- Python Set(1)
- Python Set(1)
- Python set()
- Python set()(1)
- python set - Python 代码示例
- python中的set方法(1)
- Python set()函数(1)
- Python set()函数
- python代码示例中的set方法
- JavaScript中的Set
- JavaScript中的Set(1)
- $set - Javascript (1)
- set c++的元素(1)
- $set - Javascript 代码示例
- Python集合set
- Python集合set(1)
- Python集合Set(1)
- Python集合Set
- Python 集合set
- javascript中的set方法(1)
- python set contains - Python (1)
- “set -x” - Shell-Bash (1)
- C++ STL 中的 set 与 unordered_set
- C++ STL 中的 set 与 unordered_set
- C++ STL 中的 set 与 unordered_set(1)
- C++ STL 中的 set 与 unordered_set(1)
- set c++代码示例的元素
- Python中set clear
- Python中set clear(1)
📅 最后修改于: 2020-10-30 06:01:10 🧑 作者: Mango
Python Set
Python集是无序项目的集合。集合中的每个元素必须是唯一的,不可变的,并且集合会删除重复的元素。集是可变的,这意味着我们可以在创建后对其进行修改。
与Python的其他集合不同,集合的元素没有附加索引,即,我们无法通过索引直接访问集合的任何元素。但是,我们可以将它们全部print在一起,也可以通过遍历集合来获取元素列表。
创建一个集合
可以通过用大括号{}括起逗号分隔的不可变项来创建该集合。 Python还提供了set()方法,该方法可用于通过传递的序列来创建集合。
示例1:使用花括号
Days = {"Monday", "Tuesday", "Wednesday", "Thursday", "Friday", "Saturday", "Sunday"}
print(Days)
print(type(Days))
print("looping through the set elements ... ")
for i in Days:
print(i)
输出:
{'Friday', 'Tuesday', 'Monday', 'Saturday', 'Thursday', 'Sunday', 'Wednesday'}
looping through the set elements ...
Friday
Tuesday
Monday
Saturday
Thursday
Sunday
Wednesday
示例2:使用set()方法
Days = set(["Monday", "Tuesday", "Wednesday", "Thursday", "Friday", "Saturday", "Sunday"])
print(Days)
print(type(Days))
print("looping through the set elements ... ")
for i in Days:
print(i)
输出:
{'Friday', 'Wednesday', 'Thursday', 'Saturday', 'Monday', 'Tuesday', 'Sunday'}
looping through the set elements ...
Friday
Wednesday
Thursday
Saturday
Monday
Tuesday
Sunday
它可以包含任何类型的元素,例如整数,浮点数,元组等。但是可变元素(列表,字典,集合)不能是集合的成员。考虑以下示例。
# Creating a set which have immutable elements
set1 = {1,2,3, "JavaTpoint", 20.5, 14}
print(type(set1))
#Creating a set which have mutable element
set2 = {1,2,3,["Javatpoint",4]}
print(type(set2))
输出:
Traceback (most recent call last)
in
4
5 #Creating a set which holds mutable elements
----> 6 set2 = {1,2,3,["Javatpoint",4]}
7 print(type(set2))
TypeError: unhashable type: 'list'
在上面的代码中,我们创建了两个集合,集合set1具有不可变元素,而set2具有一个可变元素作为列表。在检查set2的类型时,它引发了一个错误,这意味着set只能包含不可变元素。
创建一个空集有点不同,因为空的花括号{}也也用于创建字典。因此, Python提供了不带参数的set()方法来创建空集。
# Empty curly braces will create dictionary
set3 = {}
print(type(set3))
# Empty set using set() function
set4 = set()
print(type(set4))
输出:
让我们看看如果我们向集合提供重复元素会发生什么。
set5 = {1,2,4,4,5,8,9,9,10}
print("Return set with unique elements:",set5)
输出:
Return set with unique elements: {1, 2, 4, 5, 8, 9, 10}
在上面的代码中,我们可以看到set5由多个重复元素组成,当我们打印它时,从集合中删除了重复项。
将项目添加到集合中
Python提供了add()方法和update()方法,可用于将某些特定项目添加到集合中。 add()方法用于添加单个元素,而update()方法用于向集合添加多个元素。考虑以下示例。
示例:1-使用add()方法
Months = set(["January","February", "March", "April", "May", "June"])
print("\nprinting the original set ... ")
print(months)
print("\nAdding other months to the set...");
Months.add("July");
Months.add ("August");
print("\nPrinting the modified set...");
print(Months)
print("\nlooping through the set elements ... ")
for i in Months:
print(i)
输出:
printing the original set ...
