- Python集合set(1)
- Python 集合set
- Python集合Set
- Python 集合set add()
- Python 集合set add()(1)
- Python 集合set remove()(1)
- Python 集合set remove()
- Python中的集合
- Python中的集合(1)
- Python 集合set clear()(1)
- Python 集合set clear()
- Python集合set| update
- Python集合set| update(1)
- C++ 集合Set的遍历
- C++ 集合Set的遍历(1)
- Python 集合set pop()
- Python 集合set pop()(1)
- Python集合set add函数
- Python集合set add函数(1)
- Python set集合 copy()(1)
- Python set集合 copy()
- Python set()(1)
- Python Set
- Python Set(1)
- Python Set(1)
- Python set()
- Python Set
- Python集合set| pop函数(1)
- Python集合set| pop函数
📅 最后修改于: 2020-09-20 13:39:14 🧑 作者: Mango
在本教程中,您将学习有关Python集的所有知识。如何创建它们,添加元素或从中删除元素,以及在Python对集合执行的所有操作。
集合是项目的无序集合。每个set元素都是唯一的(没有重复),并且必须是不可变的(无法更改)。
但是,集合本身是可变的。我们可以从中添加或删除项目。
集还可以用于执行数学集运算,例如联合,相交,对称差等。
创建Python集
通过将所有项目(元素)放在大括号{} (用逗号分隔)或使用内置的set() 函数来创建set() 。
它可以具有任意数量的项目,并且它们可以具有不同的类型(整数,浮点数,元组, 字符串等)。但是集合不能将诸如列表,集合或字典之类的可变元素作为其元素。
# Different types of sets in Python
# set of integers
my_set = {1, 2, 3}
print(my_set)
# set of mixed datatypes
my_set = {1.0, "Hello", (1, 2, 3)}
print(my_set)输出
{1, 2, 3}
{1.0, (1, 2, 3), 'Hello'}也尝试以下示例。
# set cannot have duplicates
# Output: {1, 2, 3, 4}
my_set = {1, 2, 3, 4, 3, 2}
print(my_set)
# we can make set from a list
# Output: {1, 2, 3}
my_set = set([1, 2, 3, 2])
print(my_set)
# set cannot have mutable items
# here [3, 4] is a mutable list
# this will cause an error.
my_set = {1, 2, [3, 4]}输出
{1, 2, 3, 4}
{1, 2, 3}
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "", line 15, in
my_set = {1, 2, [3, 4]}
TypeError: unhashable type: 'list' 创建一个空集有点棘手。
空括号{}将在Python创建一个空字典。为了创建没有任何元素的集合,我们使用不带任何参数的set() 函数 。
# Distinguish set and dictionary while creating empty set
# initialize a with {}
a = {}
# check data type of a
print(type(a))
# initialize a with set()
a = set()
# check data type of a
print(type(a))输出
在Python修改集合
集是可变的。但是,由于它们是无序的,因此索引没有意义。
我们无法使用索引或切片来访问或更改集合的元素。设置数据类型不支持它。
我们可以使用add()方法添加一个元素,并使用update()方法add()多个元素。 update()方法可以将元组,列表,字符串或其他集合用作其参数。在所有情况下,都避免重复。
# initialize my_set
my_set = {1, 3}
print(my_set)
# if you uncomment line 9,
# you will get an error
# TypeError: 'set' object does not support indexing
# my_set[0]
# add an element
# Output: {1, 2, 3}
my_set.add(2)
print(my_set)
# add multiple elements
# Output: {1, 2, 3, 4}
my_set.update([2, 3, 4])
print(my_set)
# add list and set
# Output: {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8}
my_set.update([4, 5], {1, 6, 8})
print(my_set)输出
{1, 3}
{1, 2, 3}
{1, 2, 3, 4}
{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8}从集合中删除元素
可以使用discard()和remove()方法从集合中删除特定项目。
两者之间的唯一区别是,如果元素不存在于集合中,则discard() 函数将使集合保持不变。另一方面, remove() 函数将在这种情况下引发错误(如果集合中不存在元素)。
以下示例将说明这一点。
# Difference between discard() and remove()
# initialize my_set
my_set = {1, 3, 4, 5, 6}
print(my_set)
# discard an element
# Output: {1, 3, 5, 6}
my_set.discard(4)
print(my_set)
# remove an element
# Output: {1, 3, 5}
my_set.remove(6)
print(my_set)
# discard an element
# not present in my_set
# Output: {1, 3, 5}
my_set.discard(2)
print(my_set)
