- 带有JAX-RS的Apache CXF
- Apache CXF教程
- Apache CXF-简介(1)
- Apache CXF-简介
- 讨论Apache CXF
- 带有POJO的Apache CXF
- 带有POJO的Apache CXF(1)
- 带有JMS的Apache CXF
- 带有JMS的Apache CXF(1)
- Apache CXF-有用的资源
- Apache CXF-有用的资源(1)
- apache ws 代理 (1)
- Apache CXF-结论(1)
- Apache CXF-结论
- ws (1)
- apache ws 代理 - 任何代码示例
- ws - 任何代码示例
- 调试 cxf - Java (1)
- 首先使用WSDL的Apache CXF
- 首先使用WSDL的Apache CXF(1)
- JBoss Fuse-Apache CXF(1)
- JBoss Fuse-Apache CXF
- 调试 cxf - Java 代码示例
- 安装 ws-redis (1)
- Spring WS-概述(1)
- Spring WS-概述
- Jax-RS 路径注释 - Java (1)
- Jax-RS 路径注释 - Java 代码示例
- Jax-RS POST 注释 - Java (1)
📅 最后修改于: 2020-10-28 05:32:55 🧑 作者: Mango
在此JAX-WS应用程序中,我们将使用Apache CXF-first方法,就像早期的POJO应用程序一样。因此,首先我们将为我们的Web服务创建一个接口。
声明服务接口
与前面的情况一样,我们将创建一个简单的服务,该服务只有一个接口方法称为greetings。服务接口的代码如下所示-
//HelloWorld.java
package com.tutorialspoint.cxf.jaxws.helloworld;
import javax.jws.WebService;
@WebService
public interface HelloWorld {
String greetings(String text);
}
我们用@WebService标记注释接口。接下来,我们将实现此接口。
实施Web界面
Web界面的实现如下所示-
//HelloWorldImpl.java
package com.tutorialspoint.cxf.jaxws.helloworld;
public class HelloWorldImpl implements HelloWorld {
@Override
public String greetings(String name) {
return ("hi " + name);
}
}
问候方法使用@Override标记进行注释。该方法向呼叫者返回“ hi”消息。
接下来,我们将编写用于开发服务器的代码。
开发服务器
与POJO应用程序不同,我们现在将使用CXF提供的Endpoint类来发布服务来解耦接口。这在以下两行代码中完成-
HelloWorld implementor = new HelloWorldImpl();
Endpoint.publish(
"http://localhost:9090/HelloServerPort",
implementor,
new LoggingFeature()
);
publish方法的第一个参数指定将向客户提供我们的服务的URL。第二个参数指定我们服务的实现类。服务器的整个代码如下所示-
//Server.java
package com.tutorialspoint.cxf.jaxws.helloworld;
import javax.xml.ws.Endpoint;
import org.apache.cxf.ext.logging.LoggingFeature;
public class Server {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
HelloWorld implementor = new HelloWorldImpl();
Endpoint.publish("http://localhost:9090/HelloServerPort",
implementor,
new LoggingFeature());
System.out.println("Server ready...");
Thread.sleep(5 * 60 * 1000);
System.out.println("Server exiting ...");
System.exit(0);
}
}
要部署我们的服务器,您将需要对项目进行一些其他修改,如下所示。
部署服务器
最后,要部署服务器应用程序,您将需要在pom.xml中进行另一处修改,以将您的应用程序设置为Web应用程序。您需要在pom.xml中添加的代码如下:
server
test
org.codehaus.mojo
exec-maven-plugin
1.6.0
test
java
com.tutorialspoint.cxf.jaxws.helloworld.Server
在部署应用程序之前,您需要再向项目中添加两个文件。这些显示在下面的屏幕截图中-
这些文件是CXF标准文件,它们定义CXFServlet的映射。这里显示了web.xml文件中的代码,供您快速参考-
//Web.xml
cxf