{'February', 'May', 'April', 'March', 'June', 'January'}
Adding other months to the set...
Printing the modified set...
{'February', 'July', 'May', 'April', 'March', 'August', 'June', 'January'}
looping through the set elements ...
February
July
May
April
March
August
June
January
要在集合中添加多个项目, Python提供了update()方法。它接受iterable作为参数。
考虑以下示例。
示例-2使用update()函数
Months = set(["January","February", "March", "April", "May", "June"])
print("\nprinting the original set ... ")
print(Months)
print("\nupdating the original set ... ")
Months.update(["July","August","September","October"]);
print("\nprinting the modified set ... ")
print(Months);
输出:
printing the original set ...
{'January', 'February', 'April', 'May', 'June', 'March'}
updating the original set ...
printing the modified set ...
{'January', 'February', 'April', 'August', 'October', 'May', 'June', 'July', 'September', 'March'}
从集合中删除项目
Python提供了throw()方法和remove()方法,可用于从集合中删除项目。这些函数之间的区别是,如果该项在集合中不存在,则使用discard()函数,则该集合保持不变,而remove()方法将出现错误。
考虑以下示例。
示例1:使用discard()方法
months = set(["January","February", "March", "April", "May", "June"])
print("\nprinting the original set ... ")
print(months)
print("\nRemoving some months from the set...");
months.discard("January");
months.discard("May");
print("\nPrinting the modified set...");
print(months)
print("\nlooping through the set elements ... ")
for i in months:
print(i)
输出:
printing the original set ...
{'February', 'January', 'March', 'April', 'June', 'May'}
Removing some months from the set...
Printing the modified set...
{'February', 'March', 'April', 'June'}
looping through the set elements ...
February
March
April
June
Python还提供了remove()方法来从集合中删除项目。考虑以下示例,使用remove()方法删除项目。
示例2-使用remove()函数
months = set(["January","February", "March", "April", "May", "June"])
print("\nprinting the original set ... ")
print(months)
print("\nRemoving some months from the set...");
months.remove("January");
months.remove("May");
print("\nPrinting the modified set...");
print(months)
输出:
printing the original set ...
{'February', 'June', 'April', 'May', 'January', 'March'}
Removing some months from the set...
Printing the modified set...
{'February', 'June', 'April', 'March'}
我们还可以使用pop()方法删除该项目。通常,pop()方法将始终删除最后一项,但是集合是无序的,我们无法确定将从集合中弹出哪个元素。
考虑以下示例,使用pop()方法从集合中删除该项目。
Months = set(["January","February", "March", "April", "May", "June"])
print("\nprinting the original set ... ")
print(Months)
print("\nRemoving some months from the set...");
Months.pop();
Months.pop();
print("\nPrinting the modified set...");
print(Months)
输出:
printing the original set ...
{'June', 'January', 'May', 'April', 'February', 'March'}
Removing some months from the set...
Printing the modified set...
{'May', 'April', 'February', 'March'}
在上面的代码中,Month集合的最后一个元素是March,但是pop()方法删除了June和January,因为该集合是无序的,并且pop()方法无法确定该集合的最后一个元素。
Python提供了clear()方法来删除集合中的所有项目。
考虑以下示例。
Months = set(["January","February", "March", "April", "May", "June"])
print("\nprinting the original set ... ")
print(Months)
print("\nRemoving all the items from the set...");
Months.clear()
print("\nPrinting the modified set...")
print(Months)
输出:
printing the original set ...
{'January', 'May', 'June', 'April', 'March', 'February'}
Removing all the items from the set...