# remove an element
# not present in my_set
# you will get an error.
# Output: KeyError
my_set.remove(2)输出
{1, 3, 4, 5, 6}
{1, 3, 5, 6}
{1, 3, 5}
{1, 3, 5}
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "", line 28, in
KeyError: 2 同样,我们可以使用pop()方法删除并返回一个项目。
由于set是无序数据类型,因此无法确定将弹出哪个项目。这是完全任意的。
我们还可以使用clear()方法从集合中删除所有项目。
# initialize my_set
# Output: set of unique elements
my_set = set("HelloWorld")
print(my_set)
# pop an element
# Output: random element
print(my_set.pop())
# pop another element
my_set.pop()
print(my_set)
# clear my_set
# Output: set()
my_set.clear()
print(my_set)
print(my_set)输出
{'H', 'l', 'r', 'W', 'o', 'd', 'e'}
H
{'r', 'W', 'o', 'd', 'e'}
set()Python设置操作
集合可用于执行数学集合运算,例如并集,交集,差和对称差。我们可以使用运算符或方法来做到这一点。
让我们考虑以下两组用于以下操作。
>>> A = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
>>> B = {4, 5, 6, 7, 8}设置联盟
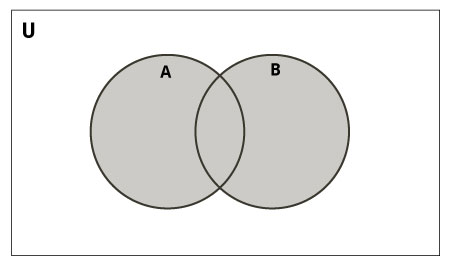
A和B并集是两个集合中所有元素的集合。
联合使用| 运算符。使用union()方法可以完成相同的操作。
# Set union method
# initialize A and B
A = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
B = {4, 5, 6, 7, 8}
# use | operator
# Output: {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8}
print(A | B)输出
{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8}在Python shell上尝试以下示例。
# use union function
>>> A.union(B)
{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8}
# use union function on B
>>> B.union(A)
{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8}设置相交
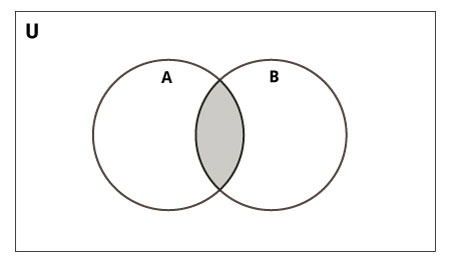
A和B交集是在这两个集合中都相同的一组元素。
交叉使用& 运算符执行。使用intersection()方法可以完成相同的操作。
# Intersection of sets
# initialize A and B
A = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
B = {4, 5, 6, 7, 8}
# use & operator
# Output: {4, 5}
print(A & B)输出
{4, 5}在Python shell上尝试以下示例。
# use intersection function on A
>>> A.intersection(B)
{4, 5}
# use intersection function on B
>>> B.intersection(A)
{4, 5}设置差异

集B与集A ( A – B )的区别是一组仅在A而不在B的元素。类似地, B – A是一组中的元素的B但不是在A 。
差异是使用- 运算符执行的。使用difference()方法可以完成相同的操作。
# Difference of two sets
# initialize A and B
A = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
B = {4, 5, 6, 7, 8}
# use - operator on A
# Output: {1, 2, 3}
print(A - B)输出
{1, 2, 3}在Python shell上尝试以下示例。
# use difference function on A
>>> A.difference(B)
{1, 2, 3}
# use - operator on B
>>> B - A
{8, 6, 7}
# use difference function on B
>>> B.difference(A)
{8, 6, 7}设置对称差异
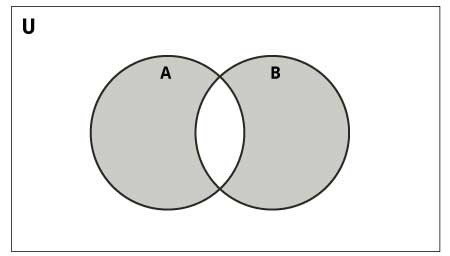
的对称差A和B是一组中的元素的A和B但不是在两者(不包括的交点)。
对称差使用^ 运算符执行。使用symmetric_difference()方法可以实现相同的目的。
# Symmetric difference of two sets
# initialize A and B
A = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
B = {4, 5, 6, 7, 8}
# use ^ operator
# Output: {1, 2, 3, 6, 7, 8}
print(A ^ B)输出
{1, 2, 3, 6, 7, 8}在Python shell上尝试以下示例。
# use symmetric_difference function on A
>>> A.symmetric_difference(B)
{1, 2, 3, 6, 7, 8}
# use symmetric_difference function on B
>>> B.symmetric_difference(A)
{1, 2, 3, 6, 7, 8}其他Python设置方法
设置方法有很多,上面已经使用了其中的一些方法。以下是set对象可用的所有方法的列表:
其他设置操作
设置会员资格测试
我们可以使用in关键字测试项目是否存在于集合in 。
# in keyword in a set
# initialize my_set
my_set = set("apple")
# check if 'a' is present
# Output: True
print('a' in my_set)
# check if 'p' is present
# Output: False
print('p' not in my_set)输出
True
False遍历一组
我们可以使用for循环遍历集合中的每个项目。
>>> for letter in set("apple"):
... print(letter)
...
a
p
e
l带内置功能
诸如all() , any() , enumerate() , len() , max() , min() , sorted() , sum()等内置函数通常与集合一起使用以执行不同的任务。
Python Frozenset
Frozenset是具有集合特征的新类,但是一旦分配,就不能更改其元素。元组是不可变的列表,而冻结集是不可变的集合。
可变的集合不可散列,因此不能用作字典键。另一方面,frozensets是可哈希化的,可用作字典的键。
可以使用Frozenset() 函数创建Frozensets。
此数据类型支持诸如copy() , difference() , intersection() , isdisjoint() , issubset() , issuperset() , symmetric_difference()和union() 。由于是不可变的,因此没有添加或删除元素的方法。
# Frozensets
# initialize A and B
A = frozenset([1, 2, 3, 4])
B = frozenset([3, 4, 5, 6])在Python shell上尝试这些示例。
>>> A.isdisjoint(B)
False
>>> A.difference(B)
frozenset({1, 2})
>>> A | B
frozenset({1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6})
>>> A.add(3)
...
AttributeError: 'frozenset' object has no attribute 'add'