Apache CXF Endpoint
cxf
cxf
org.apache.cxf.transport.servlet.CXFServlet
1
cxf
/services/*
60
在cxf-servlet.xml中,声明服务端点的属性。这显示在下面的代码片段中-
在这里,我们定义了服务端点的ID,可以使用该服务的地址,服务名称和端点名称。现在,您了解了如何通过CXF Servlet路由和处理服务。
最终的pom.xml
pom.xml包含更多的依赖项。除了描述所有依赖关系之外,我们还包括以下pom.xml的最终版本:
4.0.0
com.tutorialspoint
cxf-jaxws
1.0
jar
UTF-8
1.8
1.8
server
test
org.codehaus.mojo
exec-maven-plugin
1.6.0
test
java
com.tutorialspoint.cxf.jaxws.helloworld.Server
client
test
org.codehaus.mojo
exec-maven-plugin
test
java
com.tutorialspoint.cxf.jaxws.helloworld.Client
org.apache.cxf
cxf-rt-frontend-jaxws
3.3.0
org.apache.cxf
cxf-rt-transports-http
3.3.0
org.apache.cxf
cxf-rt-features-logging
3.3.0
org.apache.cxf
cxf-rt-transports-http-jetty
3.3.0
请注意,它还包括一个用于构建客户端的配置文件,我们将在本教程的后续部分中学习该配置文件。
运行HelloWorld服务
现在,您可以运行网络应用了。在命令窗口中,使用以下命令运行构建脚本。
mvn clean install
mvn -Pserver
您将在控制台上看到以下消息-
INFO: Setting the server's publish address to be http://localhost:9090/HelloServerPort
Server ready…
与之前一样,您可以通过在浏览器中打开服务器URL来测试服务器。
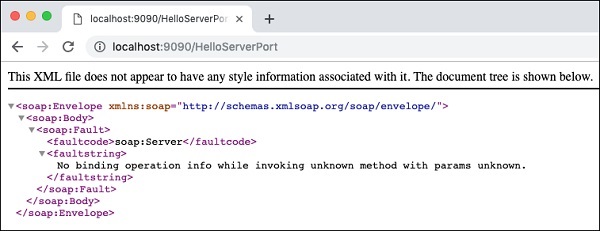
由于我们未指定任何操作,因此我们的应用程序仅将错误消息返回到浏览器。
现在,尝试将?wsdl添加到您的URL中,您将看到以下输出-
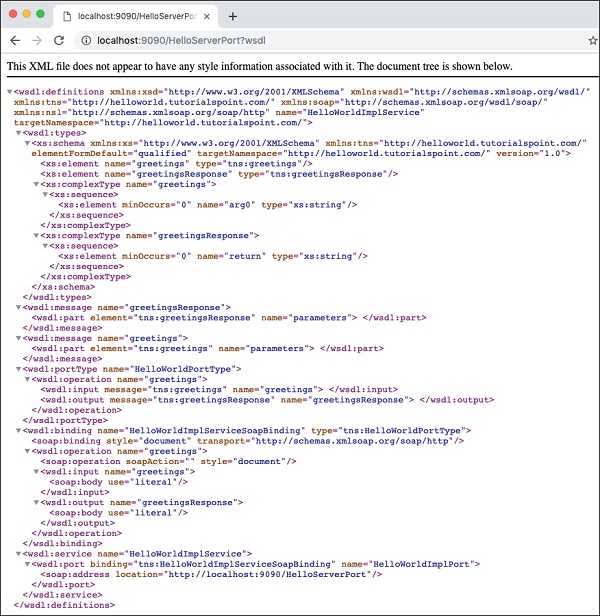
因此,我们的服务器应用程序正在按预期运行。您可以使用SOAP Client(如先前所述的Postman)进一步测试您的服务。
在下一节中,我们将学习如何编写使用我们服务的客户端。
发展中的客户
在CXF应用程序中编写客户端与编写服务器一样简单。这是客户端的完整代码-
//Client.java
package com.tutorialspoint.cxf.jaxws.helloworld;
import javax.xml.namespace.QName;
import javax.xml.ws.Service;
import javax.xml.ws.soap.SOAPBinding;
public final class Client {
private static final QName SERVICE_NAME
= new QName("http://helloworld.jaxws.cxf.tutorialspoint.com/",
"HelloWorld");
private static final QName PORT_NAME
= new QName("http://helloworld.jaxws.cxf.tutorialspoint.com/",
"HelloWorldPort");
private Client() {
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Service service = Service.create(SERVICE_NAME);
System.out.println("service created");
String endpointAddress = "http://localhost:9090/HelloServerPort";
service.addPort(PORT_NAME, SOAPBinding.SOAP11HTTP_BINDING,
endpointAddress);
HelloWorld hw = service.getPort(HelloWorld.class);
System.out.println(hw.greetings("World"));
}
}
在这里,我们使用CXF提供的Service类绑定到已知服务。我们在Service类上调用create方法以获取服务的实例。我们通过在服务实例上调用addPort方法来设置已知端口。
现在,我们可以使用服务了,首先通过在服务实例上调用getPort方法来获取服务接口。最后,我们调用greetings方法在控制台上打印greetings消息。
现在,当您通过使用Apache CXF-First方法学习了CXF的基础知识时,您将在下一章中学习如何将CXF与WSDL-First方法一起使用。