Printing the modified set...
set()
Dispose()和remove()之间的区别
尽管discard()和remove()方法都执行相同的任务,但是discard()和remove()之间有一个主要区别。
如果使用set()中不存在要使用set()删除的键,则Python将不会给出错误。该程序将保持其控制流。
另一方面,如果集合中不存在使用remove()从集合中删除的项目,则Python会引发错误。
考虑以下示例。
例-
Months = set(["January","February", "March", "April", "May", "June"])
print("\nprinting the original set ... ")
print(Months)
print("\nRemoving items through discard() method...");
Months.discard("Feb"); #will not give an error although the key feb is not available in the set
print("\nprinting the modified set...")
print(Months)
print("\nRemoving items through remove() method...");
Months.remove("Jan") #will give an error as the key jan is not available in the set.
print("\nPrinting the modified set...")
print(Months)
输出:
printing the original set ...
{'March', 'January', 'April', 'June', 'February', 'May'}
Removing items through discard() method...
printing the modified set...
{'March', 'January', 'April', 'June', 'February', 'May'}
Removing items through remove() method...
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "set.py", line 9, in
Months.remove("Jan")
KeyError: 'Jan'
Python设置操作
可以执行数学运算,如并集,相交,差和对称差。 Python提供了使用运算符或方法执行这些操作的工具。我们将这些操作描述如下。
两套并集
使用管道(|)运算符可计算出两组的并集。这两个集合的并集包含两个集合中都存在的所有项目。
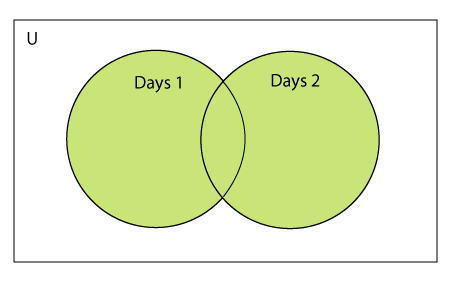
考虑以下示例来计算两个集合的并集。
示例1:使用union |运算符
Days1 = {"Monday","Tuesday","Wednesday","Thursday", "Sunday"}
Days2 = {"Friday","Saturday","Sunday"}
print(Days1|Days2) #printing the union of the sets
输出:
{'Friday', 'Sunday', 'Saturday', 'Tuesday', 'Wednesday', 'Monday', 'Thursday'}
Python还提供了union()方法,该方法还可用于计算两个集合的并集。考虑以下示例。
示例2:使用union()方法
Days1 = {"Monday","Tuesday","Wednesday","Thursday"}
Days2 = {"Friday","Saturday","Sunday"}
print(Days1.union(Days2)) #printing the union of the sets
输出:
{'Friday', 'Monday', 'Tuesday', 'Thursday', 'Wednesday', 'Sunday', 'Saturday'}
两套相交
两组的交集可以通过&和运算符或交集()函数。这两个集合的交集作为两个集合中共有的元素的集合给出。
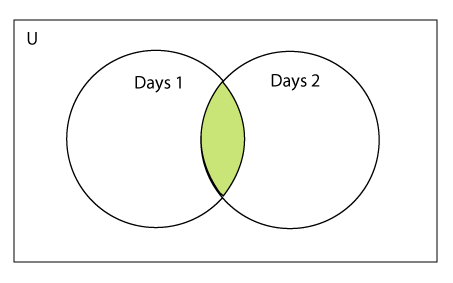
考虑以下示例。
示例1:使用&运算符
Days1 = {"Monday","Tuesday", "Wednesday", "Thursday"}
Days2 = {"Monday","Tuesday","Sunday", "Friday"}
print(Days1&Days2) #prints the intersection of the two sets
输出:
{'Monday', 'Tuesday'}
示例2:使用intersection()方法
set1 = {"Devansh","John", "David", "Martin"}
set2 = {"Steve", "Milan", "David", "Martin"}
print(set1.intersection(set2)) #prints the intersection of the two sets
