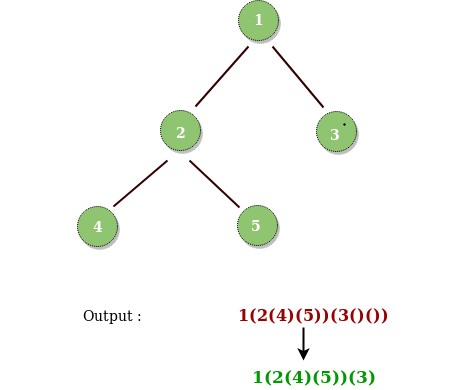
情况4:当前节点只存在右孩子。在这种情况下,我们需要考虑左孩子的空括号。这是因为,在前序遍历过程中,需要首先考虑左孩子。因此,为了表明当前节点后面的孩子是右孩子,我们需要为左孩子放置一对空括号。
C++
/* C++ program to construct string from binary tree*/
#include
using namespace std;
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left
child and a pointer to right child */
struct Node {
int data;
Node *left, *right;
};
/* Helper function that allocates a new node */
Node* newNode(int data)
{
Node* node = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
node->data = data;
node->left = node->right = NULL;
return (node);
}
// Function to construct string from binary tree
void treeToString(Node* root, string& str)
{
// bases case
if (root == NULL)
return;
// push the root data as character
str.push_back(root->data + '0');
// if leaf node, then return
if (!root->left && !root->right)
return;
// for left subtree
str.push_back('(');
treeToString(root->left, str);
str.push_back(')');
// only if right child is present to
// avoid extra parenthesis
if (root->right) {
str.push_back('(');
treeToString(root->right, str);
str.push_back(')');
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
/* Let us construct below tree
1
/ \
2 3
/ \ \
4 5 6 */
struct Node* root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
root->right->right = newNode(6);
string str = "";
treeToString(root, str);
cout << str;
} Java
// Java program to construct string from binary tree
class GFG
{
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left
child and a pointer to right child */
static class Node
{
int data;
Node left, right;
};
static String str;
/* Helper function that allocates a new node */
static Node newNode(int data)
{
Node node = new Node();
node.data = data;
node.left = node.right = null;
return (node);
}
// Function to construct string from binary tree
static void treeToString(Node root)
{
// bases case
if (root == null)
return;
// push the root data as character
str += (Character.valueOf((char)
(root.data + '0')));
// if leaf node, then return
if (root.left == null && root.right == null)
return;
// for left subtree
str += ('(');
treeToString(root.left);
str += (')');
// only if right child is present to
// avoid extra parenthesis
if (root.right != null)
{
str += ('(');
treeToString(root.right);
str += (')');
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
/* Let us construct below tree
1
/ \
2 3
/ \ \
4 5 6 */
Node root = newNode(1);
root.left = newNode(2);
root.right = newNode(3);
root.left.left = newNode(4);
root.left.right = newNode(5);
root.right.right = newNode(6);
str = "";
treeToString(root);
System.out.println(str);
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumarPython3
# Python3 program to construct string from binary tree
# A binary tree node has data, pointer to left
# child and a pointer to right child
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.left = None
self.right = None
# Function to construct string from binary tree
def treeToString(root: Node, string: list):
# base case
if root is None:
return
# push the root data as character
string.append(str(root.data))
# if leaf node, then return
if not root.left and not root.right:
return
# for left subtree
string.append('(')
treeToString(root.left, string)
string.append(')')
# only if right child is present to
# avoid extra parenthesis
if root.right:
string.append('(')
treeToString(root.right, string)
string.append(')')
# Driver Code
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Let us construct below tree
# 1
# / \
# 2 3
# / \ \
# 4 5 6
root = Node(1)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(3)
root.left.left = Node(4)
root.left.right = Node(5)
root.right.right = Node(6)
string = []
treeToString(root, string)
print(''.join(string))
# This code is contributed by
# sanjeev2552C#
// C# program to construct string from binary tree
using System;
class GFG
{
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left
child and a pointer to right child */
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node left, right;
};
static String str;
/* Helper function that allocates a new node */
static Node newNode(int data)
{
Node node = new Node();
node.data = data;
node.left = node.right = null;
return (node);
}
// Function to construct string from binary tree
static void treeToString(Node root)
{
// bases case
if (root == null)
return;
// push the root data as character
str += (char)(root.data + '0');
// if leaf node, then return
if (root.left == null && root.right == null)
return;
// for left subtree
str += ('(');
treeToString(root.left);
str += (')');
// only if right child is present to
// avoid extra parenthesis
if (root.right != null)
{
str += ('(');
treeToString(root.right);
str += (')');
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
/* Let us construct below tree
1
/ \
2 3
/ \ \
4 5 6 */
Node root = newNode(1);
root.left = newNode(2);
root.right = newNode(3);
root.left.left = newNode(4);
root.left.right = newNode(5);
root.right.right = newNode(6);
str = "";
treeToString(root);
Console.WriteLine(str);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Princi SinghJavascript
输出:
1(2(4)(5))(3()(6))时间复杂度:O(n)前序遍历在 n 个节点上完成。
空间复杂度: O(n) 。在倾斜树的情况下,递归树的深度可以达到 n。