输出:
{'Martin', 'David'}
范例3:
set1 = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7}
set2 = {1,2,20,32,5,9}
set3 = set1.intersection(set2)
print(set3)
输出:
{1,2,5}
section_update()方法
section_update()方法从原始集中删除两个集中都不存在的项目(如果指定了多个,则为所有集中)。
交集更新()方法与交集()方法的不同之处在于,它通过删除不需要的项来修改原始集,而交集()方法返回一个新集。
考虑以下示例。
a = {"Devansh", "bob", "castle"}
b = {"castle", "dude", "emyway"}
c = {"fuson", "gaurav", "castle"}
a.intersection_update(b, c)
print(a)
输出:
{'castle'}
两组之间的差异
可以通过使用减法(-)运算符或交集()方法来计算两组的差。假设有两个集合A和B,并且差为AB,则表示将获得集合B中不存在的A元素,从而得到结果集合。
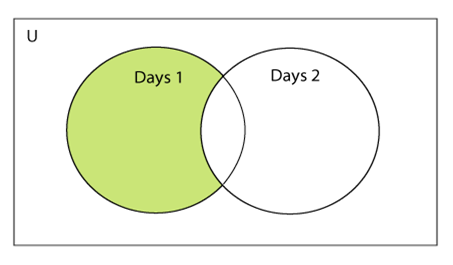
考虑以下示例。
示例1:使用减法(-)运算符
Days1 = {"Monday", "Tuesday", "Wednesday", "Thursday"}
Days2 = {"Monday", "Tuesday", "Sunday"}
print(Days1-Days2) #{"Wednesday", "Thursday" will be printed}
输出:
{'Thursday', 'Wednesday'}
示例2:使用difference()方法
Days1 = {"Monday", "Tuesday", "Wednesday", "Thursday"}
Days2 = {"Monday", "Tuesday", "Sunday"}
print(Days1.difference(Days2)) # prints the difference of the two sets Days1 and Days2
输出:
{'Thursday', 'Wednesday'}
两组的对称差
两组的对称差通过^运算符或symmetric_difference()方法计算。集的对称差异,它删除了两个集中都存在的元素。考虑以下示例:
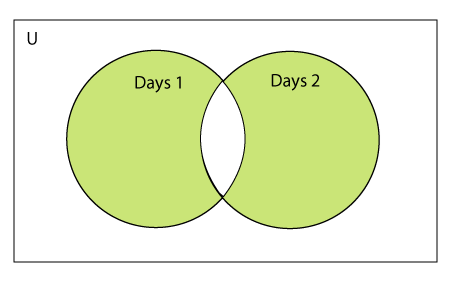
示例-1:使用^运算符
a = {1,2,3,4,5,6}
b = {1,2,9,8,10}
c = a^b
print(c)
输出:
{3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10}
示例-2:使用symmetric_difference()方法
a = {1,2,3,4,5,6}
b = {1,2,9,8,10}
c = a.symmetric_difference(b)
print(c)
输出:
{3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10}
设置比较
Python允许我们通过使用我们可以检查一组是否是一个子集,超集,或等同的其他组使用比较运算符,即,<,>,<=,> =,==与集。根据集合中存在的项目返回布尔值true或false。
考虑以下示例。
Days1 = {"Monday", "Tuesday", "Wednesday", "Thursday"}
Days2 = {"Monday", "Tuesday"}
Days3 = {"Monday", "Tuesday", "Friday"}
#Days1 is the superset of Days2 hence it will print true.
print (Days1>Days2)
#prints false since Days1 is not the subset of Days2
print (Days1输出:
True
False
False
冷冻套
冻结集是普通集的不变形式,即,冻结集的项目无法更改,因此可以用作字典中的键。
创建后,冻结集合的元素无法更改。我们不能通过使用诸如add()或remove()之类的方法来更改或追加冻结集的内容。
Frozenset()方法用于创建Frozenset对象。可迭代的序列将传递给此方法,该方法将转换为冻结集,作为该方法的返回类型。
考虑以下示例以创建冻结集。
Frozenset = frozenset([1,2,3,4,5])
print(type(Frozenset))
print("\nprinting the content of frozen set...")
for i in Frozenset:
print(i);
Frozenset.add(6) #gives an error since we cannot change the content of Frozenset after creation
输出:
printing the content of frozen set...
1
2
3
4
5
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "set.py", line 6, in
Frozenset.add(6) #gives an error since we can change the content of Frozenset after creation
AttributeError: 'frozenset' object has no attribute 'add'
字典的Frozenset
如果将字典作为序列传递给Frozenset()方法内的序列,它将仅接收字典中的键,并返回一个包含字典键作为其元素的Frozenset。
考虑以下示例。
Dictionary = {"Name":"John", "Country":"USA", "ID":101}
print(type(Dictionary))
Frozenset = frozenset(Dictionary); #Frozenset will contain the keys of the dictionary
print(type(Frozenset))
for i in Frozenset:
print(i)
输出:
Name
Country
ID
设置编程示例
示例-1:编写程序以从集中删除给定的数字。
my_set = {1,2,3,4,5,6,12,24}
n = int(input("Enter the number you want to remove"))
my_set.discard(n)
print("After Removing:",my_set)
输出:
Enter the number you want to remove:12
After Removing: {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 24}
示例-2:编写一个程序将多个元素添加到集合中。
set1 = set([1,2,4,"John","CS"])
set1.update(["Apple","Mango","Grapes"])
print(set1)
输出:
{1, 2, 4, 'Apple', 'John', 'CS', 'Mango', 'Grapes'}
示例-3:编写程序以查找两个集合之间的联合。
set1 = set(["Peter","Joseph", 65,59,96])
set2 = set(["Peter",1,2,"Joseph"])
set3 = set1.union(set2)
print(set3)
输出:
{96, 65, 2, 'Joseph', 1, 'Peter', 59}
例4:编写程序以查找两个集合之间的交集。
set1 = {23,44,56,67,90,45,"Javatpoint"}
set2 = {13,23,56,76,"Sachin"}
set3 = set1.intersection(set2)
print(set3)
输出:
{56, 23}
示例-5:编写程序以将元素添加到Frozenset。
set1 = {23,44,56,67,90,45,"Javatpoint"}
set2 = {13,23,56,76,"Sachin"}
set3 = set1.intersection(set2)
print(set3)
输出:
TypeError: 'frozenset' object does not support item assignment
上面的代码提出了一个错误,因为冻结集是不可变的,创建后无法更改。
示例-6:编写程序以查找issuperset,issubset和superset。
set1 = set(["Peter","James","Camroon","Ricky","Donald"])
set2 = set(["Camroon","Washington","Peter"])
set3 = set(["Peter"])
issubset = set1 >= set2
print(issubset)
issuperset = set1 <= set2
print(issuperset)
issubset = set3 <= set2
print(issubset)
issuperset = set2 >= set3
print(issuperset)
输出:
False
False
True
True
Python内置设置方法
Python包含以下与这些集合一起使用的方法。
| SN | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | add(item) | It adds an item to the set. It has no effect if the item is already present in the set. |
| 2 | clear() | It deletes all the items from the set. |
| 3 | copy() | It returns a shallow copy of the set. |
| 4 | difference_update(….) | It modifies this set by removing all the items that are also present in the specified sets. |
| 5 | discard(item) | It removes the specified item from the set. |
| 6 | intersection() | It returns a new set that contains only the common elements of both the sets. (all the sets if more than two are specified). |
| 7 | intersection_update(….) | It removes the items from the original set that are not present in both the sets (all the sets if more than one are specified). |
| 8 | Isdisjoint(….) | Return True if two sets have a null intersection. |
| 9 | Issubset(….) | Report whether another set contains this set. |
| 10 | Issuperset(….) | Report whether this set contains another set. |
| 11 | pop() | Remove and return an arbitrary set element that is the last element of the set. Raises KeyError if the set is empty. |
| 12 | remove(item) | Remove an element from a set; it must be a member. If the element is not a member, raise a KeyError. |
| 13 | symmetric_difference(….) | Remove an element from a set; it must be a member. If the element is not a member, raise a KeyError. |
| 14 | symmetric_difference_update(….) | Update a set with the symmetric difference of itself and another. |
| 15 | union(….) | Return the union of sets as a new set. (i.e. all elements that are in either set.) |
| 16 | update() | Update a set with the union of itself and others. |